* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Packet #9
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
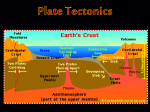
Nam me:________ ____________Date: ______________ _ UN NIT T FO OU UR Dy ynam mic E Earthh *Ded dicated to: __ ____________ ___________ ____ Nam me:________ ____________Date: ______________ _ ABSTRACT A T AND RATIIONALE To ddesign structu ures that can n withstand earthquakes, e , engineers m must understtand the stressses caused bby shaking. To thhis end, scientists and en ngineers placce instrumen nts in structuures and nearrby on the grround to measure how the sstructures resspond during g an earthqu uake to the motion m of the ground benneath. Every time a stronng earthhquake occurs, the new information i gathered enaables engineeers to refinee and improvve structural designs and d buildding codes. Today T there are instrumeents installed d in hospitalls, bridges, ddams, aqueduucts, and othher structures throuughout the earthquake-prone areas of o the United d States incluuding other sseismically aactive regionns of the natioon. TASK K STATEMEN ENT/PROBLE EM BASED LEARNING G/REAL WO ORLD PROBL LEM: After this unit, you and yo our group members m will explore eaarthquake haazards and damage to bbuildings by y consstructing mo odel building gs and subjeecting the bu uildings to gground vibraation (shakinng similar too earthquakee vibraations) on a small shakee table. The buildings b wiill be construucted by twoo- or three-pperson teamss of studentss. After constructio on, the build dings are tested by subjeecting them to earthquakke shaking tto see whichh designs and d consstructions aree successful.. Rulees: 11. Materialss are limited d (realistic) 22. Completee constructio on in limited d time (realisstic) Matterial: 11. Posterboard (lightweeight posterb board; note: there t is a diffference in qquality and thherefore streength of ght pasteboaard; the best posterboard p has one smoooth, almostt glossy side and on dull side; lightweig lightweig ght posterboaard can be purchased at most booksttores, convennience stores, Wal-Martt and KMart.) 22. Scotch Tape T (2 cm orr 3/4” wide) 100 cm leng gth (Plan acccordingly!) 33. Scissors 44. Ruler 55. 4 – 8 x 8 cm squares 66. 12 – 1½ x 10 cm strip ps 77. 12 – 1½ x 15 cm strip ps 88. 1 – 30 x 8 cm Topiccs that we’lll cover in deetail to help p on your tassk statemen nt: Cause off earthquakess Movement of earthqu uakes Earthquaake intensity Calculatiing earthquake’s arrival time, origin time and disstance from the origin. Effects of o earthquakee Nam me:________ ____________Date: ______________ _ Read d page#172-194 in your Ea arth Science textbook. t Answer the que estions below (specifically ffor each sectiion of the readiing). Remem mber, try to be e honest and not n make up any a answers.. This is a wa ay for me to u understand wh here you are havin ng difficulty. Page e #172 1. Exxplain Wegn ner’s hypothe esis AND list three obse ervations tha at supported his idea. ____ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ _ ____ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ _ ____ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ _ ____ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ _ ____ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ _ ____ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ _ ____ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ _ e#173 Page 2. W What does ea arthquake an nd volcanoes s relate to th he theory of plate tectonics? ____ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ _ ____ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ _ Nam me:________ ____________Date: ______________ _ Page e #174 3. To o your best ability, a expla ain how study ying the mag gnetic prope erty of igneo ous rock on tthe ocean flo oor supports the ttheory of pla ate tectonics ____ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ _ ____ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ _ ____ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ _ 4. W Write down tw wo questions s you have on o that sectio on ____ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ _ ____ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ _ ____ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ _ 5. W Write down th hree vocabularies you stumbled on while w reading g the text. ____ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ _ ____ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ _ Page e#174 How does the e age of the rock at the center c of the e mid ocean ridge comp pare to the siide? 