* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 42 / Internal Transport: Circulatory Systems I. Introduction A
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
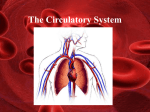
Randa, Bio102 Chapter 42 / Internal Transport: Circulatory Systems I. Introduction A. General components 1. Blood--transport material; has pigments 2. Pumping organ (heart)--move blood through body 3. Spaces or blood vessels--carry blood to different parts of body B. Types 1. Open a. heart pumps blood into open space b. blood re-enters heart through holes or open vessels c. found in arthropods and mollusks 2. Closed a. completely closed network of blood vessels b. may or may not have heart c. substances diffuse through vessels to surrounding cells d. more efficient e. found in cephalopods, annelids, chordates 3. No circulatory system a. diffusion --gas exchange through skin or pseudocoelom --other systems move nutrients and wastes --body movements important b. gastrovascular cavity --circulating fluid --body movements important 1 Randa, Bio102 II. Blood -- Vertebrates A. Plasma 1. Mainly water; also proteins, salts, gases, hormones, dissolved nutrients 2. Proteins a. clotting b. immune response c. maintain proper fluid volume d. maintain proper pH B. Cells 1. Erythrocytes a. biconcave disk b. contains hemoglobin c. lifespan ca. 120 days 2. Leukocytes a. granular 1) neutrophils 2) eosinophils 3) basophils b. agranular 1) monocytes 2) lymphocytes leukemia = leukocyte cancer 3. Thrombocytes a. play an important role in clotting for stoppage of bleeding b. involves clotting factors Hemophilia = one of clotting factors absent; inherited trait 2 Randa, Bio102 III. Blood Vessels Artery: carries blood away from heart; muscular, elastic walls Arterioles and Metarterioles: can vasoconstrict and vasodilate Capillaries: smallest vessels Venules and Veins: Carry blood toward the heart; have valves IV. Heart A. Number of chambers valves, walls atria: receive blood from body via veins ventricles: receive blood from atria; pump blood into arteries 1. 2-chambered heart 1 atrium, 1 ventricle e.g., fish 2. 3-chambered heart 2 atria, 1 ventricle e.g., amphibians 3. Incomplete 4-chambered heart 2 atria, 2 ventricles partially separated e.g., reptiles (except crocodiles) 4. 4-chambered heart 2 atria, 2 ventricles separates blood flow into Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits e.g., crocodiles, birds, mammals 3 Randa, Bio102 Know pattern of blood flow through 4-chambered heart. B. Parts of the heart pericardium septum AV valves semilunar valves C. Pacemaker of heart 1. conduction system that ensures rhythmic beating 2. specialized cardiac muscle tissue 3. rhythm results in 2 heart sounds--valve closures pulse = expansion and elastic recoil of an artery 4. conduction of pacemaker → electrical activity can record via EKG (ECG) 5. pacemaker regulated by nervous system a. can function on its own but may adjust according to body’s needs b. different effects of sympathetic and parasympathetic systems 4