* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Physics Charge-to-mass Ratio Questions
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
History of subatomic physics wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatics wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
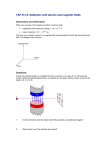
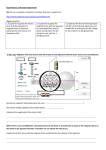
Physics Charge-to-mass Ratio Questions 1) A beam of cathode rays with velocity 106 m/s is passed through an electric field of 103 V/m and is deflected, as a result. What strength magnetic field will compensate the electric field effect? 2) A charge-to-mass ratio experiment has the following data; i) Particles deflect (in magnetic field only) in a radius of 109 mm when the magnetic field was 1.23 mT. ii) An electric field produced by 130. V between a parallel plate apparatus separated by 12.0 mm made the beam straighten. a) Find the speed of the electrons. b) Find the charge-to-mass ratio of the electrons. c) Find the percent error in ii. 3) In a mass spectrograph, the masses of ions are determined by their radii in a magnetic field. A keen student uses chlorine ions (charge of -1) at a speed of 5.00 x 104 m/s which are fired into a 0.150 T magnetic field. The two isotopes have masses of 5.81 x 10-26 kg (Cl-35) and 6.14 x 10-26 kg (Cl-37). Find the radii of the two ions. 4) A proton is placed into a magnetic field of 4.00 mT and deflects into a radius of 4.00 cm. An electric field straightens the path (supplied by 200 V between parallel plates). Find the plate separation and the velocity of the protons. 5) In a charge to mass ratio experiment, our pal J.J. found that a magnetic field of 3.0 x 10-3 T caused some unknown particles (not electrons) to deflect into a radius of 0.230 m. The beam of particles could be straightened by an electric field produced by 2 plates separated by 1.50 cm when 125 V are applied to the plates on either side of the beam. a) Find the velocity of the particles. b) Find the charge to mass ratio of these particles!! 6) A charge to mass ratio experiment had the following data: electron velocity = 2.7 x 106 m/s, B = 2.4 x 10-4T a) Find the radius of the circular path in which the electron moves. b) What is the electric field strength through which the electron moves? c) What is the electric force exerted on the electron by the electric field? d) Find the charge to mass ratio for the electron using this data. 7) Alpha particles have a velocity of 5.0 x 106 m/s and pass through a magnetic field of 2.0 mT. What electric field will cause the particles to travel in a straight line? 8) Charge-to-mass ratio experiments occur with new particles. A magnetic field of 2.0 mT causes the particles to move in a radius of .150 m. The beam can be straightened by 300 V across parallel plates 2.0 cm apart. a) Find the speed of the particles. b) Find the charge-to-mass ratio of the particles. 9) A particle of charge +4e is travelling through perpendicular electric and magnetic fields such that the particle's path is un-deflected. It then continues into an area where the electric field has been eliminated. It then travels in a circular path of radius 25.0 cm. If the electric field is determined by 125V applied between 2 parallel plates separated by 10.0 cm and the magnetic field 40.0 T, find the velocity and charge to mass ratio of this particle!! Answers: 1) 10-3T 2a) 8.81 x 106 m/s 2b) 6.57 x 1010 C/kg 2c) 62.6% 3) 0.121 m, 0.128 m 4) 3.27 m, 1.53 x 104 m/s 5a) 2.8 x 106m/s 5b) 4.0 x 109 C/kg 6a) 6.4 cm 6b) 6.5 x 102 N/C 6c)1.0 x 10-16 N 6d) 1.8 x 1011 C/kg 7) 1.0 x 104 V/m 8a) 7.5 x 106 m/s 8b) 2.5 x 1010 C/kg 9) 31.3 m/s, 3.13 C/kg