* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch 11 Heart Physiology
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
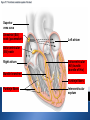
Pages 363-370 Cardiac muscle cells contract: Spontaneously Independently Two systems regulate heart rhythm: Intrinsic Conduction System Uses the specialized cardiac muscle cells (nodal tissue) 75 beats per minute Autonomic nervous system Speed up or slow down Sinoatrial (SA) node Atrioventricular (AV) node Atrioventricular (AV) bundle (bundle of His) Discovered by Wilhelm His in 1893 Bundle branches Purkinje fibers © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Superior vena cava Sinoatrial (SA) node (pacemaker) Left atrium Atrioventricular (AV) node Right atrium Bundle branches Atrioventricular (AV) bundle (bundle of His) Purkinje fibers Purkinje fibers Interventricular septum Sinoatrial Node = the heart’s natural pacemaker From the SA node the impulse spreads: The “SA Node” Located in the right atrium Starts each heartbeat; sets the pace To the AV node – atria contract … Then the impulse travels to the: AV bundle > Bundle branches > Purkinje fibers Ventricles contract toward atria, ejecting blood http://highered.mheducation.com/sites/0072495855/stu dent_view0/chapter22/animation__conducting_system_of_ the_heart.html Ischemia —lack of adequate oxygen supply to heart muscle results in fibrillation Fibrillation—a rapid, uncoordinated the heart muscle shuddering of Major cause of death from heart attacks Use of defibrillator can save life by restoring natural rhythm using electrical current Tachycardia —rapid heart rate over 100 bpm Prolonged can progress to fibrillation Bradycardia —slow heart rate less than 60 bpm © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Cardiac cycle refers to one complete heartbeat Refers to the sounds of the ventricles Systole contraction Diastole relaxation beats about 75 times per minute length of beat is about 0.8 seconds © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Two distinct sounds “Lub” – closing of the AV valves ventricular systole (systolic blood pressure) “Dup” – closing of the semilunar valves Ventricular diastole (diastolic blood pressure) Faulty valves reduce efficiency of the heart Can lead to abnormal heart sounds (murmurs) Sounds like a whooshing or swishing 1. Autonomic Nervous System Sympathetic nervous system Parasympathetic nervous system 2. Hormones and ions via Endocrine System 3. Epinephrine and thyroxine increase heart rate Imbalances of Ca⁺⁺ or K⁺ can depress, stop, or increase heart rhythms Physical factors Age : faster in young Gender : faster in females Exercise Body temperature © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.