* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
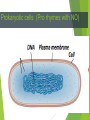
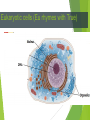
Obj. I will be able to tell the difference between a prokaryote and a eukaryote cell. Pages: 11-12 Heading: Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells Homework: Test Corrections Cell Analogy Project Do First 1. There are approximately 10 billion cells in the human body. False; there are more than 100 TRILLION (100,000,000,000) 2. You have billions of bacteria inside your body right now. True! 3. Cells are about the size of atoms. False! They are WAY bigger! 4. It is unhealthy to eat food containing microorganisms (microscopic living things). False! (sometimes) 5. Microorganisms cannot live in extreme heat or cold. False! Do First 6. Bacteria make up about 1 percent of your dry body weight. False! They make up 10%! 7. Microorganisms produce some of the oxygen we breathe. True! 8.There are over 350 species of bacteria living inside your mouth. True! 9. Antibiotics kill viruses. False! They kill bacteria 10.The bubonic plague bacteria was responsible for killing one-third of the population in Europe. True! Today’s Objective: SWBAT differentiate between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. The Two Types of Cells As microscopes got more powerful, scientists started look at the parts inside cells. An organelle is a small, specialized structure inside a cell. The Two Types of Cells All cells can be divided into two categories: Eukaryotic Cells Prokaryotic Cells Prokaryotic cells (Pro rhymes with NO) Prokaryotic Cells Do NOT contain a nucleus or any other membrane-bound organelles. DNA floats around in the cytoplasm Very small. Smaller than eukaryotic cells. Usually found in bacteria and other unicellular organisms Eukaryotic cells (Eu rhymes with True) DNA Eukaryotic cells Contain a nucleus or any other membrane-bound organelles. DNA located in the nucleus. Very large. Smaller than eukaryotic cells. Usually found in animals, plants, fungus, protist and other multicellular organisms