* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Quantum Numbers and Periodic Table Test Review 1) Identify which
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Ferromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Molecular Hamiltonian wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Auger electron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Tight binding wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
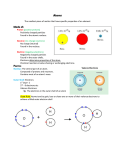
Quantum Numbers and Periodic Table Test Review 23) Write the electron dot structures for the following elements: 1) Identify which waves move contain more energy. A. Blue light or red? B. orange or violet a. Cs C. x-ray or yellow D. infrared or indigo b. I c. Sn d. Po e.Ca f. Zn 24) Name an element for each of the following: 2) In a hydrogen atom rank the following jumps of an excited electron form highest energy photon a. a halogen used in pool maintenance g. an actinide metal ending in f8 released to lowest energy b. a member of Group 15 in Period 3 h. a lanthanide metal ending in f3 photon released. A. 3rd energy level to 1st energy level B. 6th energy level to the 3rd energy level c. an element that has 3 valence electrons C. 2nd energy level to the 1st energy level D. 4th energy level to the 2nf energy level d. a noble gas with the smallest radius i. 3 transition metals found in jewelry j. 2 metalloids in Period 4 3) Calculate the frequency of a wave that has a wavelength of 0.031 m. e. an alkali metal that is the MOST reactive k. achalcogen needed for combustion 4) Without looking at your notes, write down the Periodic and Group Trends for: f. an alkaline earth metal important in bone health l. an inner transition metal used in nuclear plants a. Ionization Energy d. Activity or Reactivity 25) Name an element for each of the following: b. Atomic Radius e. Ionic Radius a. the element in Group 2 and Period 5 c. Electronegativity b. The element in Group 18 and Period 4 c. an element with a -3 oxidation number in Period 3 5) How many energy levels exist in an atom? d. an element with a +2 oxidation number in Period 5 6) How many sublevel exist in an atom? e. an element with a +1 oxidation number in period 4 7) For the “f” sublevel, how many orbitals exist? f. the element whose e- config. ends with 5p1 8) For the “d” sublevel, how many orbitals exist? g. the element whose e- config. ends with 7s2 9) How many electrons can live in the “s” sublevel? h. the elements whose e- config. ends with 4d4 10) How many electrons can live in the “p” sublevel? i. the element whose e- config. ends with 3d1 11) Determine how many electrons total can live on the 3rd energy level. 12) Determine how many electrons total can live on the 4th j. the element whose e- config. ends with 5d8 k. an element that has the valence of s2p4 energy level. l. an element that has a valence of s2p1 13) Determine the higher energy orbital in each of the following pairs. 26) Within each of the following groups, state which is the larger: A. 3d or 4s a. Li and Be B. 4d or 4f C. 6d or 7s D. 5p or 4f 14) Write the orbital notation for A. Fe B. Br b. F and Ne e. O and C. Al D. N O-2 c. Rb and Rb+1 d. Au and Ag f. Br and I and Cl 27) Within each of the following groups, state which has the largest ionization energy: 15) How many half filled orbitals exist for Al? a. Li and Be b. F and Ne 16) How many empty orbitals exist for Al? e. K and Na f. N and Na 17) What is the highest occupied energy in Br? 28) Within each of the following groups, state which has the greatest electronegativity: 18) What is the electron configuration for A. Sr. B. Sc C. Cl D. P 19) How many valence electrons do the following have? A. Cu B. P C. Ar E. Al D. [Xe]6s1 b. Ra C. [Kr]5s24d5 c.F and Ne d.K d. C and O e. Hg and Zr f. Xe and I g. Cs and K [Kr] 5s2 4d3 [Ne] 3s2 3p5 [Xe] 6s1 Te Ra 31) Rank the following from least to most active (within each set)): E. [Xe] 6s24f145d6 c.Xe b. F and Fr Mn B. 1s22s22p1 a. 22) How many valence electrons do the following elements have? a. Rn a. Li and Be 30) Write Noble Gas configurations for: 21) Determine the element represented below 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d1 d. B and Al 29) Identify the following: D. Br 20) Draw the Lewis dot structure for the elements in # 20. A. c.C and O Mg, Al, Ba b. Br, Ar, I, Ne c. Si, P, S, O 33) What is the relationship in size between -neutral metallic atoms and the ions they form? e.Hg f. As -neutral non-metallic atoms and ions they form? A. WAVES E. NOBLE GAS NOTATION: An abbreviated way to write electron configuration. The noble gases are the last column of the periodic table. Total the number of electrons represented and determine the element. Ex [Ne]3s23p4 represents the element sulfur Where is the wavelength represented? What letter marks the amplitude? Waves move energy from one place to another. A list of the different type of waves is the Electromagnetic Spectrum. Here is the list from low energy to high. Radio Micro Infrared Visible Ultra Violet X-ray Gamma Visible light can be broken into the 7 