* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Elias James Corey wikipedia , lookup
Hofmann–Löffler reaction wikipedia , lookup
Wolff–Kishner reduction wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Nucleophilic acyl substitution wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic resolution wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
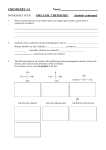
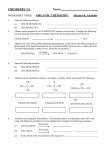
Homework Sheet #2 Name: th Due 27 February 2015 1. 2. Name the following alkenes. (a) CH3CHCHCH2CH2CH3 2-hexene hex-2-ene (b) CH3CH2CHC(CH3)2 2-methyl-2-pentene 2-methylpent-2-ene Alkenes can be prepared by an ELIMINATION reaction on an alcohol. Complete the following reaction showing what alkene is produced. Conc. H2SO4 CH3CH2CH2OH CH3CHCH2 + H2O heat 3. 4. Name the following alcohols. (a) CH3CH2CH2CH2OH 1-butanol butan-1-ol (b) CH3CHOHCH(CH3)2 3-methyl-2-butanol 3-methylbutan-2-ol Alcohols can be classified as primary, secondary or tertiary. Name and classify the following. CH3 H OH CH3 C OH CH3 C OH CH3CH2 CH3 CH CH3 CH3 secondary tertiary secondary OH CH3CH2 CH2 CH2OH CH3CH2C (CH3)2OH primary 5. 6. tertiary CH3CH CH2 CH2 CH2 CH3 secondary Alcohols can be prepared from alkenes. Concentrated sulfuric acid diluted to about 50% with water will effectively add H2O across the double bond. Complete the following equations. Dil. H2SO4 (a) CH3CH=CHCH3 (b) CH2=CHCH3 (c) (a) In (b), which of the two products is the major one? The second one (the rich get richer) Describe the trend in boiling points in the series methanol, ethanol, propanol, butanol. Dil. H2SO4 CH3CHOHCH2CH3 CH2OHCH2CH3 + CH3CHOHCH3 Boiling points increase. The alcohols are all primary and hydrogen bond, the only difference is in the length of the carbon chain. The longer the carbon chain the more weak intermolecular forces between the compounds (b) Explain why an alcohol such as propanol has a much higher boiling point than its corresponding alkane, propane. Propanol can form hydrogen bonds while propane cannot. Hydrogen bonds are stronger intermolecular forces which are harder to break meaning that propanol has a higher boiling point than propane (c) 7. Explain why the lower molecular weight alcohols are soluble in water while the higher ones are not. Alcohols can be oxidised by strong oxidising agents such as Cr2O72- and MnO4-. Primary alcohols are first oxidised to aldehydes and then to carboxylic acids. Secondary alcohols are oxidised to ketones . Tertiary alcohols are not able to be oxidised. 8. The following alcohols are reacted with acidified potassium permanganate solution. Under each formula, draw and name the product(s) of their oxidation. If no reaction occurs, write no product in the box. CH3 CH3 C H OH CH3 no product CH3 C OH OH CH3 propanone CH3CH2 CH CH3 2-butanone OH CH3CH2 CH2 CH2OH butanoic acid 9. CH3CH2 CH (CH3)2OH no product CH3CH CH2 CH2 CH2 CH3 2-hexanone Explain why tertiary alcohols cannot be oxidised in this way. Tertiary alcohols can not be oxidised because there are no hydrogens to be removed from the carbon that is bonded to the alcohol group. For oxidation to occur there must be hydrogen available to be removed from the carbon atom that is bonded to the alcohol group.