* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download STUDY GUIDE - West Ashley High School
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Vestigiality wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
The eclipse of Darwinism wikipedia , lookup
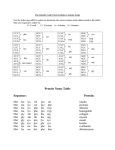
STUDY GUIDE- EVOLUTION Evolution: the process by which species change over time. (requires thousands or millions of years) Individuals do NOT evolve, populations do! Artifical Selection : when humans breed animals to have certain desired traits. (ex. Dogs) Natural Selection : survival of the fittest: the driving force behind evolution 1. Over Production of Offspring : more offspring produced than can survive (increases competition) 2.Variation: (diversity) Some traits are more favorable than others 3. Selection for Adaptations : organisms that are better adapted: + will survive + will reproduce + will pass on their adaptation 4.Descent with Modifications: more individuals will have successful traits in following generations. Fitness: measures how much a trait will contribute to reproductive success. Survive and Reproduce! Microevolution: evolution on a small scale, with a population Macroevolution: evolution on a large scale, involved many different species Genetic Variability: a variety of genotypes and phenotypes that can lead to evolution - Causes: 1. Genetic drift: rare alleles disappear from a population 2. Gene Flow: alleles enter and exit a population (immigration and emigration) 3. Natural Selection: traits that increase fitness are selected for, unhealthy traits are selected against 4. Mutation: errors or changes in DNA (Important for genetic diversity!) 5. Non-random mating: mates are chosen due to specific qualifications (ex. Peacock feathers) Speciation: forming a new species from a pre-existing one (species = able to breed together, same gene pool) 1. Behavioral Isolation – different mating rituals (dance vs sing) 2. Temporal Isolation – different mating seasons (spring vs summer) 3. Geographic Isolation – separated by a mountain range or river 4. Reproductive Isolation – the sex cells are incompatible Patterns of Evolution Gradualism: gradual change in a species over time (Ex. Giraffe) Punctuated Equilibrium: abrupt and quick change in a species, due to environmental pressure (Ex. Dark and Light moths due to factory pollution) Divergent Evolution Species diverge (split off) from a common ancestor Similar characteristics that help them survive in a different niche Homologous structures Ex. Trunk on an elephant and trunk on a Wooly Mammoth Homologous structures: similar traits resulting from common ancestry (ex. similar bones in limbs of different animals) Convergent Evolution Develop similar characteristics due to similar environments They are NOT closely related , no common ancestor Develop analogous structures Analogous structures: structures similar in function, but with different evolutionary origins (Ex. Wings of a bat and wings of a butterfly) Coevolution: when 2 species evolve together. (Ex. Faster lion = faster zebra) Evidence of Evolution Anatomy Analogous structures due to convergent evolution (no common ancestor) Homologous structures due to divergent evolution (common ancestor) Vestigial structures - structures with little or no function to the organism. (Ex. Wings on an ostrich, appendix in a human) Embryology – the study of embryonic (pre-birth) development Similarities are more evident in earlier forms of the zygote More similarities in embryos = the more closely related the organisms. Paleontology – the study of pre-historic life Fossil records = see a pattern of gradual change. The fossil record is NOT complete, many organisms do not form fossils. The older the fossil, the less resemblance there is to modern species Transitional fossils – show links between groups of organisms Biochemistry study of genes and proteins More similar the DNA and amino acid sequence (protein) = more closely related Example: 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 Human Chimp Gorilla Rhesus Horse Kangaroo ASN ASN ASN ASN ASN ASN PHE PHE PHE PHE PHE PHE ARG ARG LYS LYS ARG LYS LEU LEU LEU LEU LEU LEU LEU LEU LEU LEU LEU LEU GLY GLY GLY GLY GLY GLY ASN ASN ASN ASN ASN ASN VAL VAL VAL VAL VAL ILE LEU LEU LEU LEU LEU ILE VAL VAL VAL VAL ALA VAL Human and Chimp = 0 amino acid differences (most related) Human and Gorilla = 1 amino acid difference Human and Kangaroo = 6 amino acid differences (least related) CYS CYS CYS CYS LEU ILE VAL VAL VAL VAL VAL CYS LEU LEU LEU LEU VAL LEU ALA ALA ALA ALA ALA ALA HIS HIS HIS HIS ARG GLU