* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Conducting System - Cardiac and Stroke Networks in
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
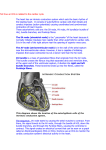
The Conducting System Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network Overview The heart beats because of the spread of electrical impulses to the heart muscle, causing it to contract. Cardiac conducting system - network of specialised tissue , endocardium to epicardium enclosing all myocardial tissue LBB AnteroSuperior division SA Node AV Node LBB PosteroInferior division Bundle of His }Purkinje Fibres Right Bundle Branch Sino-Atrial Node Natural Pacemaker Neuromyocardial cells 5 X 20 mm Epicardial upper RA close to SVC, RAA Atrial Depolarisation From SA node across myocardial cells Propagated action potential results in myocardial contraction Passes to AV node in the floor of the RA ? Tracts - Bachman, Thorel & Wenkebach Muscular ridges SA Node IDR - 80 bpm sympathetic & parasympathetic innervation Sympathetic - ↑ HR Parasympathetic ↓ HR RCA or LCX – occasionally from both vessels SA Node Represented on the ECG as P wave AV Node Spread of depolarisation - from atrial myocardium tadpole shaped 2 X 5 mm endocardial, septum at junction of atria and ventricles AV Node delay 0.15 seconds – time atria to expel blood – time for ventricular filling – protection to ventricles re; atrial arrhythmias IDR - 60 bpm AV Node Autonomic nervous control - not as pronounced as SA Node Sympathetic stimulation - ↑ IDR & ↓ AV nodal conduction time Parasympathetic stimulation - opposite RCA - 95 %, LCX - 5 %, occasionally from both AV Node AV nodal conduction is represented on the ECG as the PR Interval The Bundle Of His Directly continuous with the AV node 20 mm long Endocardial Within the Interventricular septum Only normal pathway Atria → Ventricles Bundle of discreet fibres - crosses AV ring The Bundle of His IDR - 50 bpm Nervous stimulation - minor effect no dedicated blood supply (mostly LAD) Depolarisation of the Bundle is not seen on the surface ECG The Bundle Branches Bundle of His separates into 2 main branches, left & right Left bundle - Antero-Superior division Postero-Inferior division IDR - 40 bpm The Purkinje Fibres Bundle Branches divide further - small, dense network conducting tissue Endocardial → Epicardial Entire musculature depolarizes quickly IDR - 20 bpm Nervous stimulation - minor effect only No dedicated blood supply Ventricular Depolarisation The Bundle Branch and purkinje fibre depolarisation constitutes ventricular depolarisation Represented on the ECG as the QRS Repolarisation Repolarisation is smaller in amplitude & slower than depolarisation Atrial repolarisation occurs within the QRS & therefore is masked Ventricular repolarisation is represented on the ECG as a T wave Summary Body at rest - SA nodal emission 70bpm – normal range 60 - 100 bpm Exitory - sympathetic Inhibitory - parasympathetic All parts which are responsible for hearts electrical activity - conducting system Electrical activation → mechanical activity – production ventricular contraction (BP response 120/70 mmHg)