* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
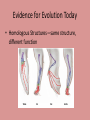
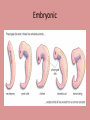
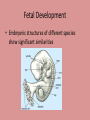
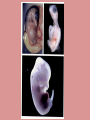
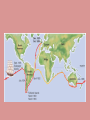
Evolution Objectives: 1. Explain evidence for evolution What evolution is NOT • Not a theory (it is a fact, it has been observed directly, and its extension to all life is supported by more evidence than there is for the spherical shape of planets, and there is no evidence against it. • Not something one should believe in (based on science, not faith) • Not concerned with the origin of life(only with origin of species) • Not concerned with the origin of humans • Not discovered by Darwin • Not the same as natural selection(the HOW of evolution) • Not something that happened only in the past • Not something that happens to individuals • Not an accidental or random process— • Does not have any evidence against it • Not contrived to undermine religion • Does not deny the existence of God • Does not conflict with religion (since it is another way of trying to make sense of the natural world, based on scientific observations and critical analysis. Most religions have not problem with evolution, and those that do typically base their objections on an inaccurate view of science and evolution History of Evolution • Aristotle—believed species were fixed creations arranged by their complexity • Believed for about 2000 years Contributions to Evolution • Charles Lyell—uniformitarianism—geologic process still changing earth (sediment layers in rock) • Georges Cuvier—Catastrophism—species extinction • Thomas Malthus—resources—struggle for existence More Contributors • James Hutton—Gradualism • John Baptiste Lamarck—inheritance of acquired traits—Law of use and disuse • Alfred Russel Wallace—organisms evolved from a common ancestor Catastrophism • Proposed by George Cuvier • Studied fossils in the sedimentary rock strata • Found some species completely disappeared in more recent layers • Though species disappeared due to catastrophic events of the earths crust. (volcano, earthquake, etc,) Geological Change • James Hutton studied invertebrate fossils • Described the geological forces that have changed life on earth over millions of years ago (erosion, earthquakes, etc. ) • Changes in earths crust due to slow continuous processes • Gradualism Uniformitarianism • Charles Lyell • Geological processes at uniform rates building and wearing down Earth’s crust • Proposed that the Earth was millions of years old instead of thousands of years The Dummy • Lamarck—changes occur over time • Stated that changes are adaptations to environment acquired in an organisms lifetime • Acquired traits are passed to offspring More about the Dummy • Law of Use and Disuse • If a body part were used, it got stronger • If not part was used, it deteriorated Lamarck’s Theory of Evolution Lamarck’s Mistakes • Did not know how traits were inherited • Genes are not changed by activities in life • Change through mutations occur before an organism is born Evidence for Evolution Today • Homologous Structures—same structure, different function More structures • Analogous—different structure, same function (fly wing and bat wing)…NOT evidence for evolution • Vestigial structure—remnant of organ from Embryonic Fetal Development • Embryonic structures of different species show significant similarities DNA Sequence Fossil Record • Earth is billions of years old • Fossils in different layers of rock showed evidence of gradual change over time Fossil Evidence • Armadillo(N and S America) • Glyptodon Fossils • Marine fossils found high in the Andes mountains Geographic Distribution of Living Species • Different animals on different continents but similar adaptations to shared environments Tomorrow… • Darwin! Divergent Evolution • Accumulation of differences between groups which lead to the formation of a new species, usually a result of diffusion of the same species to different and isolated environments which blocks the gene flow and has new organisms with different traits Convergent Evolution • Same traits acquired by unrelated organisms. • Ancestors of bats and birds were land creatures. They both evolved to have wings. Darwin the Naturalist • Born 1809 • Joined crew of HMS Beagle in 1831 for 5 year voyage around the world • Avid collector of flora and fauna • Surprised by variety of life The Galapagos Islands • Small group of islands off the coast of South America • Each island has a very different climate • Animals on each island are very unique – Tortoises – Iquana – finches The Galapagos Islands • Volcanic islands • Off the coast of Ecuador Finches • Finches on the islands resembled a mainland finch. • More types of finches appeared on the islands where available food was different (seeds, nuts, berries, insect, etc…) • Had different beaks for the different foods Darwin’s Observations and Conclusions • • • • The struggle for Existence Patterns of diversity Unique adaptations of organisms Both living organisms and fossils collected Darwin’s Conclusions • If left unchecked, the number of organisms of each species will increase exponentially, generation to generation • In nature, populations tend to remain stable in size • Environmental resources are limited Natural Selection • Production of more individuals than can be supported by the environment leads to a struggle for existence among individuals • Only a fraction of offspring survive each generation • Survival of the Fittest Natural Selection • Individuals who inherit characteristics most fit for their environment are likely to leave more offspring than less fit individuals • Called Natural Selection Descent with Modification • Organisms descended form a common ancestor • Organisms change with time, diverging form a common form • Cause evolution of a new species Natural Selection • Driving force for evolution • During the struggle for resources, the strongest survive and reproduce • Fitness—ability to survive and reproduce fertile offspring • Those with the most advantageous adaptations survive • Adaptations—inherited characteristic that increases an organisms chance for survival Adaptations • Can be physical or behavioral Natural and Artificial Selection • Abandoned the idea that species were perfect and unchanging • Significant variation in all species • Farmers use variation in livestock and crops • Selective breeding Natural vs. Artificial • Natural – Differences among individuals of a species • Artificial – Selective breeding to enhance desired traits among stock or crops – Nature provides the variation among organisms and humans selected those variations they found useful