* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download GI 32
Liver support systems wikipedia , lookup
Hepatocellular carcinoma wikipedia , lookup
HFE hereditary haemochromatosis wikipedia , lookup
Bariatric surgery wikipedia , lookup
Gastric bypass surgery wikipedia , lookup
Hepatic encephalopathy wikipedia , lookup
Glycogen storage disease type I wikipedia , lookup
Wilson's disease wikipedia , lookup
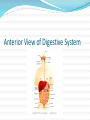
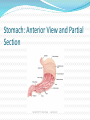
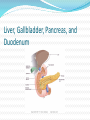
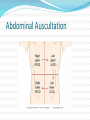
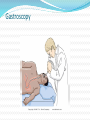
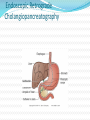
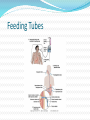
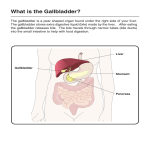
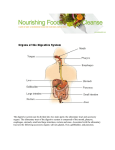
Gastrointestinal, Hepatic, and Pancreatic Systems Function, Assessment, and Therapeutic Measures Anterior View of Digestive System Stomach: Anterior View and Partial Section Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology Oral Cavity and Pharynx- mechanical digestion begins in the oral cavity. Esophagus Stomach Small Intestine Large Intestine Liver, Gallbladder, Pancreas, and Duodenum Liver Functions Carb metabolism- stores glycogen Amino acid metabolism- converts excess to urea to be removed by kidneys. Lipid metabolism- excretes excess cholestrol Produces clotting factors prothrombin and fibrinogen Form bilirubin Stores iron, copper, Vitamins A, E, D, K Detoxification (alcohol, meds, ammonia) Gallbladder/Pancreas Functions Stores bile and contracts to secrete bile into duodenum in response to cholecystokinin Pancreas secretes digestive enzymes amylase, lipase, trypsinogen, and bicarbonate juice Gallbladder stores bile Pancreas Amylase- changes Starch to Maltose Lipase – changes Emulsified Fats to Fatty Acids and glycerol Trypsinogen- changes to Trypsin in duodenum and digests polypeptides to amino acids Bicarbonate Juice- neutralizes hydrochloric acid as it enters the deudenum Aging and Gastrointestinal System Tooth Enamel Harder/More Brittle Tongue Atrophy-sweet/sour taste decrease Saliva Production Decreased 33% Esophagus Motility Less, Emptying Slower Weaker Gag Reflex Faulty absorption of B1, B12, calcium, iron Aging and Gastrointestinal System (cont’d) Decreased Motility of Stomach Decreased Gastric HCL Production Fat Absorption Slower Atrophy of Large/Small Intestine Decreased Mucous Secretions Decreased Elasticity of Rectal Wall Data Collection: Subjective Data Health History Travel (Clostridium Difficile) Elimination Medications Nutritional assessment Family History Cultural influences “Which foods do you most commonly consume?” Objective Data (cont’d) Inspection- look Jaundice, N/V, pain, distention Auscultation- listen, normal BS 5-30 per min Percussion- detect fluid, air or masses (usually NP or Dr.) Palpation- feel for masses, rigidity, pain RUQ tenderness, distended Appetite/wt changes, bowel changes, HT, Wt, body mass Physical Assessment Inspection Striae- light silver colored or thin red lines on the abdomen Bruising Caput medusae- bluish purple swollen vein pattern extended out from navel Spider angiomas- thin reddish-purple vein lines close to the skin Jaundice(icterus) yellowing of skin Jaundice Pathophysiology Destruction of old red blood cells yeild bilirubin Liver converts bilirubin to water-soluble compound for excretion Jaundice (icterus) occurs if liver unable to convert bilierubin and buildup occurs may also occur if bile drainage obstructed Abdominal Auscultation Diagnostic Lab Tests Laboratory Tests CBC- reveals anemia or infection Electrolytes- imbalance occurs from vomiting, diarrhea, or malabsorption disorders Carcinoembryonic Antigen (CEA)- monitor effectiveness of GI cancer tx and reoccurrence Liver Enzymes- ALT,AST increase indicates liver damage Stool test-test for occult blood, false + with bleeding gums and eating red meats Diagnostic Tests (cont’d) Radiographic Tests Flat Plate of the Abdomen Upper GI Series (Barium Swallow) Lower GI Series (Barium Enema) Computed Tomography (CT) Scan Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Nuclear Scan Diagnostic Tests (cont’d) Angiography Liver Scan Endoscopy Esophagogastroduodenoscopy [EGD] Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) Lower Gastrointestinal Endoscopy Proctosigmoidoscopy Colonoscopy Gastroscopy Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography Diagnostic Tests Ultrasonography- will use lubricating gel on abd with a tranducer that produces sound waves. A picture of your abd will appear on a screen Endoscopic Ultrasonography Percutaneous Liver Biopsy Oral Cholecystogram- (gallbladder series) if gallstones. Pt ingests a radiopaque dye that collects in the bile in the liver. Dye shows up in xray. Pretest- high-fat diet x2 days, low-fat day before test. Take tablets evening before test with water 5mins apart. NPO after MN Therapeutic Measures Gastrointestinal Intubation Tube feedings- Gravity, bolus, pump Gastrointestinal decompression Total Parenteral Nutrition (intravenous hyperalimentation Feeding Tubes NG Tubes Purposes Remove gas or fluids from stomach or intestines. Obtain gastric secretions fro analysis Tx obstructions or bleeding in GI tract Provide means for nutrition (gavage feeding) hydration, and medications.