6. H ____ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ _ ____ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ _ ____ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ _ Page e 194 7. S Summarize where w and ho ow volcanoe es form ____ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ _ ____ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ _ ____ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ _ ____ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ _ ____ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ _ Nam me:________ ____________Date: ______________ _ INTERIOR R OF THE E EARTH Lithosphe ere: ______ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ _______ Asthenos sphere: ____ __________ __________ ___________ __________ __________ _______ Nam me:________ ____________Date: ______________ _ How w do we know w about eartth’s interiorr? ANS S: _________ __________ ___________ __________ _________ Refraction: ____ __________ ___________ __________ ___________ ___________ __________ __________ _________ Nam me:________ ____________Date: ______________ _ Use pa age 10 of th he Earth Science Referrence Table e to answer the following question ns. 1 1. Approxim mately how thick is the litthosphere? 2 2. What are e the two ma ajor types of crust on Earth’s surface e? 3 3. Which type of the cru ust is the denser? How much dense er? 4 4. How hot is the Earth at 3000km deep? 5 5. What’s th he pressure 1000km dee ep? 6 6. In which Earth layer does the pre essure reach h 3.5 million atmosphere es? 7 7. Which layer is responsible for ca ausing plate tectonics? 8 8. What forms as a resu ult of subduc ction zone between b two plates? 9 9. What is the t name of the boundarry between the t crust and d the mantle e? Name:_________________Date: _____________ Plate Tectonic Notes Types of plates and features of interactions Nam me:________ ____________Date: ______________ _ Plate Tec ctonics Cla ass Exercisse (ESRT pg. 5) 1. Liist three pieces of evvidence of continenta al drift: a. b. c. 2. W What is believed to ca ause the pllates to mo ove? 3. D Describe th he differen nce betwee en a contine ental plate e and an oce ean plate: 4. W Write the name n of eac ch type of plate boun ndary and tthe main fe eatures th hat form. Nam me _______ _________ Name: ___________________ Keyy Features: __________ _ ________ Key Feattures: ________________ Nam me: _______ _________ Name: _______________ Keyy Features: __________ _ ____ Key Feeatures: ________________ Nam me:________ ____________Date: ______________ _ 5. a a. What type e of bounda ary exists be etween the North Ame erican Plate and the Eu urasian Plate e? ________ ____ b b. What feature is form ming at thatt boundary? ? ________ _________ ________ 6. a a. What type e of bounda ary exists be etween the Philippine PPlate and th he Pacific Plate? _________ _ __________ ___ b b. What feature is form ming at thatt boundary? ? _______ __________ _________ 7. a a. What type e of bounda ary exists be etween the Nazca and South Ame erican Platess? _______ _____ b b. What feature is form ming at thatt boundary? ? _______ __________ _____ 8. a a. What type e of plate boundary exists on the west coast of the USA A in Californ nia? ______ _____ b.. What featture is occurring at tha at boundary? _______ __________ _________ _ 9. a a. Name fourr hot spots:: ________ _________ _________ __________ __________ _ 10. a. When an ocean plate e collides with a contine ental plate, which plate e will go und derneath tthe other? _______ __________ _________ ______ b b. Why? _________ _ _________ _________ __________ _________ _________ __________ ____ 11. a a. What do we know about the age e of the rocks at mid-occean ridgess? b b. What happens to the e age as you get farther from the ridges? 12. Look at the e Nazca and South Ame erican plate. Which platte is going uunderneath the other? ? Nam me:________ ____________Date: ______________ _ ots Define Hot Spo ____ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ _ ____ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ _ ____ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ _ ____ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ _ Nam me:________ ____________Date: ______________ _ Mid--ocean Ridg ge: How w do the rock ks at MOR in ndicate abou ut the Earth’s s magnetic ffield? ____ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ _ ____ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ _ ____ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ __________ ___________ __________ _ Name:_________________Date: _____________ Name:_________________Date: _____________ Name:_________________Date: _____________ Name:_________________Date: ____________ Read page#214-220 in your Earth Science textbook. Answer the questions below (specifically for each section of the reading). Remember, try to be honest and not make up any answers. This is a way for me to understand where you are having difficulty. Page #214 1. Write a summary that explains the cause of earthquakes _____________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________ Page#215 2. Write down three things you learned about P and S waves _____________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. Write down two questions for each section of the reading Question about reading on page 216: ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ Page #217 4. To your best ability, explain how seismograph works _____________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________ Page#219 5. How many seismographs are needed to find the epicenter of an earthquake?____________________________ Page#220 6. Write down two questions you have on that section _____________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________ 6. Write down three vocabularies you stumbled on while reading the text. _____________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________ Nam me:________ ____________Date: ______________ _ 1 1. Where do d most of the t earthqu uakes and volcanoes v h happen? __ _________ __________ _________ __________ __________ __________ __________ _________ ____ 2 2. Define an a epicenter? _______ __________ __________ __________ _________ __________ ____ __ _________ __________ _________ __________ __________ __________ __________ _________ _____ 3 3. Define a focus: __ _________ __________ _________ __________ __________ __________ __________ ________ P wave S wav ve 1) 1) 2) 2) 3) 3) Nam me:________ ____________Date: ______________ _ Nam me:________ ____________Date: ______________ _ EXA AMPLE#1 How lon ng does it ta ake for S-W Wave to trav vel 5,000km m? _______ __________ ______ EXA AMPLE #2 The reco ording station tells us it took 6 minutes and 2 20 secondss for the P-W Wave to re each them. How far away from the epicen nter of the earthquake e must they be? __________ _________ __________ _ ANS:___ EXA AMPLE#3 How lon ng does it ta ake for P-wa ave to trave el 6000km? ? ________ __________ ________ EXA AMPLE#4 The reco ording station tells us it took 3 minutes and 4 40 secondss for the S w wave to rea ach them, how far away from the epicenter of the earthquake must they b be? ANS: __ __________ _________ __________ ___ AT IF BOTH H P AND S WAVE AR RE KNOWN N? WHA Station A: A San Fra ancisco, Ca alifornia P-Wa ave arrival 3:02:20 3 S-W Wave arrival 3:06:30 What W is the e time difference betw ween P and d S wave a arrivals? _________ __________ _________ ________ ANS:____ Distance to th he Epicenterr? ________ ___________ __________ __________ _______ Nam me:________ ____________Date: ______________ _ Station S B: Denver, C Colorado P-Wa ave arrival 3:01:40 3 S-W Wave arrival 3:04:10 What W is the e time difference betw ween P and d S wave a arrivals? __________ _________ __________ ________ ANS: ___ Distance e to the Epic center? ____ __________ __________ ___________ __________ __ Station S C: Missoula,, Montana P-Wa ave arrival 3:01:20 3 S-W Wave arrival 3:03:00 What W is the e time difference betw ween P and d S wave a arrivals? ANS: ___ __________ _________ __________ ________ Distanc ce to the Epic center? ____ __________ __________ __________ ___________ __ Individual Practice Find th he epicente er of each se eismic statiion P arrival time S arrival time 4:10:25 4:13:05 4:05:00 4:10:00 4:03:30 4:09:00 Lag Tiime center Dista ance Epic Nam me:________ ____________Date: ______________ _ (Seismogra ph from a seiismic station)) 1. In addition to o the seismic station above, how manyy additional onnes scientist need to predict an earthquake? ________ ____________ __ 2. Which plate motions are involved in th he earthquake e in Sumatra and Japan? _____________ ___________ ____________ ___________ ___________________________________________________ 3. How can the distance from m an epicente er determine e the level of ddanger? _____________ ____________ ___________ ___________ ____________________________________________________ 4. In United Staates, where could be a pottential danger for