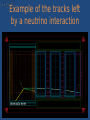
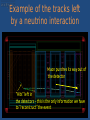
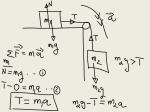
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Detecting particles in particle physics
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Bruno Pontecorvo wikipedia , lookup
Large Hadron Collider wikipedia , lookup
Relational approach to quantum physics wikipedia , lookup
Search for the Higgs boson wikipedia , lookup
Peter Kalmus wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Grand Unified Theory wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Identical particles wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical formulation of the Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
ALICE experiment wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light neutrino anomaly wikipedia , lookup
Neutrino oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Future Circular Collider wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Weakly-interacting massive particles wikipedia , lookup
Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Super-Kamiokande wikipedia , lookup