* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Seismic Waves
Ionospheric dynamo region wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
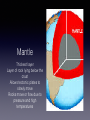
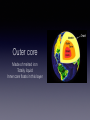
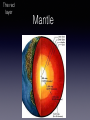
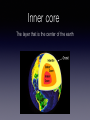
INSIDE EARTH By Brooke E. Introduction Earthquakes are movements or vibrations in the Earth. They are caused the release of stored energy in earth's outer layer. There is also an instrument that detects, measures, and records the energy of an earthquake.This is called a seismograph, and it produces seismograms. Pressure within the earth can cause rocks in its outer layer to break. These breaks are called faults. When an earthquake begins, pressure deep within Earth causes rocks along faults to move and break. As they move, energy is released as vibrations. These vibrations are called seismic waves. As seismic waves move through Earth and along its surface, they are felt as shakings and vibrations. Primary Waves Called P waves Fastest waves First to arrive at a distant point Travels through solids, liquids, and gases Secondary Waves Called S waves Slower that P waves Arrives later at a distant point Travels through solids only Surface Waves Called L waves Slowest waves of all Felt at the surface Causes the most damage Introducing... The layers of the Earth! Crust Thinnest layer Grass, dirt, and sand Contains oxygen Deeper under continents than oceans Earth's most outer layer We live on it Solid rock The thin yellow layer is the crust Mantle Thickest layer Layer of rock lying below the crust Allows tectonic plates to slowly move Rocks move or flow due to pressure and high temperatures Outer core Made of melted iron Totally liquid Inner core floats in this layer Inner core Solid sphere Center of the earth Spins at a different rate than the rest of the planet Earthquake Fault Tectonic plates Richter scale Seismograph/ Seismogram The yellow section Crust The red layer Mantle Outer core The yellow layer is the... Inner core The layer that is the center of the earth