* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 01 Basic Cardiology
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
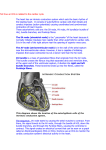
Basic Cardiology The Heart ❖ Pericardium ❖ Epicardium ❖ Myocardium ❖ ❖ atrial muscle ❖ ventricular muscle ❖ conductive tissue Endocardium The Heart Myocardium ❖ branch ❖ intercalated disks with gap junctions Intercalated Disc Electrical Stimulation of the Heart Sinoatrial (SA) Node ❖ Right atrium ❖ Inherent rhythm 80-100 bpm) ❖ Usually sets the heart rate (sinus rhythm) Internodal & Interarterial Pathways ❖ ❖ Internodal ❖ Anterior ❖ Middle (Wenckebach branch) ❖ Posterior Interatrial ❖ Anterior Interarterial band or Bachmann’s bundle Atrioventricular (AV) Junction ❖ AV Node ❖ Located at the base of the right atria near the interventricular septum ❖ Smaller cells, fewer gap junctions, slower ❖ Maximal rate is ~230 per minute; also maximal ventricular rate AV Junction ❖ ❖ AV Bundle or Bundle of His ❖ Only cellular connection between atria and ventricles ❖ Together with AV node make up the AV junctional tissue ❖ Intrinsic heart rate of 40-60 bpm ❖ If SA node fails, AV junctional tissue can control heart rate Slows down the cardiac impulse Bundle Branches ❖ Right and left branches ❖ ❖ Two left branches (sometimes three) ❖ Left anterior fascicle or left anterior bundle branch; thinner, carries impulses to septum, left anterior wall, and anterior papillary muscle ❖ Left posterior fascicle or l. post. bundle branch; thicker, carries impulses to posterior, inferior, left ventricular free wall and posterior papillary m. with dual blood supply, less likely to become ischemic, Both left and right BB travel down towards the apex of the heart where they fan out into Purkinje fibers Purkinje Fibers ❖ Pass through the ventricular myocardium ❖ Contraction starts at the apex ❖ Fast rate of action potential generation, numerous sodium ion channels and mitochondria and fewer myofibrils Electrical Stimulation of the Heart ❖ Video “If you understand the normal physiologic stimulation of the heart, you have the basis for understanding the abnormalities of heart rhythm and conduction the produce distinctive ECG patterns.” p. 5 Electrocardiogram SA node AV node Atrial depolarization Bundle branches Ventricle depolarization Ventricle repolarizatio Purkinje fibers Electrocardiogram Rhythms ❖ Normal conduction ❖ ❖ Sinus Rhythm Abnormal conduction ❖ Junctional rhythm ❖ ❖ e.g. escape pacemaker Ventricular rhythm Cardiac Conductivity ❖ SA node - slow ❖ Internodal pathways - fast ❖ AV node - slow ❖ Purkinje fibers - faster Cardiac Automaticity ❖ ❖ Automaticity ❖ SA node - primary pacemaker ❖ Other sites e.g. AV junction Certain conditions increase the automaticity of ectopic pacemakers ❖ Ectopic = outside of the sinus node pacemaker (nonsinus) Abnormalities ❖ AV heart block = blockage of stimuli through AV junction ❖ Bundle Branch Block = disease of bundle branches ❖ ST segment changes = damage to ventricular muscle Coronary Arteries Coronary Arteries ❖ The Left Main (LM) ❖ Left Anterior Descending (LAD) ❖ Left Circumflex (LCX). ❖ The Right Coronary Artery (RCA) ❖ The RCA on the posterior part of the heart is often called the Posterior Descending Artery (PDA), in most cases it originate from the RCA but in some cases it comes from LCX. Coronary Artery Perfusion LAD Supply the anterior septum, the anterior wall, and in most cases apex. 9 o'clock to 1 o'clock. Supply the lateral wall LCX 2 o'clock to 4 o'clock RCA Supply the posterior lateral segments, the inferior segments, and the posterior septum. 5 o'clock to 8 o'clock Class Organization 1. Resting 12 lead ECG 1. Understanding normal 12 lead ECG and conditions that cause abnormal depolarization and repolarization 2. Recognizing abnormal rhythms and AV conduction disturbances 3. Associating the ECG arrhythmia with its pathology 2. Exercise ECG 1. Recognizing abnormal rhythms and AV conduction disturbances 2. Associating the ECG arrhythmia with its pathology