Tsunam i and how sho ould you prep pare? ______________ ___________ ___________ ____________ ____________________________________________________ 5. How does the e speed of seismic waves cchange? ________________ ___________ ____________ ___________ ______________________________________ Traveel time: Arrivval time: Origiin time: 6 6. Which graaphs above sh hows the stattion is located d farthest fro m the epicen nter distance?? Nam me:________ ____________Date: ______________ _ 1. Ba ase your ans swer to the following f que estion on the e cross secttion of a porttion of Earth h’s interior be elow. The cross section shows the foca al depth of some s earthquakes that o occurred went of the Ton nga Trench Data were colle ected along the t 22 paralllel. a a. State the e relationship p between th he depth of an a earthqua ke’s focus a and the earth hquake’s disstance from the Tong ga Trench. b b. The Tong ga Trench is s the crustal surface bou undary betwe een two tecttonic plates. State the n names of the e two plate es. cc. Describe e the relative e motion of th he plates alo ong this bou ndary Nam me:________ ____________Date: ______________ _ ase your ans swer to the following f que estion on the e map below w which show ws the locattion of the ep picenter of 2. Ba an earthquake th hat occurred d on April 20, 2002, abou ut 29 kilome eters southwest of Plattsburgh, New York he map show ws the epice enter of an earthquake happening h ne ear Plattsburgh, New Yo ork on April 2 20, 2002. a. Th b b. State the e latitude and d longitude of o this earthq quake epice enter. Express your answ wers to the nearest tenth of a degree and d include the e compass directions. d Nam me:________ ____________Date: ______________ _ cc. What is the t minimum m number of seismograp phic stations needed to lo ocate the ep picenter of a an earthqua ake? d d. Explain why w this eartthquake was s most likely felt with gre eater intensitty by people e in Peru, Ne ew York, than by people p in Lake Placid, New York. he epicenterr recorded th he P-wave a and S-wave a arrival times s 3. A seismic stattion located 1,800 kilometers from th ke. Notice th he difference e between P and S wave e arrival time at station A and statio on B. of this earthquak a a. Explain how h the seis smograph recorded at station A is fa arther from th he earthquakke epicenterr than station n B. b b. Seismic station s A is located l 5,40 00 kilometers s from the ep picenter of the earthqua ake. How mu uch time would it take t for the first f S-wave produced by this earthq quake to rea ach seismic sstation A? Nam me:________ ____________Date: ______________ _ Station San Jose P-wave arrival 13:17:50 0 S-wa ave arriv val 13:21:00 New w York 13:19:10 0 13:23:20 San Francisco 13:19:35 5 13:23:35 Station San Jose P-wave arrival 01:17:00 0 S-wa ave arriv val 01:22 2:30 New w York 01:24:00 0 01:29:40 San Francisco 01:20:50 0 01:24 4:10 Station San Jose P-w wave arrrival 03:13:40 S-wave arrival 03:17:00 New w York 03:14:10 03:16:50 San Francisco 03:14:00 03:20:00 S-P S Diistance P wave trave el time Oriigin Time S-P S Diistance P wave trave el time Oriigin Time S-P Distance P wave tra avel time O Origin Time Name:_________________Date: _____________ Base your answers to questions 1 through 4 on the generalized map below, which shows a portion of the Atlantic Ocean floor located between South America and Africa. Isolines show the approximate age, in million years, of the ocean-floor bedrock on each side of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Points A, B, and X represent locations on the ocean floor. 1. On the grid in your answer booklet, construct a line graph of bedrock age by plotting the age of the bedrock shown by each isoline that crosses line AB. Points A and B are plotted on the grid. Connect the plots from A to B with a line. 2. Estimate the age of the ocean-floor bedrock at point X. 3. Name:_________________Date: _____________ 4. Explain why the age of the ocean-floor bedrock increases as the distance from the Mid-Atlantic Ridge increases. 