* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slayt 1
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Hindu views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
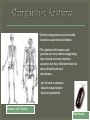
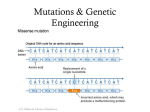
Week III Lecturer: Faruk Berat AKCESME (MSc) HUM 101 Spring semester 2013-2014 Origin of species? Origin of Human? TIME LINE for the last 3.6 billion years, simple cells (prokaryotes); for the last 3.4 billion years, cyanobacteria performing photosynthesis; for the last 2 billion years, complex cells (eukaryotes); for the last 1 billion years, multicellular life; for the last 600 million years, simple animals; for the last 550 million years, bilaterians, animals with a front and a back; for the last 500 million years, fish and proto-amphibians; for the last 475 million years, land plants; for the last 400 million years, insects and seeds; for the last 360 million years, amphibians; for the last 300 million years, reptiles; for the last 200 million years, mammals; for the last 150 million years, birds; for the last 130 million years, flowers; for the last 60 million years, the primates, for the last 20 million years, the family Hominidae (great apes); for the last 2.5 million years, the genus Homo (human predecessors); for the last 200,000 years, anatomically modern humans. ASSUMPTIONS! All living things share a common ancestor. We can draw a Tree of Life to show how every species is related. Evolution is the process by which one species gives rise to another and the Tree of Life grows • The theory of Evolution deals with how Evolution happens. Our understanding of this process is always changing. Science? Ideology? Belief? Source? Fact? Part 1: How was evolution discovered? Discussion: Should Creationism and Evolution be given “equal time” in science lessons? Part 2: How does evolution work? Part 3: What is the evidence for evolution? Fixed Species! Evolving species! • Around 1800, scientists began to wonder whether species could change or transmute. • Lamarck thought that if an animal acquired a characteristic during its lifetime, it could pass it onto its offspring. • Hence giraffes got their long necks through generations of straining to reach high branches. Jean Baptiste de Lamarck William Smith, his geology map & some of his fossil specimens At about the same time, geologists like William Smith were mapping the rocks and fossils of Britain. He and others showed that different species existed in the past compared with today. • From 1831-1836, a young naturalist called Charles Darwin toured the world in HMS Beagle. • He was dazzled by the amazing diversity of life and started to wonder how it might have originated Voyage of the Beagle Natural Selection explains adaption • In his Origin of Species, published in 1859, Darwin proposed how one species might give rise to another. • Where food was limited, competition meant that only the fittest would survive. • This would lead to the natural selection of the best adapted individuals and eventually the evolution of a new species. Darwin in 1860 Mendel and his peas • From 1856-63, a monk called Gregor Mendel cultivated 29,000 pea plants to investigate how evolution worked i.e., how characteristics were passed down the generations. • He figured out the basic principles of genetics. He showed that offspring received characteristics from both parents, but only the dominant characteristic trait was expressed. Mendel’s work only came to light in 1900, long after his death • The genetic make-up of an organism is known as its genotype. • An organism’s genotype and the environment in which it lives determines its total characteristic traits i.e. its phenotype. Genotype Phenotype • The double-helix structure of DNA was discovered in 1953. • This showed how genetic information is transferred from Watson and Crick and their model of DNA DNA replication one cell to another almost without error. Types of mutation • However, occasional mutations or copying errors can and do occur when DNA is replicated. • Mutations may be caused by radiation, viruses, or carcinogens. Mutant fruitfly • Mutations are rare and often have damaging effects. Consequently organisms have special enzymes whose job it is to repair faulty DNA. • Nevertheless, some mutations will persist and increase genetic variation within a population. • Variants of a particular gene are known as alleles. For example, the one of the genes for hair colour comprises brown/blonde alleles. ? Selection of dark gene • Mutant alleles spread through a population by sexual reproduction. • If an allele exerts a harmful effect, it will reduce the ability of the individual to reproduce and the allele will probably be removed from the population. • In contrast, mutants with favorable effects are preferentially passed on Any mutation with favorable effects ? Discussion based on the current information of molecular