* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture notes 1 - University of Washington
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
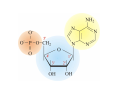
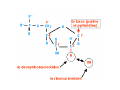
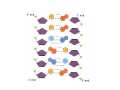
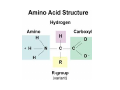
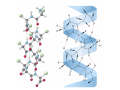
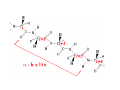
Mathematics of Genome Analysis and Molecular Modeling Hong Qian, Department of Applied Mathematics, University of Washington, Seattle, WA 98195, USA E-mail: [email protected] Abstract. Contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Introductory Molecular Biology 2.1 Nucleotides and Amino Acids . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.1.1 Various sugars . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.1.2 Nitrogenous bases: A, T, G, C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.1.3 Nucleotide = nucleoside phosphate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.1.4 Amino acids . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.1.5 Peptide bond . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.2 Biopolymers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.2.1 Polynucleotides — deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.2.2 Polyamino acids, polypeptides, and proteins . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.2.3 Forces that shape the biopolymer structures . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.3 Central dogma of molecular biology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.3.1 Replications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.3.2 Transcriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.3.3 Translations and protein biosynthesis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.3.4 Codons . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.3.5 Differential equation models for gene expression dynamics . . . . 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 3 Introduction to Probability Theory and Markov Chains 3.1 Review of discrete probability . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.1.1 Discrete random variable and probability mass function . . . . . . 3.1.2 Expection, variance, and conditional probability . . . . . . . . . . 5 5 5 5 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 5 5 CONTENTS 4 2. Introductory Molecular Biology 2.1. Nucleotides and Amino Acids 2.1.1. Various sugars Sucrose, lactose, glucose, ribose and deoxyribos. positions 3 and 5 . 2.1.2. Nitrogenous bases: A, T, G, C A and G are called purines, T and C are called pyrimidines. 2.1.3. Nucleotide = nucleoside phosphate A nucleoside consists of a nitrogenous base covalently attached to a sugar (ribose or deoxyribose) but without the phosphate group. A nucleotide consists of a nitrogenous base, a sugar (ribose or deoxyribose) and one to three phosphate groups. nucleoside = sugar + base. nucleotide = sugar + base + phosphate. 2.1.4. Amino acids 2.1.5. Peptide bond The carboxyle group of one amino acid reacts with the amino group of another forms a peptide bond. Due to a double bond, the peptide has a planar rigid structure. This uniquely defines the notion of (φ, ψ) angle. 2.2. Biopolymers 2.2.1. Polynucleotides — deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) Base paring: A—T and G—C; double helix structure. 2.2.2. Polyamino acids, polypeptides, and proteins primary sequence, secondary structures: α-helix, β-sheets, Ramachandran plot. 2.2.3. Forces that shape the biopolymer structures Hydrogen bonds, responsible for α-helix formation? Hydrophobic interactions, responsible for protein tertiary, globular structure. 2.3. Central dogma of molecular biology 2.3.1. Replications 2.3.2. Transcriptions 2.3.3. Translations and protein biosynthesis AMATH 532 Introductory Molecular Biology • Nucleotides and amino acids • Biopolymers: polynucleotides — deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid • (RNA); poly‐amino acids, polypeptides, and proteins • Central dogma of molecular biology; mathematical models for gene expressions • Hydrogen bond, Ramachandran plot, and helix‐coil transition theory • Advanced topics: Buckling and mechanical instability; supercoil, linking number and White’s formula Various sugars sucrose lactose glucose ribose deoxyribose The forces that shape the protein structure • • • • hydrogen bonds, helices, hydrophobic interactions, globular proteins Central Dogma of Molecular Biology Codons