* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture4_Paleoclimate_Solar_Climate
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Snowball Earth wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on Australia wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
Years of Living Dangerously wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Solar activity and climate wikipedia , lookup
IPCC Fourth Assessment Report wikipedia , lookup
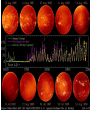
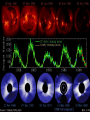
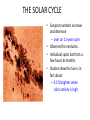
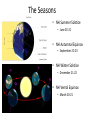
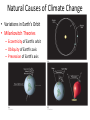
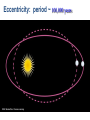
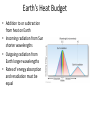
Earth’s Climate System • Climate – long term atmospheric conditions in a region • Earth’s climate includes interactions of: – – – – – Atmosphere Hydrosphere Geosphere Biosphere Cryosphere • Climate system – exchanges of energy and moisture between these spheres Earth’s Climate System Earth’s Climate System • Feedback loops – modify atmospheric processes – Positive feedback loops – enhance initial change – Negative feedback loops – counteract initial change Determining Causes of Earth’s Climate Change • Paleoclimatology • Proxy data – indirect evidence using natural recorders of climate variability – – – – – – Sea floor sediments Coral deposits Glacial ice rings Tree rings Pollen Historical documents Temperature: the last 400,000 years From the Vostok ice core (Antarctica) Natural Climate Change • External Forcing: – The agent of change is outside of the Earth-atmosphere system • Internal Forcing: – The agent of change is within the Earthatmosphere system itself External Forcing • Variations in solar output • Orbital variations • Meteors Natural Causes of Climate Change • Solar energy changes – Variable energy from the Sun over time – Luminosity – Sunspots Solar Variations Sunspots correlate with solar activity More sunspots, more solar energy • Sunspots are the most familiar type of solar activity. SOLAR ACTIVITY • Sunspots are the most familiar type of solar activity. THE SOLAR CYCLE • Sunspot numbers increase and decrease – over an 11-year cycle • Observed for centuries. • Individual spots last from a few hours to months. • Studies show the Sun is in fact about – 0.1% brighter when solar activity is high. The Seasons • The Earth has seasons because the axis is tilted. • Earth rotates on its axis as it orbits the Sun. • Earth’s axis ALWAYS points in the same direction… • but Earth’s location in its orbit around the Sun determines whether the NH or SH is pointed toward the Sun. The Seasons • NH Summer Solstice – June 20-21 • NH Autumnal Equinox – September 22-23 • NH Winter Solstice – December 21-22 • NH Vernal Equinox – March 20-21 Earth’s orbit: an ellipse • Perihelion: place in the orbit closest to the Sun • Aphelion: place in the orbit farthest from the Sun Earth’s orbit: an ellipse • Perihelion: place in the orbit closest to the Sun • Aphelion: place in the orbit farthest from the Sun THE MAUNDER MINIMUM • An absence of sunspots was well observed – from 1645 to 1715. • The so-called “Maunder minimum” coincided with a cool climatic period in Europe and North America: – “Little Ice Age” • The Maunder Minimum was not unique. • Increased medieval activity – correlated with climate change. 17 Natural Causes of Climate Change • Variations in Earth’s Orbit • Milankovitch Theories – Eccentricity of Earth’s orbit – Obliquity of Earth’s axis – Precession of Earth’s axis Orbital changes • Milankovitch theory: • Serbian astrophysicist in 1920’s who studied effects of solar radiation on the irregularity of ice ages • Variations in the Earth’s orbit – Changes in shape of the earth’s orbit around sun: • Eccentricity (100,000 years) – Wobbling of the earth’s axis of rotation: • Precession (22,000 years) – Changes in the tilt of earth’s axis: • Obliquity (41,000 years) Eccentricity: period ~ 100,000 years Natural Causes of Climate Change • Volcanic eruptions • Volcanic ejecta may block sunlight • Need many eruptions in short time period • Not observed in recent history Natural Causes of Climate Change • Movement of Earth’s Plates – Change ocean circulation – Extremely slow process – Climate change would be very gradual over millions of years • Linked to Pleistocene Ice Age, Little Ice Age, Medieval Warm Period Documenting Human-Caused Climate Change • Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) – Global group of scientists – Published assessments since 1990 – Predict global temperature changes of 1.4–5.8°C (2.5–10.4°F) • Climate change models can mimic modern conditions only if human emissions are taken into account. Atmosphere’s Greenhouse Effect • Global warming – increase in Earth’s global temperatures • Greenhouse effect – keeps Earth’s surface habitable – Incoming heat energy is shorter wavelengths – Longer wavelengths – some trapped, some escape, net warming effect Earth’s Heat Budget • Addition to or subtraction from heat on Earth • Incoming radiation from Sun shorter wavelengths • Outgoing radiation from Earth longer wavelengths • Rates of energy absorption and reradiation must be equal Earth’s Heat Budget Greenhouse Gases • Water vapor – Most important – 66–85% of greenhouse effect • Carbon dioxide – Natural part of atmosphere – Greatest relative contribution from human activities – Burning of fossil fuels Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide Greenhouse Gases • Methane – Second most abundant human-caused greenhouse gas – Great warming power per molecule – Landfill decomposition – Cattle • Other trace gases – Nitrous oxide, CFCs, ozone Human-Caused Greenhouse Gases