* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Endocrine system - Chagrin Falls Schools
Polycystic ovary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
History of catecholamine research wikipedia , lookup
Glycemic index wikipedia , lookup
Cryptorchidism wikipedia , lookup
Menstrual cycle wikipedia , lookup
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (female-to-male) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
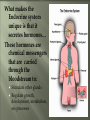
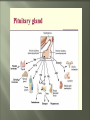
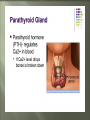
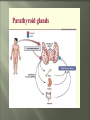
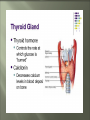
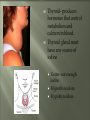
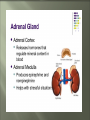
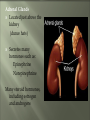
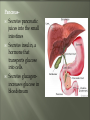
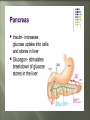
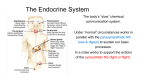
Glands and Hormones What makes the Endocrine system unique is that it secretes hormones… These hormones are chemical messengers that are carried through the bloodstream to: Stimulate other glands Regulate growth, development, metabolism, sex processes Hormones work by finding that specific receptor on a specific cell to do their job… Major Glands of the Endocrine System Pituitary – also referred to as the “master gland” as it regulates all other endocrine glands Thyroid –responsible for metabolism and growth, how your body uses oxygen and nutrients Parathyroid – regulate calcium and phosphorus in the body Adrenal – secrete adrenaline in emergency or stressful situations Pancreas – responsible for secreting insulin to regulate blood sugar levels in the bloodstream Ovaries – female gonad, responsible for ovum production, estrogen secretion and progesterone release Testes - male gonad, responsible for sperm production and testosterone secretion Master gland of body Located in the depression of sphenoid bone Produces many hormones that affect other glands Thyroid stimulating hormone Somatotropin- growth hormone Lutenizing (LH)- causes ovulation ICSH- causes testes to secrete testosterone Melanocyte stimulating- distribution of melanin in skin ADH- antidiuretic hormone Giantism- would be oversecretion of somatotropin before puberty Dwarfism- would be undersecretion of somatotropin. Cause: tumor, injury, infection, genetics Diabetes insipidusdecreased ADH Thyroid- produces hormones that control metabolism and calcium in blood. Thyroid gland must have any source of iodine Goiter- not enough iodine Hyperthyroidism Hypothyroidism Adrenal Glands Located just above the kidney (dunce hats) Secretes many hormones such as: Epinephrine Norepinephrine Many steroid hormones, including estrogen and androgens Pancreas Secretes pancreatic juices into the small intestines Secretes insulin, a hormone that transports glucose into cells. Secretes glucagonincreases glucose in bloodstream Diabetes Mellitus Cause – malfunction of gland, decreased secretion of insulin Symptoms Excessive thirst, excessive urination, hyperglycemia, slow healing of skin infections Affects 21 million in US: 7% of population Estimated 1/3 of people who have diabetes don’t know it 225,000 die each year 132 billion/year- 10% of our health care spending