* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mechanism of Natural Selection
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary landscape wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
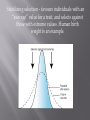
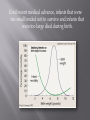
How does natural selection change a population? P. 247-248 What are the five important principles of natural selection? P. 250 What are two sources of variation? What is a niche? P. 258 - 259 What is a species ? What does it mean to be reproductively isolated? What is divergent evolution? What is adaptive radiation? What is convergent evolution? P. 252 -253 What are stabilizing, directional, and disruptive selections (include drawings) Changes that occur within a population of a single species. It includes the process of natural selection, changes in allele frequencies, and changes in populations that result over time. Development of antibiotic resistant bacteria is an example of microevolution. Video: Why does evolution matter now? Macroevolution refers to large scale and longterm evolutionary patterns among many species. The evolution of new species from a common ancestor, as seen in Darwin’s finches, or the extinction of the dinosaurs are all examples. Stabilizing selection – favours individuals with an “average” value for a trait, and selects against those with extreme values. Human birth weight is an example. Until recent medical advance, infants that were too small tended not to survive and infants that were too large died during birth. Directional selection – favours individuals possessing values for a trait at one extreme of the distribution, and selects against the average and other extreme. The development of antibiotic resistant bacteria is an example of directional selection. Only those bacteria that can tolerate the presence of an antibiotic survive. Video: Evolution of the peppered moth Industrial Melanism Disruptive selection – favours individuals at both ends of the distribution and selects against the average. Marine organisms known as limpets have shell colours that range from white to dark brown. The dark coloured limpets attached to dark coloured rocks in the ocean and light coloured limpets attached to light coloured rocks tend to be less visible to predators and have a higher survival rate. The intermediate coloured limpets (tan coloured) are highly visible to predators and are consumed. The intermediate colour is therefore being selected against. http://www.biologycorner.com/worksheets/pe pperedmoth.html Class Height Chart Directional? Stabilizing? Disruptive?