* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
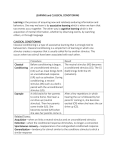
Psychology Study Guide Chapters 9 – Learning: Principles & Applications NOTES: Chapter 9, Section 1: Classical Conditioning Vocabulary o Classical conditioning – a learning procedure in which associations are made between a neutral stimulus and an unconditioned stimulus o Neutral stimulus – a stimulus that does not initially elicit any part of an unconditioned response o Unconditioned stimulus (US) – an event that elicits a certain predictable response typically without previous training o Unconditioned response (UR) – an organism’s automatic (or natural) reaction to a stimulus o Conditioned stimulus (CS) – a once neutral event that elicits a given response after a period of training in which it has been paired with (occurred just before) an unconditioned stimulus o Conditioned response (CR) – the learned reaction to a conditioned stimulus o Generalization – responding similarly to a range of similar stimuli o Discrimination – the ability to respond differently to similar but distinct stimuli o Extinction – the gradual disappearance of a conditioned response when the conditioned stimulus is repeatedly presented without the unconditioned stimulus What did Ivan Pavlov show with his experiments with dogs? What could he accomplish? (please refer to the above chart/diagram) What are taste aversions? How can you develop a taste aversion? What is behaviorism and who are behaviorists? Review the case of ‘Little Albert’ (page 249) Be able to identify the neutral stimulus, US, UR, CS, and CR of an experiment (like in an experiment like Pavlov’s Dogs) THIS IS VERY IMPORTANT