colors of the rainbow. ROYGBIV. Red is lowest energy and Violet is highest. Each wave has the characteristics: Wavelength - complete crest and complete trough ( ) Frequency - # waves that pass per second. measured in Hertz ( ) These two properties can be interrelated with the equation c = Where c is the speed of light: 3.0 x108 m/sec Frequency and energy can be related by the formula: E = hv where h is Planck’s constant 6.63 x10-34 B. ELECTRON CONFIGURATION - address of each electron in the atom Electrons live in atom houses called orbitals. Orbitals have a distinct size shape and orientation. These can be represented in three ways: Electron Configuration (1s2 2s2 etc), Orbital Notation (lines with arrows) and Lewis Dot Structures (dots for valence e ) To locate electrons in an atom look at the Quantum Numbers. - . Principle Quantum Number (n) - energy level denotes the size of the orbital or closeness to nucleus. There are 7 in an atom. 1 is the closest to nucleus, smallest and lowest energy 7 is the farthest biggest, and highest energy - Orbital Quantum Number ( l) - sublevel refers to the shape of the orbital - s,p,d,f s - sphere p - dumbbell d – double dumbbell Notes: Scientists involved with developing the Periodic Table Mendeleev – Came up with the first Periodic Table - Arranged elements by increasing ATOMIC MASSES Moseley - Revised Mendeleev’s table and gave us the one we use today - Elements arranged by increasing ATOMIC NUMBERS! Periodic Table Organized by elements’ atomic numbers so that those with similar properties line up in the same columns. Period – horizontal row – tells the energy level electrons live in. Numbered 1 - 7 Group – vertical column – matches number of valence electrons in the Representative elements (“A” groups) Metal – left side of table – malleable, ductile, shiny, conduct electricity and heat, Lose electrons to become + charged (cations) when reacting and bonding. Lose enough electrons to achieve the electron configuration of a noble gas Non-metals – right side of table – brittle, do not conduct electricity/heat , Gain electrons to become – charged (anions) when reacting and bonding. Gain enough electrons to achieve the electron configuration of a nobel gas Metalloids – along stair step line dividing metals and non-metals Groups or Blocks of Elements to know: Alkali Metals Nitrogen Group Representative Elements Alkaline Earth Metals Oxygen Group (Chalcogens) Transition Metals Boron Group Halogens Inner Transition Metals – Lanthanide & Actinide Series Carbon Group Noble Gases Trends: 2. Atomic Radius (size of atoms) Trend for atomic radius- 3. Ionic Radius Atoms that lose electrons (Metals) form cations AND the ion radius < atomic radius Atoms that gain electrons (NonMetals) form anions AND the ionic radius > atomic radius 4. 5. Ionization Energy, IE – energy required to pull an electron from an atom. Electronegativity, EN – the desire an atom has for an electron (Noble gases have EN = 0) Metals are generous! They like to give away electrons so they have low EN and IE. f – funny, freaky -- most complex - . Magnetic Quantum Number (m) - tells how many orientations or how many orbital of each shape exist on each energy level. s - 1 on every level p - 3 starting on 2nd energy level d - 5 starting on 3rd energy level f - 7 starting on 4th This means that on the 2nd energy level there are three “p” shaped orbitals. Also on the 5th energy level there are another three “p” shaped orbitals. Non-metals are greedy! They want more electrons and have high EN and IE. Large - . Spin Quantum Number (s) - there can be two electrons in each orbital. They spin in different directions. s can hold 2 electrons p can hold 6 electrons d can hold 10 electrons f can hold 14 electrons C. SCIENTISTS: - .According to Aufbau, electrons always fill in orbitals of lowest energy first! If the electrons do fill the lowest energy orbitals they are in the ground state. If for some reason they jump to a higher energy level, the electrons are excited state. They will give off light in packets of energy when excited. Trend for IE and EN 6. 7. 8. 9. Small Valence – same as Roman Numeral Group Number in “A” Groups (# of bonding electrons!) Oxidation Number(charge) - +1, +2, +3, +4, -3, -2, -1, 0 Know all s, p, d, and f blocks Overall Activity or “Reactivity” - desire to react - Hund stated that orbitals of the same size and same shape will be filled in individually first before pairing up. For example, when you do orbital notation diagrams and are filling electrons in the three 2 p orbitals , give each one 1 electron first before pairing them up. - Pauli Exclusion Principle - no two electrons have the exact same quantum numbers. Although 2 electrons can live in the same orbital, they move in opposite directions, thus distinguishing them. D. LEWIS DOT STRUCTURES: Represent the valence electrons. Valence electrons are the electrons in the largest energy level. They are the electrons that are involved in reaction. You will never have more than 8 valance electrons or 8 dots. Metals more Active Fr Nonmetals F more active