* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Endocrine system notes
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Pituitary apoplexy wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
The Endocrine System Notes
I. Hormones:
A. ______________produces hormones that are important in maintaining ________________&
regulating__________________________&__________________________.
B. A _______________ is a chemical messenger produced by a cell that effects specific change in the
cellular activity of other cells (______________________)
C. Unlike _______________________that release their products at the body’s surface or into body cavities
through____________, the ____________________glands do not secrete substances into ducts instead
their hormones are secreted directly into the surrounding______________ space & then diffuse into
nearby _____________________& are transported throughout the body in the_________________.
D. The endocrine & ___________________systems often work together to maintain homeostasis.
E. The nervous system uses ____________________________ to act on cells (which is
usually____________________) to maintain homeostasis
F. The __________________system uses __________________(which effects last__________) to produce
homeostasis.
G. Hormones are classified into 2 basic categories: ________________(including amino acids, polypeptides,
& proteins) & _________________(complex rings of carbon & hydrogen atoms)
II. Hormone Action
A. Hormones activate target cells by 1 of 2 methods, depending upon the chemical nature of the hormone:
1) ______________hormones {water soluble} that bind to a ________________________on the plasma
membrane of the cell. The receptor protein, then stimulates the production of a
___________________________ (either cAMP or calcium.)
2) _______________hormones {____________soluble} that ____________through the plasma membrane
of the target cell & bind to receptor protein present in the cytoplasm that activates a DNA segment that turns
on specific genes.
III. Control of Hormone Production
A. Endocrine glands release hormones in response to 1 or more of the following stimuli:
1. Hormones form other _______________________________
2. _____________________ characteristics of the blood
3. ______________________stimulation
4. most hormone production is regulated by ________________________________system.
a. ___________feedback: hormones secretion is triggered by some _________________
__________________, then rising hormones levels ____________further hormone release resulting in blood
levels of many hormones varying only within a very narrow margin.
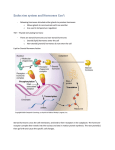
IV. Communication b/w the Hypothalamus & Pituitary Glands
A. Communication b/w the hypothalamus & the ________________________Gland occurs through
_____________________that are produced by the ________________________& delivered to the ant.
pituitary through blood vessels.
B. Communication b/w the hypothalamus & the ______________________Gland occurs through
___________________cells that connect the 2 glands.
V. Antagonistic Hormones
A. When the body hormone levels drop below normal homeostasis levels the ____________ hormones are
secreted to bring the body back to______________________.
B. Ex. Bundles of cells in the __________________called the __________ of __________________ contain
2 kinds of cells ______________(secrete glucagons) & _______________(secrete insulin) cells, that control
blood glucose concentrations by producing the antagonistic hormones insulin & glucagon
VI. Major Endocrine Organs
Gland
Hormone Released
Pineal
Melatonin
Hypothalamus
Hypothalamic-releasing &
release-inhibiting
hormones
Anterior
Pituitary
Growth hormone (GH)
Soft tissues, bones
______________________
Mammary glnds
Luteininzing Hormone;
_______________
Reg. Oogenesis & spermatogenesis
Follicle stimulating
hormone (FSH);
_______________
____________________________
Adrenocorticotropic
hormone (ACTH)
________________
Stimulate secretion of glucocorticoids
Posterior
Pituitary
Thyroid
Target Tissue /
Organ
Chief Function of Hormone
Involved in daily rhythms; possibly
involved in maturation of sex organs
Regulate anterior pituitary hormones
Stimulates protein synth. & bone
growth
Stimulates milk production &
secretion
Thyroid stimulating
(TSH)
________________
Stimulate secretion of ________
______________________
Uterus,mammary
glands
Uterine contractions, release of milk
Antidiuretic Hormone
(ADH);
Kidneys, sweat
glands
____________________
All tissues
_____________________
Bones, kidneys,
intestine
Triiodothyronine (T3)
________________
______________________________
Increases metabolic rate; helps to
reglt. growth & development
_____________________________
Increases rate of cellular metabolism
Parathyroid
Thymus
Adrenal Gland
Adrenal
Medulla
Adrenal Cortex
Parathyroid hormone
(PTH)
Thymosin
Bones, kidneys,
______________________________
intestine
_________________ Stimulates maturation of T
lymphocytes
Epinephrine &
Norepinephrine
Cardiac & other
muscles
________________
Stimulate ____________________
reaction; raise blood __________
______________________________
________________
Increase reabsorption of ______ & to
excrete __________
Glucocorticoids ex.
Cortisol
Mineralcorticoids ex.
Aldosterone
Androgens ex. DHEA
________________
Stimulate onset of ___________,
female sex drive
Lowers blood ________________
Glucagon
Liver, muscles,
adipose tissues
_______________
Gonads
Ovaries
____________________
Uterus
Testes
_____________________
_____________________
______________________
_____________________
Uterus
Regulates menstrual cycle,
secondary sex characteristics.
Inhibin
_______________
Pancreas
_____________________
Pelvis, cervix
Ant. pituitary
Testes
___________blood glucose levels
Reg.menstrual cycle, pregnancy
Dilates cervix & birth canal
Inhibits ____________________
Regult. spermatogenesis, secondary
sex characteristics
inhibits FSH release