* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 12
Environmental, social and corporate governance wikipedia , lookup
Socially responsible investing wikipedia , lookup
Rate of return wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative easing wikipedia , lookup
Investment management wikipedia , lookup
Interbank lending market wikipedia , lookup
History of investment banking in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Internal rate of return wikipedia , lookup
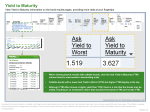
Investment Analysis Lecture 16 (cont’d …) Fixed Income Securities Investment Analysis Uses of YTM • Main uses of YTM are: – A measure of bond’s return. – A tool for choosing between different bonds. Investment Analysis YTM and Return: Zero-Coupon Bonds • • • • • • The YTM of a zero-coupon bond is the spot rate corresponding to the bond’s time to maturity. This is the return of investing in the bond and holding it until maturity. But it is not the return for any other investment horizon. Example: consider a zero-coupon bond with 3 years to maturity and YTM 6%. The return of investing in the bond and holding it for 3 years is 6%. However, the return of investing in the bond and selling it after one year is unknown today. – The return depends on the bond’s price next year. – The price next year depends on the 2 year spot rate that will prevail next year. This spot rate is unknown today. Investment Analysis YTM and Return: Coupon Bonds • The YTM of a coupon bond is the return of investing in the bond, holding it until maturity and reinvesting the coupons at a rate to the YTM. • The YTM is not the return for any investment horizon other than maturity. This is for the same reason as for zero-coupon bonds. • The YTM is not the return even for investment horizon equal to maturity. This is because the future spot rates at which coupons will be reinvested may be different than the YTM. Investment Analysis The YTM as a Tool for Comparing Bonds • Using the YTM for comparing bonds is correct only when the bonds have the same coupon and time to maturity. In all other cases it can be very misleading. • Suppose, for instance, that the bonds have different time to maturity: – Recall that the YTM is at best the return of investing until maturity. – Therefore, by comparing YTMs we compare returns for different investment horizons. • The correct way to compare bonds is simply to compute the PV of their cash flows. Investment Analysis 1st Basic Fact about Interest Rates • Bond prices are sensitive to interest rate movements. They go down when interest rates go up and vice versa. • Bond prices are negatively related to interest rates. • Bond prices are the PV of bonds cash flows. If interest rates go up, cash flows are discounted more heavily and the PV goes down. • Suppose that interest rates go up. Investors will sell bonds in order to invest in the higher interest rates. Therefore, bonds prices will decrease. Investment Analysis 2nd Basic Fact about Interest Rates • Prices of long term bonds are more interest rate sensitive than prices of intermediate term bonds. • The interest rate sensitivity of bond prices increases with maturity. • The cash flows of long term bonds are farther in the future, and are more heavily discounted than the cash flows of short term bonds. • Therefore, the PV of the cash flows is more interest rate sensitive for long term bonds than for short term bonds. Investment Analysis Measuring and Managing Interest Rate Risk • We showed that interest rate risk is important and impacts bond prices. • Many market participants need to measure and manage interest rate risk. – – – – Bonds Banks Pension Funds Insurance Companies etc. • Interest Rate can be measured and managing by using Duration and Convexity.