* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BSC 2085C
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
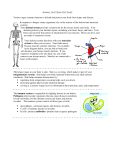
BSC 2085C/L ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I COURSE DESCRIPTION BSC 2085C Anatomy and Physiology I (4) (A.A.): Three hours lecture and three hours lab per week. Prerequisite: 83 or higher on the ACCUPLACER test OR 106 or higher on the PERT (Postsecondary Education Readiness Test). Students who graduated with a Florida standard diploma after 2009 are exempt from the aforementioned prerequisites. This course meets Area V requirements for the A.A./A.A.S./A.S. general education requirements. This course begins with a review of basic chemistry and cell biology, then proceeds with the anatomy and physiology of human tissues and the following organ systems: integumentary, skeletal, muscular, and nervous. It is strongly recommended that students without recent course work in biology take BSC 1007 or BSC 1008 BEFORE taking BSC 2085C. STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES At the successful completion of this course, the student should be able to: 1. Recall basic anatomical and physiological terminology, including body regions, body planes, abdominopelvic regions/quadrants, and directional terms. 2. Describe homeostasis, including the roles of intrinsic and extrinsic regulatory mechanisms and the roles of negative and positive feedback mechanisms in maintaining homeostasis. 3. Describe important concepts relevant to the chemical level of organization, including atomic structure and chemical bonds, properties of water, acids, bases, and buffers. 4. Describe the basic structure and function of the following organic molecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids and ATP. 5. Distinguish the basic structures and functions of the plasma membrane and cell organelles, in addition to the different modes of transport across the plasma membrane. 6. Differentiate the appearances, locations, and functions of the epithelial, connective, muscular, and nervous tissues, as well as the importance of epithelial and connective tissue membranes and cellular junctions. 7. Describe the key anatomical components for the following organ systems: integumentary, skeletal, muscular, and nervous, including those associated with the special senses. 8. Describe the physiological functions of and homeostatic mechanisms of the integumentary system, including but not limited to the layers of skin, the accessory organs within skin and body temperature regulation. 9. Describe the physiological functions of and homeostatic mechanisms of the skeletal system, including but not limited to the cells of bone tissue, osteogenesis, fracture repair and calcium homeostasis. 10. Describe the physiological functions and homeostatic mechanisms of the muscular system, including but not limited to neuromuscular junction physiology, the contraction cycle and cellular respiration. Page 1 of 2 11. Explain how the nervous system uses electrical signals and neurotransmitters to regulate homeostasis including action potential generation and propagation, synaptic transmission and summation. Date of Original Submission: Date of Last Revision: Date of Last Review: _______________ __July 21, 2006__ __May 10, 2014__ Page 2 of 2