* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapters 15 and 16
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
The Selfish Gene wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
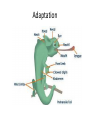
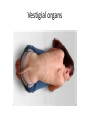
Chapters 15 and 16 •Change over time is known as… Evolution • The individual who contributed significantly to our understanding of evolution was… Charles Darwin • Shortly after completing his college studies, Darwin joined the crew of the ship… H.M.S Beagle •The remains of ancient organisms are known as… Fossils • Of all the Beagle’s ports of call, the one that influenced Darwin the most was a group of small islands 1000 km west of South America known as… Galapagos Islands • What question did Darwin ask himself about fossils? • Why had so many of the species disappeared? • How were they related to living species? • What detail confounded Darwin about the characteristics he had observed in the many plants and animals? How they varied so noticeably from one island to another •Hutton and Lyell helped scientists to recognize that the Earth… Is millions of years old .. •And that the processes that changed the earth then… Are the same ones that operate today. •What is GEOLOGY? The study of rocks and rock formations • Darwin’s understanding of geology, thanks to his friend Charles Lyell, influenced him in two ways. One was, “ If the Earth could change over time… Might LIFE change as well? • Lamarck proposed that all organisms have an innate tendency toward complexity and perfection. • Do you agree or disagree and why? • Malthus reasoned that if human population continued to grow unchecked, sooner or later, what would happen? There would be insufficient living space and food. •Was he right? Explain… •In ………… …………….., nature provided the variation and humans selected those variations that they found useful. Artificial selection • Darwin realized that high birth rates and a shortage of life’s basic needs would eventually force organisms into a competition for resources. This is known as… Struggle for existence •The ability to survive AND reproduce in a specific environment is called… Fitness •Any inherited characteristic that increases an organism’s chance of survival is known as… Adaptation • Individuals that are better suited to their environment-that is, with adaptations to enable fitness, survive and reproduce most successfully. In Darwin’s terms, that is… Survival of the fittest • Over time, changes in the inherited characteristics of a population that increases a species’ fitness are called… Natural Selection • Darwin’s proposed that over time, natural selection produces organisms that have different structures, establish different niches or occupy different habitats. As a result, species today look different than their ancestors. This principle is called…. Descent with modification • One argument that living things have been evolving on Earth for millions of years can be found in… • Fossil records • Geographical distribution of living species • Homologous structures of living organisms • Similarities in early development, or embryology. • An organism possesses organs with little of no function. They are called… Vestigial organs • A ___________ _________ consists of ALL genes, including all the different alleles, that are present in a population. Gene Pool • The number of times that an allele occurs in a gene pool, compared with the number of times other alleles for the same gene occur is…. Relative Frequency • In genetic terms, evolution is any _______ in the relative frequency of alleles in a population. Change •One of the two main sources of genetic variation is …. • Mutation • Genetic shuffling that results from sexual reproduction • A ___________ is any change in a sequence of DNA and can occur because of mistakes in the replication of DNA or as a result of radiation or chemicals in the environment. Mutation Yes or No?? • Do mutations always affect the phenotype? •NO • Let’s say there is a family with 4 siblings. One of the offspring does not look like his biological parent even though they provided him with all his genes. • What can we attribute that to? Gene shuffling • A widow’s peak is controlled by a single gene with two allelles.The widow’s peak allele is dominant over the allele for a hairline that has no peak. The widow’s peak can be described as… Single-gene trait • Many traits are controlled by two or more genes. They are called… Polygenic Traits When individuals at one end of the curve have higher fitness than individuals in the middle or at the other end, this occurs… Directional selection • When individuals near the center of the curve have higher fitness than individuals at either end of the curve, this occurs… Stabilizing selection • What happens when disruptive selection takes place if the pressure of natural selection is strong enough and lasts long enough??? Selection creates two distinct phenotypes • Natural selection is NOT the only source of evolutionary change… • Recall that genetics is controlled by the laws of probability. • The smaller a population is, the farther the results may be from what the laws of probability predict. • This kind of random change in allele frequency is called… Genetic drift • Genetic drift may occur when a small group of individuals colonizes a new… Habitat • A situation in which allele frequencies change as a result of the migration of a small subgroup of a population is called…. The founder effect What do you call what happens when: • 1. There is random mating. • 2. The population is very large. • 3. There is no movement into or out of the populations. • 4. There are no mutations. • 5. There is no natural selection? Genetic equilibrium •What is the cool word that means changes that lead to the formation of new species? Speciation • What three varieties of reproductive isolation are there? • Behavioral (they way they act) • Geographic (where they are) • Temporal (when they reproduce)