* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1 - Dr. Tricia Britton
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Group selection wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
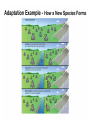
Chapter Thirteen: Evolution • 13.3 Natural Selection 13.3 Natural Selection • Adaptations are changes that enable an organism to survive environmental changes. • Adaptations are inherited- that is- passed from one generation to the next . Bill Nye 100 greatest discoveries • http://www.sciencechannel.com/tv-shows/greatest-discoveries/videos/100-greatest-discoveries-shortsnatural-selection.htm • What was driving force behind all life? (answer this question- listen to the video) Mutations • Since Darwin’s time, there has been a growing body of knowledge about heredity. • Today, scientists know that variations in the population of a species are caused by random mutations in genes. • Random mutations in genes produce variations of traits in a population. 13.3 The importance of genetic variation • Some mutations are harmful because they cause genetic disorders. • Mutations may also be helpful because they contribute to genetic variation. • Page 272 for picture A mutation story • http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/evolution/library/01/2/quicktime/l_012_02.html • Listen to the video and answer…. • What is the name of the trait? • From what disease does this protect humans? The importance of genetic variation • Genetic variation refers to the variety of alleles in a population. • Genetic variation is necessary for natural selection and ensures that a population has a better chance of survival should the environment change. How a new species evolves • One way for a species to evolve happens in 3 steps: 1) Isolation 2) Adaptation 3) Differentiation See page 273 How a new species evolves 1) Isolation happens when a population becomes divided by an event such as storms, floods, volcanic eruptions, earthquakes. The original population becomes divided into smaller populations. 2) Adaptation 3) Differentiation How a new species evolves 1) Isolation 2) Adaptation happens through natural selection. The event that causes isolation may also change the environment. The separated populations must adapt to their environments. Each population will have different adaptations. 3) Differentiation How a new species evolves 1) Isolation 2) Adaptation 3) Differentiation happens when the isolated populations become so different that they can no longer interbreed. Over many generations, the populations become genetically different. One or more new species is formed. 13.3 Extinction • Extinction occurs when the environment changes and the adaptations of a species are no longer sufficient for its survival. 13.3 Extinction • The dodo bird is an example of how human impact may contribute to extinction. • The dodo was first sighted around 1600 on Mauritius, an island in the Indian Ocean. • The dodo was extinct less than eighty years after its discovery. Why does evolution matter now? • http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/evolution/library/11/2/quicktime/e_s_6.html • Listen to the video and answer these questions. • What disease is the subject of this video clip? • What are symptoms people have? • What is the adaptation of this bacterium that allows it to survive? __________