* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Adult with Transposition
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
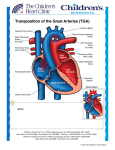
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
3/5/2015 Forms of Transposition The Adult with Transposition • L-Transposition of the Great Vessels • D-Transposition without pulmonary stenosis Do two wrongs make a right? • − Atrial Repair − Anatomic repair (arterial switch) D-Transposition, VSD, pulmonary stenosis − Figure 3. Relative survival of patients and patient groups. Nieminen H et al. Circulation 2001;104:570-575 Rastelli repair L-transposition of the Great Vessels • Rare: Less than 1 % of congenital heart disease • Atrioventricular discordance and ventriculoarterial discordance • If no major associated anomalies, survival to adulthood without intervention is common • High frequency of major anomalies that can dominate early history Copyright © American Heart Association L-TGV: Two wrongs Normal vs. L-TGV 1 3/5/2015 L-transposition: tricuspid valve closer to apex L-transposition: mitral-pulmonary valve continuity L-transposition • L-transposition Associated anomalies − VSD in 70% − PS 40% − Systemic AV valve abnormalities Ebstein’s Anomaly Progressive Tricuspid Regurgitation − • Conduction system abnormalities − Dual AV node anatomy and abnormal His bundle − Progression to AV Block estimated at 2% per year Progressive dysfunction of systemic right ventricle 2 3/5/2015 L-TGV: ECG L-TGV: Echocardiography • Tricuspid valve closer to cardiac apex − • Mitral-pulmonary valve continuity • Aorta usually anterior and to the left of pulmonary artery L-transposition: tricuspid regurgitation L-transposition: right ventricular function RV failure D-TGV • • In those without associated lesions, some degree on CHF in about 1/3 by fifth decade − • Importance of tricuspid regurgitation Role of tricuspid regurgitation Frequency greater in patients with previous heart surgery Ventriculoarterial discordance − D-loop, RV on right side of heart − Ao tends to be on right and anterior • Cyanosis • Associated lesions • Role of PS 3 3/5/2015 Atrial Repair • Atrial repair Senning 1958, Mustard later − Baffle atrial blood to contralateral AV valve Atrial repair • Good early results • Late complications − − Sinus node dysfunction; sinus rhythm in 77% at 5 years, 40% in 20 years Atrial flutter may be marker of sudden death Atrial repair • Late ventricular dysfunction and tricuspid regurgitation • Actuarial survival 80% at 20 years • Evaluation of RV function difficult due to different architecture of RV • Baffle leaks and obstruction (SVC>IVC>pulmonary venous) • Pulmonary hypertension more frequent in those operated at > 2 years of age Atrial repair • Actuarial survival • Mortality 1-5 % • Late sudden death • High frequency of good functional class (80% symptom free with NYHA Class I) • Progressive increase in RV dysfunction, TR, arrhythmias − Atrial repair • Loss of sinus rhythm • Increase in atrial arrhythmias • Late sudden death 2.5% early mortality, 2.5% late mortality 4 3/5/2015 Atrial repair of D-TGV Atrial Repair: Echo • • Evaluate right (systemic) ventricular function − RV size and contractility (often subjective) − Tricuspid regurgitation Evaluate for baffle obstruction − Systemic venous (more common) − Pulmonary venous Atrial repair: Pulmonary venous baffle Atrial repair: Pulmonary venous baffle Atrial repair: Tricuspid regurgitation Arterial switch • Introduced by Jatene in 1976 • Transect great arteries, transpose them and move coronaries • Distortion of branch pulmonary arteries, aortic insufficiency, coronary occlusion early postoperatively 5 3/5/2015 Arterial switch • Advantage: Left ventricle is the systemic ventricle • Substantial morbidity and mortality in early experience • Recent