* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Structural Organization of Plants
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
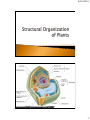
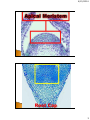
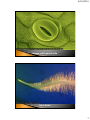
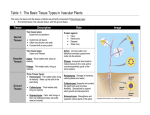
4/15/2014 1 4/15/2014 1. 2. 1. 2. 3. Meristematic tissues are cells or group of cells that have the ability to divide. These tissues in a plant consist of small, densely packed cells that can keep dividing to form new cells. Permanent tissues do not have the ability to divide. These cells are already differentiated in different tissue types and is now specialized to perform specific functions. Apical meristem a. Shoot apical meristem b. Root apical meristem Lateral meristem Intercalary meristem 2 4/15/2014 3 4/15/2014 Root tip showing apical meristem Dermal tissue a. Epidermis 2. Vascular tissue a. Xylem b. Phloem 3. Fundamental tissue a. Parenchyma b. Chlorenchyma c. Collenchyma d. Sclerenchyma 1. 4 4/15/2014 The epidermis is the outermost cellular layer which covers the whole plant structure. It covers roots, stem, leaves, flowers and fruit. The outer walls, which are exposed to the atmosphere and usually thickened, and may be covered by a waxy, waterproof cuticle which are made up of cutin. 5 4/15/2014 Stoma is an opening (pore) which is bounded by two bean shaped cells called guard cells. The thin-walled epidermal cells of roots give rise to root hairs. Hair- like outgrowths may also be found in the epidermis of leaves and stems. Onion cells 6 4/15/2014 Stoma with guard cells Root hairs 7 4/15/2014 The epidermal cells protect the underlying cells The waxy cuticle prevents the loss of moisture from the leaves and stems The transparent epidermal cells allow sunlight for photosynthesis The stomata of leaves and stems allow gaseous exchange The root-hairs absorb water and dissolved ions from the soil 8 4/15/2014 Vascular bundle Xylem tissues are hollow tubular cells important for upward movement of water and nutrients. 9 4/15/2014 Xylem tissues Xylem is an important strengthening tissue Xylem vessels and tracheids transport water and mineral salts Starch is sometimes stored in the xylem fibers and xylem parenchyma 10 4/15/2014 Phloem tissues are vessel cells important for transport of food and nutrients throughout the whole plant. Phloem tissues 11 4/15/2014 Sieve tubes transport organic compounds The phloem fibers give the plant mechanical strength The phloem parenchyma stores compounds such as starch 12 4/15/2014 Parenchyma is the most common plant tissue. The thin-walled parenchyma cells have large vacuoles and distinct intercellular spaces. 13 4/15/2014 Parenchymal and collenchymal tissues The most important function of the parenchyma cells of roots and stem is the storage of food (starch) and water The intercellular air spaces permit gaseous exchange 14 4/15/2014 Chlorenchyma cells are actually parenchyma cells but they contain chloroplasts like the parenchyma cells of leaves and stems. Chlorenchymal tissues 15 4/15/2014 The chlorenchyma are the main photosynthetic cells of the plant and manufacture carbohydrates during photosynthesis Collenchyma cells have thick cellulose cell walls which thickened at the corners. The cells contain living protoplasm and they sometimes contain chloroplasts. 16 4/15/2014 Parenchymal and collenchymal tissues The collenchyma serve as supporting and strengthening tissue In collenchyma, chloroplast is where photosynthesis takes place 17 4/15/2014 Mature sclerenchyma cells are dead and have secondary cell walls thickened with cellulose and usually filled with lignin. In contrast to collenchyma, which is pliable, sclerenchyma is elastic. Sclerenchymal tissues 18 4/15/2014 Sclerenchyma is an important supporting tissue in plants Fibres probably play a role in the transport of water in the plant 19