* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download human anatomy and physiology name - H
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Drug-eluting stent wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
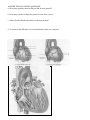
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Name: EXAMINATION AND DISSECTION OF A HEART 1) Rinse heart the thoroughly. 2) Look for evidence of the pericardium; find the epicardium and try to separate a small portion of it from the myocardium. 3) Identify the right and left ventricles by squeezing the heart. is thicker. The left ventricle wall feels firmer and 4) Locate the anterior interventricular groove and locate the left coronary (4,6)artery within the groove. Using the next page as a guide, try to find the right coronary artery (3), the circumflex branch of the left coronary artery(5), and the coronary sinus(9). Fat may obscure these structures but do not try to remove the fat. 5) Identify the aorta, pulmonary trunk, pulmonary veins, and the inferior vena cava and superior vena cava, if present. A considerable amount of fat and connective tissue may have to be removed to expose some of these vessels. 6) Looking through the top of the right atrium, identify the tricuspid valve. Over a sink, fill the right ventricle and gently squeeze the ventricle to observe the closing action of the valves. 7) Insert one blade of your scissors into the superior vena cava and cut down through the right atrium and right ventricle toward the apex of the heart. 8) Locate the opening of the coronary sinus into the right atrium. Find the papillary muscles and chordae tendineae. 9) With scissors, cut through the right ventricular wall up along its lower margin parallel to the anterior inter-ventricular wall. Continue the cut through the exit of the right ventricle into the pulmonary trunk. 10) Locate the pulmonary semilunar valve and the opening (valve) to the coronary sinus. 11) Insert one blade of your scissors into the left atrium and cut through the left atrium into the left ventricle. Cut from the left ventricle through the aorta. Locate the column-like trabeculae carneae on the interior walls of the ventricles. 12) Find the bicuspid valve, aortic semilunar valves, and the openings to the coronary arteries which are located just past the semilunar valves. 1 ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS: a. How many papillary muscles did you find in each ventricle? b. How many pouches or flaps are present in each of the valves? c. Where does the blood enter and leave the myocardium? d. Account for the difference in size and thickness of the two ventricles. 2