* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Crusades
Church of the Holy Sepulchre wikipedia , lookup
Livonian Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Third Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Siege of Acre (1189–1191) wikipedia , lookup
Savoyard crusade wikipedia , lookup
Rhineland massacres wikipedia , lookup
Despenser's Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Albigensian Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Nicopolis wikipedia , lookup
Siege of Acre (1291) wikipedia , lookup
History of Jerusalem during the Kingdom of Jerusalem wikipedia , lookup
Fourth Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Second Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Northern Crusades wikipedia , lookup
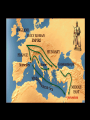
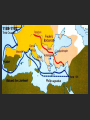
The Crusades Islam • A Muslim is a follower of Islam. • Islam was founded in 622 CE by Muhammad the Prophet. He lived from about 570 to 632 CE). Prelude to the Crusades • Islam spread from its origin in today’s Saudi Arabia. • By 1095CE Muslim territory included the land where Jesus lived. • Christian warriors believed they should control this area. • They considered this to be holy land. The Crusades • The crusades were a series of eight wars initiated by the Christians to win back their holy lands ( Jerusalem and other sites) from the Muslims. • Around this time the kingdoms of Europe had one thing in common – Christianity. • Muslims and Arabs had controlled the Holy Land since the 7th century, but tolerated Christian pilgrims. The 1st Crusade (1096-1099) • Pope Urban II called for a “war of the cross”, or Crusade, to take back the holy lands. • He persuaded 34,000 knights and peasants to join in the expedition. • The war offered knights a chance for glory and wealth. • Urban suggested that the knights fight Muslims instead of continuing to fight one another. • It was a success. In 1099 the crusaders captured the holy land. • It was then recaptured by the Muslims. The Second Crusade (1147-1149) • Led by the king of France and the Holy Roman Emperor, this Crusade was a disaster. • They utterly failed in their mission. The 3rd Crusade (1187-1192) • Three kings led by Richard I of England mounted to recapture Jerusalem which was under the control of Saladin, the Islamic forces greatest general. • A truce was called in 1192, allowing Christian pilgrims to visit Jerusalem. The 4th Crusade (1202) The 4th Crusade • Led by Venetian merchants (who owned the ships that the crusaders traveled on) crusaders sacked Christian Constantinople, a commercial rival of theirs. • The crusaders sacked the city and killed untold of its citizens. • The attack permanently weakened the Eastern Roman Empire. • This Crusade was viewed as an embarrassment to the church. Results of the Crusades • The Crusaders were unable in the long run to reclaim their holy lands, but the wars had other lasting effects: • Western Europeans left their homes to fight in distant wars. The stories of returning Crusaders opened the eyes of people at home to the broader world. • Exotic goods like spices and clothes that Crusaders were exposed to created new desires, and encouraged long distance trade. • The Crusades helped reintroduce books of philosophy, etc. from Classical Greece and Rome, which had been preserved and translated by the Muslims. • This helped lead to a revival of Classical learning in the Renaissance. • The need to transfer large sums of money for troops and supplies led to the development of banking and accounting techniques. • Islamic science, medicine, and architecture were transferred to the west. • For example, European castles became massive stone structures rather than smaller wooden ones.