* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Somatoform disorders - Salisbury University
Major depressive disorder wikipedia , lookup
Schizoid personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Emergency psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Schizophrenia wikipedia , lookup
Anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Bipolar disorder wikipedia , lookup
Excoriation disorder wikipedia , lookup
Sluggish schizophrenia wikipedia , lookup
Autism spectrum wikipedia , lookup
Panic disorder wikipedia , lookup
Controversy surrounding psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Separation anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Asperger syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Depersonalization disorder wikipedia , lookup
Schizoaffective disorder wikipedia , lookup
Conversion disorder wikipedia , lookup
Substance use disorder wikipedia , lookup
Antisocial personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Substance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Conduct disorder wikipedia , lookup
Mental status examination wikipedia , lookup
Pyotr Gannushkin wikipedia , lookup
Generalized anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Mental disorder wikipedia , lookup
Glossary of psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Spectrum disorder wikipedia , lookup
History of psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Narcissistic personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
Causes of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders wikipedia , lookup
Child psychopathology wikipedia , lookup
Classification of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
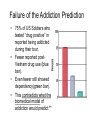
Chapter 12 Psychopathology This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display, including transmission of any image over a network; preparation of any derivative work, including the extraction, in whole or part, of any images; any rental, lease, or lending of the program. ISBN: 0-205-37181-7 Evolving Concepts of Mental Disorder • How do we define “abnormality”? • Medical model “disease” view, biological causes • Psychological models Psychogenic – Caused by psychological factors (thoughts, beliefs, childhood, experiences) Indicators of Abnormality Distress Maladaptiveness Irrationality Unpredictability Unconventional and undesirable behavior Observer discomfort Classifying System DSM-IV – (1994) Fourth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders • the most widely accepted classification system in the United States • Common terminology across disciplines • Etiology – The causes of, or factors related to, the development of a disorder Explosion of Mental Disorders • • Supporters of new categories answer that is important to distinguish disorders precisely. Critics point to an economic reason: diagnoses are needed for insurance reasons so therapists will be compensated. Problems with DSM-IV • Danger of overdiagnosis • Power of labels (self-fulfilling prophecy) • Confusion of serious disorders with normal problems • Illusion of objectivity and universality What are the Consequences of Labeling People? • Diagnostic labels can compound the problem (Rosenhan Study**) • The cultural context of mental disorder I. Anxiety Disorders :general state of apprehension or psychological tension Generalized Anxiety disorder (GAD) Post-traumatic Stress disorder (PTSD) Panic disorder – Marked by panic attacks that have no connection to events in a person’s present experience Phobias Agoraphobia- Fear of public places/open spaces Social Phobia- fear of being observed by others Anxiety Disorders Obsessive-compulsive disorder – Condition characterized by patterns of persistent, unwanted thoughts and behaviors II. Dissociative Disorders Amnesia Dissociative fugue Dissociative identity disorder A loss of memory for personal information Dissociative Disorders Amnesia Dissociative fugue Dissociative identity disorder Amnesia with the addition of “flight” from one’s home, family, and job Dissociative Disorders Amnesia Dissociative Fugue Dissociative identity disorder Condition in which individual displays multiple identities The D.I.D./M.P.D. Controversy • First view – MPD is common but often unrecognized or misdiagnosed. – The disorder starts in childhood as means of coping. – Trauma produced a mental splitting. • 2nd view – Created through pressure and suggestions by clinicians. – Range: Only Handfuls of people to 10000 since 1980. III. Mood Disorders Bipolar disorder – Mental abnormality involving swings of mood from mania to depression Mania – Pathologically excessive elation or manic excitement Depression – Pathological sadness or despair Mood Disorders Unipolar depression • Incidence • Causes of depression • Seasonal affective disorder (SAD) – Believed to be caused by deprivation of sunlight Symptoms of Depression • • • • • • • • • DSM IV Requires 5 of these within the past 2 weeks Depressed mood. Reduced interest in almost all activities. Significant weight gain or loss, without dieting. Sleep disturbance Change in motor activity Fatigue or loss of energy. Feelings of worthlessness or guilt. Reduced ability to think or concentrate. Recurrent thoughts of death. Vulnerability-Stress Model IV. Schizophrenic Disorders Schizophrenia – Psychotic disorder involving distortions in thoughts, perceptions, and/or emotions (most likely to hospitalized) Major Types of Schizophrenia Disorganized Catatonic Paranoid Undifferentiated Features incoherent speech, hallucinations, delusions, and bizarre behavior Major Types of Schizophrenia Disorganized Catatonic Paranoid Undifferentiated Involves stupor or extreme excitement Major Types of Schizophrenia Disorganized Catatonic Paranoid Undifferentiated Prominent feature: combination of delusions and hallucinations Major Types of Schizophrenia Disorganized Catatonic Paranoid Undifferentiated Persons displaying a combination of symptoms that do not clearly fit in one of the other categories Theories of Schizophrenia • • • • Genetic predispositions Structural brain abnormalities Neurotransmitter abnormalities Prenatal abnormalities V. Problem Personalities • Personality Disorder – • Narcissistic Personality Disorder – – • Rigid, maladaptive patterns that cause personal distress or an inability to get along with others. exaggerated sense of self-importance and selfabsorption. preoccupation with fantasies of success and power, and a need for constant attention Paranoid Personality Disorder – habitually unreasonable and excessive suspiciousness and jealousy. Personality Disorders cont’d Antisocial personality disorder – Characterized by aggressiveness, lack of guilt, and exploitation of others • Must have 3 of these criteria and a history of behaviors – – – – – – – Repeatedly break the law. They are deceitful, using aliases and lies to con others. They are impulsive and unable to plan ahead. They repeatedly get into physical fights or assaults. They show reckless disregard for own safety or that of others. They are irresponsible, failing to meet obligations to others. They lack remorse for actions that harm others VI. Somatoform Disorders Somatoform disorders – Psychological problems appearing in the form of bodily symptoms or physical complaints Conversion disorder – marked by paralysis, weakness, or loss of sensation, but with no discernable physical cause Somatoform Disorders Glove Anesthesia Somatoform Disorders Hypochondriasis – Somatoform disorder involving excessive concern about health and disease VII. Drug Abuse and Addiction • Biology and addiction. – a person’s biochemistry, – metabolism, and – genetic predisposition Learning, Culture, and Addiction • Addiction patterns vary according to cultural practices and the social environment. • Policies of total abstinence tend to increase addiction rates rather than reduce them. • Not all addicts have withdrawal symptoms when they stop taking a drug. • Addiction does not depend on the properties of the drug alone, but also on the reason for taking it. Failure of the Addiction Prediction • • • • 75% of US Soldiers who tested “drug positive” in reported being addicted during their tour. Fewer reported postVietnam drug use (blue bar). Even fewer still showed dependency(green bar). This contradicts what the biomedical model of addiction would predict.** Debating the Causes of Addiction • Problems with drugs are more likely when: – A person has a physiological vulnerability to a drug. – A person believes she or he has no control over the drug. – Laws or customs encourage people to take the drug in binges, and moderate use is neither tolerated nor taught. – A person comes to rely on a drug as a method of coping with problems, suppressing anger or fear, or relieving pain. – Peer group uses drugs or drinks heavily, forcing the person to choose between using drugs or losing friends.