* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Due: Tuesday February 1
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Ionospheric dynamo region wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
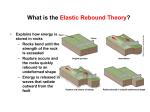
Name: ________________________ Per. ______ Due: Tuesday February 1st, 2011 Quarter 2.5 Assessment Study Guide Chapter 5 Plate Tectonics Questions: 1. Label the diagram of earth 2. What is the core made of? _____________________________________________ 3. What is the thickest layer of earth? ________________________ 4. What is the thinnest layer of earth? ________________________ 5. What happens to pressure and temperature as you down into the earth? 6. Fill in the chart about convection currents: Convection Currents are caused by Differences in __________________ and _______________ What are the effects of In Mantle: _______________________________ convection currents in each layer of earth In ________________: Cause Earth’s magnetic field 7. How did scientists know that the sea floor was spreading? What was their evidence? 8. Draw a diagram to represent what is happening at each type of boundary (HINT: USE ARROWS). Divergent Convergent Transform 9. Fill in the chart about the types of boundaries and stress Type of Boundary Type of stress How it moves What it creates Rift valley or sea floor spreading Convergent Boundary Plates slide past each other 10. Fill in the chart about the focus and epicenter Where it takes place Focus Epicenter What is happening Inside earth Vibrations have reached the surface 11. What is the difference between a seismograph and a seismogram? 12. What is a tsunami? Use the graph below to answer questions 13-17 13. How long does it take a S wave to travel 2,000 km? 14. How long does it take a P wave to travel 2,000 km? 15. How far does an S wave travel in thirty-six minutes? 16. How far does a P wave travel in ten minutes? 17. What is the relationship between distance to the epicenter and the travel time? Use the seismogram below to answer question 18-21 18. Which type of seismic wave produced the smallest ground movement? 19. Which type of seismic wave produced the largest ground movement? 20. What is the order that the waves arrive in? 21. Write an equation that shows how to find the difference in arrival times between the P waves and the surface waves shown in the graph? 22. Label the parts of the volcano 23. What is the major volcanic belt that goes around the Pacific Ocean? 24. Fill in the chart about the types of volcanoes made from lava Landform from Type of Eruption What is erupted Picture of the shape Lava Shield Volcano Bombs, cinders, ash Alternates between explosive and quiet eruption 25. What two factors affect the viscosity of magma (or how well it flows?) 26. What makes a volcano erupt? Use the pie chart to the right to answer questions 27 27. How much of basalt is made of oxides? Use the bar graph to the right to answer questions 28 - 30 28. Which month(s) is it almost certain to have the most earthquakes? 29. Which month(s) is it almost impossible to have many earthquakes? 30. Which month(s) are somewhat likely to have many earthquakes? Use the diagram to the left to answer question 31 31. The diagram is a map of the movement of the Indian plate. It shows how the plate has moved over the past 70 million years. Which direction is the indian plate moving?