biology Lets look what evolutionist present as a evidance! • Does basic similarity of all living things suggests that they evolved from a single common ancestor? • As we have already seen, all living things pass on information from generation to generation using the DNA molecule. • All living things also use a molecule called ATP to carry energy around the organism. DNA for Information Transfer ATP for Energy Transfer HUMAN CHIMPANZEE GORILLA CCAAGGTCACGACTACTCCAATTGTCACAACTGTTCCAACCGTCACGACTGTTGAACGA CCAAGGTCACGACTACTCCAATTGTCACAACTGTTCCAACCGTCATGACTGTTGAACGA CCAAGGTCACAACTACTCCAATTGTCACAACTGTTCCAACCGTCACGACTGTTGAACGA Genetic code of chimps and gorillas is almost identical to humans • If evolution is true then we might also expect that closely related organisms will be more similar to one another than more distantly related organisms. • Comparison of the human genetic code with that of other organisms show that chimpanzees are nearly genetically identical (differ by less than 1.2%) whereas the mouse differs by ≈15%. What about chickens ? Genetically identical according to what method? What about the method validity? • Similar comparisons can be made based on anatomical evidence. • The skeleton of humans and gorillas are very similar suggesting they shared a recent common ancestor, but very different from the more distantly related woodlouse… yet all have a common shared characteristic: bilateral symmetry Human and Gorilla Woodlouse The pentadactyl limb is ancestral to all vertebrates… but modified for different uses © World Health Org. en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Eopraptor_sketch5.png © NASA origins bacteria complex cells dinosaurs humans Some scientist thinks “The fossil record shows a sequence from simple bacteria to more complicated organisms through time “ They consider them as provides the most compelling evidence for evolution. • Many fossils show a clear transition from one species, or group, to another. • Archaeopteryx was found in Germany in 1861. It share many characteristics with both dinosaurs and birds. • It provides good evidence that birds arose from dinosaur ancestors Archaeopteryx Marsupials • Geographic spread of organisms also tells of their past evolution. • Marsupials occur in two populations today in the Americas and Australia. • This shows the group evolved before the continents drifted apart From geography to evolution?? or From evolution to geography?? PRO-THEORY OF EVOLUTION / ANTI-CREATIONISM > [2] Falk, Dean. Braindance, NY: Henry Holt and Co., 1992. [5] Growlett, John. Ascent to Civilization, NY: Alfred A. Knopf, 1984. [8] Howell, F. Clark. Early Man, NY: Time Life Books, 1973. [9] Johanson, David, and Maitland, Edy. Lucy, NY: Simon and Schuster, 1981. [10] Johanson, David, and Shreeve, James. Lucy's Child, NY: William Morrow and Co., 1989. [12] Leakey, Richard, and Lewin, Roger. Origins, NY: E.P. Dutten, 1977. > [13] Leakey, Richard, and Lewin, Roger. Origins Reconsidered, NY: Doubleday, 1992. > [14] Lewin, Roger. Bones of Contention, NY: Simon and Schuster, 1987. > [15] Lewin, Roger. In the Age of Mankind, Washington, D.C.: Smithsonian Books, 1988. [20] Pfieffer, John. The Emergence of Man, NY: Harper and Row, 1969. [23] Wendt, Herbert. From Ape to Man, NY: The Bubbs Merril Co., 1972. ANTI-THEORY OF EVOLUTION / PRO-CREATIONISM [1] Bliss, Richard. Origins: Creation or Evolution? El Cajon, CA: Master Books, 1988. [3] Gish, Duane T. The Amazing Story of Creation from Science and the Bible El Cajon, CA: Institute for Creation Research, 1990. [4] Graham, Keith, et al. Biology Pensacola, FL: A Beka Book Publications, 1986. [7] Ham, ken, et. al. The Answers book, El Cajon, CA: Master Books, 1992. > [11] Johnson, Phillip. Darwin on Trial, Washington, D.C.: Regnery Gateway, 1991. > [16] McDowell, Josh and Stewart, Don. Reasons Skeptics Should Consider Christianity, San Bernardino, CA: Here's Life, 1981. [17] Moreland, J.P. Scaling the Secular City, Grand Rapids: Baker Book House, 1987. > [18] Morris, Henry M. Evolution and the Modern Christian, Phillipsburg, NJ: Presbyterian and Reformed Publishing Co., 1988. [19] Morris, Henry M. The Twilight of Evolution, Grand Rapids: Baker Book House, 1967. > [22] Ranganathan, B.G. Origins?, Carlisle, PA: The Banner of Truth Trust, 1988. [24] Whitcomb, John. The Early Earth, Grand Rapids: Baker Book House, 1986. NEUTRAL REFERENCE WORKS [6] Grzimek, Bernhard, ed. Grzimek's Animal Life Encyclopedia, Vol. 10, NY: Van Nostrand Reinhold Co., 1984. [21] Pinchot, Roy, ed. The Human Body, "The Skeleton", NY: Torster Books, 1985. The number in the [ ]'s after each quote in the paper corresponds to the number in the [ ]'s above from which the quote was taken. Quotes with no [ ]'s are lost references but should be considered reliable. ">" indicates most recommended for further study. Pro-evolution books are recommended for how well they reveal the actual state of their evidence.