* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evol Theory, Evidence
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Vestigiality wikipedia , lookup
Coevolution wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
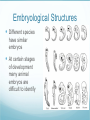
Evolutionary Theory The Theory of Evolution is based on many types of data. Fossil Record Morphological Evidence Embryological Evidence DNA Evidence Homologous Structures Body parts with the same structures but have different functions Analogous Structures Body parts with similar functions but with different anatomy (not good evidence) Vestigial Structures Body parts that are reduced in size and are no longer used Hip bones in snakes have no purpose, but they suggest that snakes evolved from ancestors with hips Embryological Structures Different species have similar embryos At certain stages of development many animal embryos are difficult to identify Theories of Evolution Jean Baptiste Lamarck (1744 – 1829) Theory of Acquired Characteristics 1. Living species descended from a common ancestor (True) 2. Acquired characteristics could be passed on to offspring (False) -an acquired trait is one that is not determined by genes. Ex.-birds’ feet, giraffe necks Charles Darwin Darwin (1809 -1882) Darwin studied many animals but the finches from the Galapagos Islands were of great interest to him. The Journey Galapagos Islands Finches Finches on different islands had different characteristics. It is thought that a single species from S. America flew to the islands and the different islands caused the finches to evolve. . Charles Darwin (1830) 1. Overproduction 2. Struggle for existence (survival) 3. Variation 4. Survival of the fittest 5. Natural selection 6. Evolution of new species Natural Selection The environment selects the most-fit organisms. The environment selects organisms with beneficial traits Natural Selection Variation exists within a species Among members of a species, traits vary Natural selection is based on . . . Non-random survival Albino squirrels Non-random mating Mate selection Woman’s choice Non-random fecundity Production of offspring Advantageous Traits/Adaptations MIMICRY- advantage gained by copying the appearance of another, more dangerous, species. Ex.- flies and hornets CAMOUFLAGE- advantage gained by blending in w/ surroundings. Ex.- walking stick, tiger, leaf fish, etc. Types of Natural Selection Stabilizing Selection Individuals with the average form of a trait have the highest fitness Types of Natural Selection Directional Selection Extreme forms of a trait are more fit Types of Natural Selection Disruptive Selection Either extreme form of a trait is more fit. Patterns of Evolution Coevolution The change of two or more species in close association with each other Parasites & host, predator & prey Patterns of Evolution Convergent Evolution The environment selects similar phenotypes even though the organisms are quite different Sharks and dolphins Patterns of Evolution Divergent Evolution Two or more related populations or species become more and more dissimilar. Galapagos finches