* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell media
Major histocompatibility complex wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
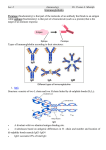
Humeral immunity *Ag recognition & presentation: this occur through APC.. -APC engulf m.o. , which under go incomplete digestion. - fragmentation of Ag to different epitopes. - epitipes exposed to the surface of APC (on MHC II ). - so the presentation of epitopes on MHC II IL-1 activate T helper. -T helper carries CD4 receptor for MHC II. - T helper stimulate B cell ( which carry BCR ) for produce plasma cells [ produce Ab ] & memory cell ( prolonged life span ). 1ry immune response 1ry immune response *The body exposed to Ag for 1st time. *plasma cell produced Ab is responsible. *longer time for Ab production. *IgM level is predominant. *the body exposed to Ag for 2nd time. *memory cell is responsible. *shorter. *IgG is predominant ( stronger IR ) Exogenous Ag B cell APC APC Active B cell Memory cell T helper MHC II Plasma cell TCR CD4 CD3 1 Th Cell mediated immunity Endogenous Ag Viral infected cell or intracellular bacterial infected cell MHC I CD4 CD3 TCR Activate Th Tc Activate T cytotoxic CD8 (CD8 cell) Cytototxicity to Ag Antibody(immunoglobulin) (Ab) (Ig) General characters of antibody 1-*Ab are group structurally related glycoprotein that are produced following stimulation of the immune system by immunogen. 2-*Ab.can binds specifically to the Ag molecules. -3Ab matches Ag much as a key match a lock . 4-*Ab found in different type of tissue , but highest conc. Is found in the blood. 5-*they are ∂ globulin& secreted by plasma cells. 2 Antibody structure Consist of four polypeptide, shaped to form. Two identical heavy chain Two identical Light chain Ag binding site VL VL Light chain chain FAb FC Heavy chain *variable protein. *constant. C i Hinge region C B S Heavy chain *tip of Y shape arms vary greatly from Ab to another . Called variable region includes the end of ( VL & VL ) heavy & light chain these unique contours in the Ag binding site. ( FAb ) fragment Ag binding. *the stemof Y shape are constants in all Ab of the same classes ( IgEs ) called ( constant region ) . Compose of Ć complement binding site & cell binding site. The antibody inactivate Ag by: A* Complement fixation. B* Neutralization. C* Agglutination. D* Precepitation. 3 Classes of Antibody ( Ig ) Nine classes.. IgG , Four type IgA , IgE , IgD & IgM 2 type ( subclasses ) ( IgG ) Gamma immunoglobulin Monomere ( 75 ) – 75% of serum IgG. IgG subclasses. IgG 1 , IgG 2 , IgG 3 , IgG 4. Differ in no of disulphide bond & length of hinge region. it is the major Ig in blood. Its mdecular weight is 160,000. IgA There are two types of IgA . the serum Iga which is similar in structure to IgG , and the secretory IgA which is composed of two molecules bound together by a secretory piece and a J chain secretory IgA is found in different body secretions e.g saliva, tears ,milk , colostrums gastrointestinal and respiratory mucous secretions. It acts as a1st line of defense against invadina bacterial and viruses at mucous Secretory piece J chain 4 IgD As IgG in structure found inserted into the membrane of B cells. IgE Is normally present in only trace amounts but it is responsible for symtoms of allergy. IgM Usually combines in star – shaped clusters . it tends to remain in the blood strem . its m.w is 1,000,000 . It has high binding capacity. Disulphide bond J chain 5 Hypersensitivity *inappropriate immune response can lead to tissue damage. *when an individual has been immunologically 2nd boosting of immue response. *however, the reaction may be excessive & lead to tissue damage ( hyper sensitivity ) Or any immune response against foreign Ag that are exaggerated beyond normal. There are 4 types … Type I .. hypersensitivity immediate hypersensitivity Type II .. hypersensitivity cytotoxic hypersensitivity. Type III .. hypersensitivity immune complex mediate h. Type IV .. hypersensitivity delayed or cell mediate h. Type I , II , III Type IV mediate by Ab. mediated by Tcell. Type I time 2-3 min *it is localized or systemic reaction that result from the release of in fl. Molecules in response to Ag. *it is group of conditions that occur in people a hereditary predisposition to develop IgE against common environmental Ag. ( Ag called allergens ) *developed in second or minutes following exposure to Ag. * it is commonly called allergies. 6 …Mechanism... Allergen ( Ag ) 1-Ag presenting cell phagocytosis & process Ag. 2-APC present Ag determinate to Th2 . 3-Th2 produce greated IL4 which stimulate B cell. 4- Bcell become plasma which secret TgE . 5- IgE binds to most cell, basophiles and eosinophite. A*sensitivation ( 1,2,3,4,5) 2nd exposure to allergen . stimulate the previous cell to produce histamine , inflammatory molecules serotonin , protease , leukotriene & prostaglandins. B*degradulation e.g 1- destruction of B.cell following incompatible blood transfusion. 2- destruction of fetal RBC's in heamolytic disease of new born. Type III 2-8 hrs Immune complex mediated hypersensitivity. …mechanism… AG—Ab complex deposited at various site induces most cell degranulation via mast cell , PMN lead to damage of tissue. Example.. Arthus reaction ( localsed) Serum sickness. 7 Type IV Delayed h. or cell mediate h. time 18-72 hrs. …mechanism… Memory Th1 release cytokines. Example.. 1-Tubercular lesion in Tuberculin Test. 2-contact dermatitis. Clinical signs… Usually localized or mild depend on site of entry Inhaled Ag hay fever (allergic rhinitis ) . Nasal discharge, watery eye, sneezing itching throat & eye. Oral Ag diarrhea. Skin Ag urticaria , itching . Example .. cat hair – penicillin – pollen grain – flowering – plant – bee venom – eggs- peanut – dust mites. Systemic anaphylaxis . Death due to systemic release of vasoactive mediators general vasodilatation & smooth muscle constriction result in sudden loss of blood pressure , massive edema , severe bronchial constriction ( systemic ). Type II : cyto toxic sensitivity time 5-8 hrs. It is damage reaction is caused by specific Ab binding to cells or tissue Ag . Often due to combined activities of Ć & Ab binding to phagocytes or by ADCC ( K cell ). Fine… 8










![[11] No. of printed pages :04](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007988662_1-961bf8618b5025cca8d341deaebfcd3c-150x150.png)