results much improved, but long term results are still evolving Surgical mortality • Only studies are retrospective • High early mortality with arterial switch, probably better long term mortality • Increased mortality with single or intramural coronaries Figure 1. Top, Actuarial survival in 1200 patients who had ASO. Numbers indicate number of patients observed at beginning of interval. Losay J et al. Circulation 2001;104:I-121-I-126 Copyright © American Heart Association ASO: Late complications • Late death relatively rare • Branch pulmonary stenosis • Progressive aortic insufficiency • Evaluate for coronary occlusion Aortic insufficiency 6 3/5/2015 Figure 3. Actuarial survival free from grade II or more AI (Ao insufficiency) for 1095 survivors. Losay J et al. Circulation 2001;104:I-121-I-126 • 19 year-old S/P arterial switch • Asymptomatic but with increasing left ventricular size Copyright © American Heart Association Arterial Switch: Aortic Insufficiency Arterial Switch: Aortic Insufficiency Arterial switch “Complex” D-TGA • Probably lower risk of late death, but population is growing older • Often asymptomatic in presence of progressive disease • Increased risk of coronary findings later in life which are difficult to visualize echocardigraphically • Most frequent complex lesion is with ventricular septal defect and pulmonary (valvar and sublalvar) stenosis • Most common mode of repair is the Rastelli procedure 7 3/5/2015 Rastelli repair • Mean age (initially) age 4 years • Current survival 93% at 20 years, but early was 52% at 20 years − • Rastelli • Late sudden death Reoperation due to progressive stenosis of RV-PA conduit Rastelli: reintervention “Complex” D-TGA: Rastelli Surgical issues—recurrent LVOTO, conduit obstruction, arrhythmias, late mortality − Perioperative heart block − Straddling tricuspid valve Rastelli: Echo • Evaluate for both LV and RV outflow obstruction • Evaluate for ventricular dysfunction • Investigate for residual VSD “Complex” D-TGA: Rastelli 8 3/5/2015 “Complex” D-TGA: Rastelli “Complex” D-TGA: Rastelli Transcatheter valve replacement “Complex” D-TGA: Rastelli, residual VSD Transcatheter valve replacement “Complex” D-TGA: Rastelli 9 3/5/2015 “Complex” D-TGA: Rastelli Suprasternal notch view for branch pulmonary arteries “Complex” D-TGA: Rastelli Prognosis in Adults Good Atrial Septal Defect Patent Ductus Arteriosus Pulmonary Stenosis Ventricular Septal Defect Intermediate Uncertain/Poor Aortic Stenosis D-Transposition (arterial switch) Tetralogy of Fallot L-Transposition D-Transposition (Senning/Mustard ) Ebstein’s Anomaly Single Ventricle Coarctation Mortality-->Insurance Lesion Late Mortality (%) Mortality Ratio Underwriting ASD/PDA/PS VSD CoA Aortic Sten. ToF Senning Single Vent. 5-12 20 16 15 14 24 85 70-200 667 320 375 350 480 >2800 100 100-200 100-300 225-400+ 200-400 Declined Declined Cognitive issues • Cognitive function probably diminished • Lower than average scores on neuropsychological testing as adolescents • Many receive remedial academic or behavioral services during school years 10 3/5/2015 Pregnancy in TGA Pregnancy Lesion Success rate Complications Reference L-TGV 83% CHF with valve replacement after delivery JACC 33:1692 (1999) Atrial Switch 82% Arrhythmias 22%, other 80% Eur Ht J 26:2588 (2005) Arterial Switch 13/17 (76%) VT, valve thrombosis AJC 106:417 (2010) Rastelli 50% Increased subaortic stenosis Aust NZ Obstet Gyn 45:243 (2005) • Prognosis dictated by ventricular function and arrhythmias • Thorough evaluation of rhythm particularly in atrial switch and L-TGV patients • Complications of valve anticoagulation • Increased risk of congenital heart disease in offspring There are more adults than children with congenital heart disease in the U.S… …boldly going where no group of patients has gone before. 11