* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 1 Notes - Sardis Secondary
Conservation biology wikipedia , lookup
Pleistocene Park wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Operation Wallacea wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Ecological resilience wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
River ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
Lake ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem services wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
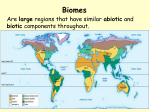
o Biosphere: anywhere on Earth living things exist. Biomes: regions with similar biotic and similar abiotic components ex. BC and New Zealand are similar biomes Science 10 Honours Biotic = living things Miss Ego Abiotic = non-living things Biomes are classified based on many qualities, such as: water o Temperature and precipitation are two of the most important abiotic factors in determining the type of biome availability temperature interactions between biotic and abiotic factors. There are eight types of biomes: boreal forest desert temperate deciduous forest grassland temperate rainforest permanent ice tropical rainforest tundra Which ones are in Canada? With a partner, discuss what you know about these biomes already. o Latitude, elevation and ocean currents also influence the type of biome in an area Latitude o influences both temperature and precipitation. Ex. The tropical zone has very warm temperatures and high precipitation because: • • Elevation o Higher elevations have less dense air so less heat is retained Elevation is the height above sea level o Windward sides of mountains are wet, leeward sides are very dry. Ocean Currents o Carry warmth and moisture to coastal areas the angle of the sun warm air holds more moisture than cooler air Climate: o the average pattern of weather conditions over a period of several years. • A climatograph shows the average temperature and precipitation for a location over a period of 30 years or more. o Climatographs can be used to help identify the biome o Biomes are often identified with characteristic biotic factors. • Ex. a cactus in the desert, or a caribou on the tundra. Adaptations: 1. Structural adaptation - a physical feature that helps an organism survive. • ex. A wolf has large paws to help it run in snow. 2. Physiological adaptation - a physical or chemical event inside the body of an organism that allows it to survive. 3. Behavioural adaptation - a behaviour that helps an organism to survive. • ex. A wolf maintains a constant body temperature. • Many of these characteristic factors have special adaptations that allow the organisms to better survive and reproduce in that biome. • Abiotic Interactions in Ecosystems 1.2 Ecosystems Ecosystem: a part of a biome in which abiotic factors interact with biotic components Can be many hectares of land, or the size of an old log. Within an ecosystem, there are many habitats. The habitat of the red fox often includes the edges of forests or marshlands ex. Wolves hunt in packs to capture large prey. It is the abiotic components that allow the biotic components to survive in an ecosystem. • Oxygen - produced by green plants & microorganisms. • • • • Water - necessary for all life. Nutrients - for growth. Light - required for photosynthesis. Soil - contains water and nutrients. Biotic Interactions in Ecosystems Community: all organisms that interact within an ecosystem. Population: all members of a certain species within an ecosystem. Species: all organisms within an ecosystem that have the same structure & who can reproduce with each other (and produce fertile offspring). Species Niches, Competition and Predation Interactions in a Community 1. Symbiosis: an interaction between the members of two different species. • Commensalism: one species benefits, one is not affected Ex. the barnacles on a whale Niche: the role an organism has within an ecosystem. • Competition: occurs when a limited resource is desired by 2 or more individuals in a niche • Is negative for all organisms involved • this limits the size & health of individual organisms, and perhaps the population • Mutualism: both species benefit Ex. a bee gathering nectar from a flower • Parasitism: one species benefits, the other is harmed Ex. a hookworm living in dogs also refers to the environment in which a species prospers Predation: the relationship between the “eaters” and the “eaten” • • Predators have adaptations to help them catch prey Prey have adaptations to help avoid predators • Ex. spines & shells, camouflage and mimicry Biodiversity in Ecosystems Biodiversity: the variety & number of different individuals & species in an ecosystem. • Healthy ecosystems generally have high biodiversity. • Most biodiversity losses occur from the loss of habitat. • Humans often have a negative impact on biodiversity. • Ecological management programs try to balance human progress with maintaining biodiversity. An Environmental Issue Assignment You and your group members have been hired as environmental consultants by large company. You have been asked to research the reasons why citizens of Chilliwack are concerned about the resource development that they are proposing. Your job is to list the ways in which the environment will be impacted negatively (and positively?), and propose sustainable solutions to these problems. You will be marked on the following: Use of Key Terms – incorporate all that connect to your topic (5) Thorough analysis of the potential environmental impact - including creative and feasible sustainable solutions (20) Presentation Quality – 5min approx. (5) Summary Report – to be handed in (10)