5. The Mid-Atlantic Ridge separates pairs of crustal plates, such as the South American Plate and the AfricanPlate. Identify one other pair of crustal plates separated by the Mid-Atlantic Ridge 6. What is the approximate time difference between the first P-wave and the first S-wave recorded at a seismic station located 8000 kilometers from an earthquake’s epicenter? (1) 8 minutes 40 seconds (2) 9 minutes 20 seconds (3) 11 minutes 20 seconds (4) 20 minutes 40 seconds 7. Which surface feature was produced by crustal movements at a transform plate boundary? (1) East African Rift (2) Aleutian Trench (3) Tasman Hot Spot (4) San Andreas Fault 8. A model of Earth’s internal structure is shown below. Analysis of which type of data led to the development of this model? (1) seismic waves (2) depth of Earth’s oceans (3) electromagnetic radiation (4) isobar gradients Name:_________________Date: _____________ Name:_________________Date: _____________ Name:_________________Date: _____________ Name:_________________Date: _____________ Name:_________________Date: _____________ Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the cross section below, which shows the type of seismic waves recorded at various locations after an earthquake has occurred. Point A is a location on Earth’s surface and X is the epicenter of the earthquake. 1. Point A is located 7600 kilometers from the epicenter of this earthquake. How many minutes did it take the first S-wave to reach point A? (1) 9 min (3) 16 min (2) 11 min (4) 20 min 2. How many kilometers did the seismic waves travel from the earthquake directly to the outside of the outer core? (1) 800 km (3) 2900 km (2) 1400 km (4) 6400 km Name:_________________Date: _____________ The Great Rift Valley Rifting of Earth’s crust in eastern Africa began during the Neogene Period as the Ethiopian and Kenyan Domes formed. These two huge domes were created as Earth’s mantle pushed up the overlying crust. As the crust was forced upward, the resulting tension cracked the crust, resulting in the eruption of volcanoes and the formation of large rifts. The crust continued to pull apart, forming rift valleys. These valleys have become deeper and are currently becoming filled with sediments, igneous rock, and water. 1. How many million years ago did the Ethiopian and Kenyan Domes form? ______mya 2. On the diagram, draw two curved arrows, one on each side of the dashed line, to show the direction of movement of the convection currents within the asthenosphere that caused the formation of the dome and the rift valley near location X. 3. Which two lithospheric plates are separated by a mid-ocean ridge in the northeastern portion of the Ethiopian Dome? _____________________________________________ 4. Which cross section best represents the convection currents in the mantle beneath the Peru-Chile Trench? Rubric for plate tectonic and earthquake unit/Learning objectives JUST STARTING Novice GETTING THERE Apprentice YOU’VE MADE IT Practitioner ABOVE AND BEYOND Expert Explain why earthquakes happen and where they happen Explain how earthquakes happen, where they happen and how they travel through the earth. Understand the basic vocabularies of an earthquake: Epicenter, origin, focus, Practitioner Plus Students built successful posterboard buildings models to with stand low to medium frequency shake test . Describe the motion of p and s P and S wave (earthquake energy) wave Not only describe the motion and understand the definitions. Students are able to explain how p and s waves behave as they travels through the interior of the earth Identify the different plate boundaries Explain the motions of the plates and how they create different intensity of earthquakes Identify and explain the different features along the plate boundaries Identify the different interactions of earthquakes Able to use the reference table to describe the motion and definition of p and s wave Calculate the p and s wave travel time Calculate and find the distance to the epicenter using the p and s wave arrival time or travel time Find the p and s wave travel time using the distance to the epicenter data Calculate, find and draw the epicenter location(s) INDICATORS Cause of earthquakes Able to know which wave arrives to the seismic station first. Result of an Earthquake Explain 1-2 cause and effect of an earthquake Understand why p and s waves are important for discovering the composition of the earth’s interior. Understand that tsunami is formed from underwater earthquakes Describe other possible nature disasters from the result of an earthquake. Use P and S waves to detect the arrival of a tsunami and the effects of a tsunami Understand in detail how the Japan tsunami and Sumatra tsunami are formed and the impact on the people Practitioner Plus Calculate the origin of the earthquake using epicenter distance data or from p and s wave travel time and arrival time data Understand Love and Raleigh waves. Practitioner Plus Describe in detail what a tsunami is and how it forms underwater