* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download eoc evolution shortened
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
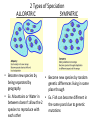
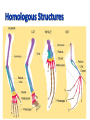
• How much biodiversity 2.0 million species and increasing! 24 March 2009 Biodiversity.ppt 2 • Species: organisms that are: -similar in structure and -can reproduce successfully • Over time, we see the following happen to species: 1. They change for the better adapt 2. They change so much they become a different species speciation 3. They go extinct Why is Earth a giant LIFE-SUPPORT SYSTEM? Earth – 4.5 billion years ago • Any water? • Any land? • Any oxygen? • JUST MOLTEN ROCK! • When gas and rocky debris CRASHED together Earth – 3.9 billion years ago 3.5 billion yrs ago – 1st life forms! • ARCHAEA BACTERIA 2.5 billion yrs ago – 2nd living thing • CYANOBACTERIA • (blue-green “algae”) millions* yrs ago (recently) • PROTISTS • Unicellular organisms amoeba algae millions* yrs ago (recently) • MULTICELLULAR tiny organisms seaweed lichens millions* yrs ago (recently) • • • • • PLANTS ANIMALS (consumers) FUNGI DINOSAURS US! So now all this life…..how are we gunna keep everything straight What is Classification? • Classification is the arrangement of organisms into orderly groups based on their similarities • Classification is also known as taxonomy • Taxonomists are scientists that identify & name organisms based upon structure • Organisms are named Genus, species – Binomial nomenclature – Linnaeus – Homo sapiens “humans” copyright cmassengale 14 • Did • King • Phillip • Come • Over • For • Good • Sex! 15 Binomial Nomenclature Which TWO are more closely related? 16 3 Domains • EUKARYA • PROKARYA • ARCHAEBACTERIA 4 Kingdoms (of Eukarya) • ANIMAL • PLANT • FUNGI • PROTIST Classify HUMANS!!!! • • • • • • • • Domain: Eukarya Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Mammalia Order: Primates Family: Hominidae Genus: Homo Species: Sapiens CHARLES DARWIN – 1809-1882 • ENGLISH, naturalist • Wrote The Origin of Species • TRAVELED AROUND THE WORLD ON THE BEAGLE SHIP • FAMOUS for studying IN THE GALAPAGOS ISLANDS • OBSERVED MANY SPECIES AND FOSSILS • Finches • His term NATURAL SELECTION • Whoever has the best adaptations will survive get to make babies 21 The Galapagos Islands • Finches on the islands resembled a mainland finch • More types of finches appeared on the islands where the available food was different (seeds, nuts, berries, insects…) • Finches had different types of beaks adapted to their type of food gathering 22 Galapagos Fur Seals – almost hunted to extinction bc of fur Galapagos Penguin – 3rd smallest type of penguin, lives in hot temperatures Flightless CORMORANT – no natural predators, you can walk right up to it! -great SWIMMERS 2 Theories of Evolution Lamarck Darwin • Evolution is caused by whoever • Evolution is caused by HAS the best adaptations, gets whoever TRIES their best to to survive better so they just survive will pass down HAVE more babies! these traits to their babies. Lamarck’s Theory of Evolution • Idea called Law of Use and Disuse • If a body part were used, it got stronger • If body part NOT used, it deteriorated 28 Lamarck’s Theory of Evolution • Inheritance Of Acquired Traits – Traits Acquired During Ones Lifetime Would Be Passed To Offspring 29 Clipped ears of dogs could be passed to offspring! How do you form an ADAPTATION at first? • Favorable variations occur by ACCIDENT, geography, or • Could be just random changes in DNA genes- MUTATION! 2 Types of Speciation ALLOPATRIC SYMPATRIC • Become new species by • Become new species by random being separated by genetic differences living in same geography place though • Ex. Mountains or Water in • Ex. Fish can become different in between doesn’t allow the 2 the same pond due to genetic species to reproduce with mutations each other 3 PATTERNS of Evolution a) Convergent evolution different species evolve similar traits. EXAMPLE: fish, water reptiles, and water mammals all evolved streamlined bodies b) Divergent evolution = adaptive radiation single ancestor splits into different species to “fit” better in environment Ex. Darwin’s finches split into different species based on what they eat d) Coevolution two species totally dependent on each other they evolved together (mutualism) Ex. Bumblebees need nectar and flowers need pollination Evolution in Anatomy • 1. Homologous structures• Similar structures, different functions • Ex. Bat wing vs human arm, etc. • 2. Analogous structures• similar functions, different structures –Ex: bird and insect wings • 3. Vestigial structures- structures that no longer used for their original function – Ex. – appendix, tonsils, coccyx, male nipples, wisdom teeth… • 4. Similar Embyros- some embryos of different species are VERY close in appearance – Did we all come from the same ancestor? Fossil Record • • • • M- mammals R- reptiles A-amphibians F-fish Cladogram- shows connection between species Bio Material you should review • • • • Scientific method (steps) Acid and base (pH scale) Macromolecules – made of carbon Enzymes- what do they do, related to what macromolecules, lock and key • Cells- organelles and pro vs eukaryotic • Homeostasis- diffusion and osmosis (high to low) a lot to a little • Equations of Cellular respiration and photosynthesis (reactants and products) • Mitosis and Meiosis- crossing over, pictures, and what type of cell each happens in. • DNA- structure, function, (replication, transcription, and translation….where each happens and the base-pairing rules) • Genetics- punnett squares/ geno vs phen/ hetero/homozygous….9:3:3:1 • • • • GOOD LUCK TOMORROW and WEDNESDAY>>>> TRY…….IT IS EASIER THAN YOU THINK……… REMEMBER, Eliminate at least two of the wrong answers Writing----- your task, use info from text, look at the rubric