* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Islamic World and India, 1600-1917
Jamaat-e-Islami Pakistan wikipedia , lookup
Islamic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Islamofascism wikipedia , lookup
Muslim world wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Islamic monuments in Kosovo wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
History of Islam wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Censorship in Islamic societies wikipedia , lookup
Morality in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Spread of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic socialism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Islamic missionary activity wikipedia , lookup
Salafi jihadism wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
Reception of Islam in Early Modern Europe wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Romania wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Islam and other religions wikipedia , lookup
Islamic schools and branches wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Islamic culture wikipedia , lookup
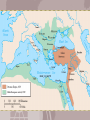
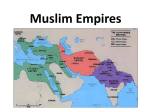
The Islamic World 1600-1917 SSWH12:a-b Time and Geography POLITICAL Strengths and Weaknesses of Ottoman Civilization • Strengths – Artistic work in literature, architecture, etc. – Commitment to justice for all – Tolerance for nonbelievers – Literary language Strengths and Weaknesses of Ottoman Civilization • Weaknesses – Government depended on 1 or 2 individuals – Government essentially military, needed conquests to justify itself – Could not adapt Islamic law to changing needs – Uninterested in secular education, technology – Excessive reverence for tradition Decline of the Ottoman Empire • Became prey for West – Russians drove back frontiers – Balkan peoples rebelled • Sultanate declined in power as bureaucracy grew • Occasional reforms, but not enough • Other contributing factors – Economic: shift of trade routes – Military: loyalties eroding – Technological: refused to give up old ways Safavid and Mughal Decline • Safavids disappeared by 1700 – Unable to develop into centralized empire – Attacked by Afghan invaders – India remained under tribal rule The Safavid Empire Safavid and Mughal Decline • Aurangzeb of India – Reintroduced Islamic character to public life – Heightened friction with other religions – Set stage for eventual Hindu rebellion The Mughal Empire in 1690 European Presence in India • Portuguese, Dutch, English, French • Mughals comfortable with British • French arrival put some strains on relationship • European wars involved India – Seven Years War put most of India in British hands • Attempts to defy British power were crushed Muslim Countries until World War I • Three Muslim empires overwhelmed by Western military, financial powers – India – outright colony – Persia – divided between Russia, Britain – Ottomans – defeated by Russia – Egypt – occupied by British Scaling the Heights of Abraham, Seven Years War Muslim Countries until World War I • Indicators of intellectual and psychological decline – Could no longer sustain image of righteous community of believers – Recognized need for including Western elements in Islam – Only adopted them sporadically – Enormous prejudice, tradition opposed Westernization The Period of Reforms Different Responses to the Challenge • • • • Ignore or reject changes Accommodate change Islamic fundamentalism Pan-Arabism, Arab nationalism Sultans of the Ottoman Dynasty Tanzimat • Sultans realized they had to modernize military • Tanzimat Reforms – Sultan Selim III tightened control over provinces – Created new schools to train officers • Next sultan ended Janissary opposition, renovated education • Rose Chamber Rescript of 1839 – revolutionized society by declaring equality of all Ottoman subjects • Young Ottomans – Young intellectuals, journalists – Pressured for liberalization of society – Got constitution, elections before being defeated Egypt, Sudan under Muhammad Ali • Reign of Muhammad Ali Pasha was unusual for longevity and for modernizing the military • Military reforms – Convinced of European superiority – used French advisers, models – Conscripted peasants, outfitted them with latest weapons – Established munitions industries • Other reforms – – – – Modern schools, public health systems Encouraged private land ownership Sugar and cotton as cash crops State monopolies of vital industries An 1840 portrait of Muhammad Ali Pasha Foreigners and Reactions • Foreigners – Foreign investments: railroads, Suez Canal – Incurred huge debts – had to sell shares in Suez Canal Company to British – Britain occupied Egypt in 1882 • The Mahdi Rebellion – Successful revolt against Egyptians, British in Sudan – Elements of national resistance and fundamentalist Islam – Lasted until British defeated rebels in 1898 Reforms under the Iranian Shahs • Did not begin reforms until mid-century • Intensified military, commercial ties with West • Cheap European goods put local industries out of business Reforms under the Iranian Shahs • Resistance to foreign interference • Western control over mineral, oil rights • Demands for constitutional government began to circulate • National Assembly called, but was weak Wahhabi Fundamentalism and Jihad • Wahhabism – militant reform begun in late 1700s • Fought jihad to purge Islam, believed it was only way for Islam to survive enemy attacks • Declared holy war on all neighboring tribes • Destroyed tombs, even markers on Muhammad’s grave • Inspired similar violent reactions to change • Wahhabism today – Thorough rejection of everything Western – Only role of government is to create reign of Allah and his faithful – Any obstacle to that must be destroyed – no compromise Salafi and Nationalism • Salafi Movement – Wanted to reform Islam to allow modern ideas, ways of life – Urged Muslims to reform themselves to meet Western challenge – Modernization on Islamic principles • Return to days of intellectual experimentation • Were sure Allah did not intend Muslims to be inferior – Most ulama ignored these ideas • Arab nationalism – Pan-Arabism – outgrowth of national consciousness – Note: “Arab” refers to ethnic group, not religious one – Christian Arabs especially important in movement Flag of the Arab League Discussion Questions 1. What connections do you see between events in the Muslim world in the 18th and 19th Centuries and the current situation in the Middle East? To what extent do you see Wahhabism as an explanation of today’s Muslim reactions to the West? To Islamic fundamentalism and the Muslim terrorists? Does the knowledge in this chapter help you to understand their attitudes today? Why and how? 2. One of the themes in world history is the rise, maturity, decline, and fall of one powerful state or empire after another. The Ottoman Empire was yet another instance of this life cycle. Can you think of any nations today which seem to be following the same evolution? Can you compare any signs of decay and decline today to what happened to the Ottomans?