* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders * 5th
Dementia praecox wikipedia , lookup
History of psychiatric institutions wikipedia , lookup
Panic disorder wikipedia , lookup
Conversion disorder wikipedia , lookup
Sluggish schizophrenia wikipedia , lookup
Glossary of psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Emergency psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Schizoid personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Obsessive–compulsive personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Bipolar disorder wikipedia , lookup
Kleptomania wikipedia , lookup
Controversy surrounding psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Bipolar II disorder wikipedia , lookup
Reactive attachment disorder wikipedia , lookup
Emil Kraepelin wikipedia , lookup
Gender dysphoria wikipedia , lookup
Anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Depersonalization disorder wikipedia , lookup
Mental status examination wikipedia , lookup
Conduct disorder wikipedia , lookup
Generalized anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems wikipedia , lookup
Separation anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Antisocial personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Autism spectrum wikipedia , lookup
Personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Schizoaffective disorder wikipedia , lookup
Asperger syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Mental disorder wikipedia , lookup
Narcissistic personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
History of psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Causes of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Pyotr Gannushkin wikipedia , lookup
Spectrum disorder wikipedia , lookup
Dissociative identity disorder wikipedia , lookup
Child psychopathology wikipedia , lookup
History of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Classification of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders wikipedia , lookup
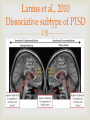
Martin Dorahy Department of Psychology University of Canterbury 2 systems used to classified Psychiatric disorders: - ICD-10 DSM Classification Issues Critical issues Reliability DSM tries to increase reliability to ensure everyone who sees client diagnoses the same thing Validity Work to increase validity by trying to ensure the key symptoms actually classify the disorder. Need to balance reliability and validity Purposes and benefits Communication Prognosis Treatment planning 4 Criticisms of DSM/Classification Comorbidity Emphasize reliability, sometimes at the expense of validity Complexity of categorizing psychopathology Pathologising normal behaviour 6 A Caution About Labeling and Stigma Problems and pitfalls with labels Negative connotations Stigmas Reification DSM-I (1952) 132 pages Definitions were simple, brief paragraphs with prototypical descriptions DSM-II (1968) 134 pages Users encouraged to record multiple psychiatric diagnoses (in order of importance) and associated physical conditions Coincided with ICD-8 (first time ICD included mental disorders) DSM-III (1980) 494 pp Descriptive and neutral “atheoretical”) regarding etiology. Coincided with ICD-9. Multiaxial classification system. Goal to introduce reliablilty. DSM-III-R (1987) 567 pp Some relabelling and reorganisation DSM-IV (1994) 886 pp Inclusion of a clinical significance criterion New disorders introduced (e.g., Acute Stress Disorder, PTSD Bipolar II Disorder, Asperger’s Disorder), others deleted (e.g., Cluttering, Passive-Aggressive Personality Disorder). DSM-IV-TR (2000) 943 pp Text revision – no change to diagnostic criteria DSM-IV and DSM-IVTR The Five DSM-IV Axes I – Major disorders II – Stable, enduring problems III – Medical conditions (related) IV – Psychosocial problems V – rating of adaptive functioning DSM-5 (2013) 947 pp “5” instead of “V” Anticipates change e.g. DSM 5.1 … 5.2 … 12 year process DSM-5 22 Chapters DSM-IV 17 Chapters Positives of DSM5 1. Broad Collaboration 2. Inclusion of Cultural Considerations 3. More Descriptive Diagnosis 4. Reorganized to reflect etiology & shared factors 18 Positives of DSM5 5. Recognition of life span issues related to specific disorders. 6. Gender & cultural notes for individual diagnosis. 7. Removed diagnostic criterion not relevant across cultural groups. 8. 30% international in each work group 19 Major Changes of DSM5 1. Elimination of 5 Axis Diagnosis 2. Significant overlap with ICD-10/11 2. Integration of emerging genetic & neuroimaging research 20 Lanius et al., 2010 Dissociative subtype of PTSD Three Major Sections 1. The Basics 2. Diagnostic Criteria & Codes 3. Emerging Measures & Models 22 DSM-5 disorder categories Neurodevelopmental disorders Schizophrenia spectrum and other psychotic disorders Bipolar and related disorders Depressive disorders Anxiety disorders Obsessive-compulsive and related disorders Trauma- and stressor-related disorders Dissociative disorders DSM-5 disorder categories Somatic symptom and related disorders Feeding and eating disorders Sleep–wake disorders Sexual dysfunctions Gender dysphoria Disruptive, impulse-control, and conduct disorders Substance-related and addictive disorders Neurocognitive disorders Paraphilic disorders Personality disorders Specific phobia criteria DSM-5 Marked fear or anxiety about a specific object or situation (e.g., flying, heights, animals, injections) The phobic object/situation almost always provokes immediate fear The phobic object/situation is actively avoided or endured with intense fear. Fear is persistent ≥ 6 months Causes sign. distress or impairment (social, occupational functioning) 26 Thoughts? What are the benefits for us as counsellors with the DSM? What are the deficits/limitations/concerns for us as counsellors with the DSM 28