* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PSY 6015 Cognitive Learning Theories
Psychophysics wikipedia , lookup
Observational methods in psychology wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral modernity wikipedia , lookup
Behavior analysis of child development wikipedia , lookup
Behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Educational psychology wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive development wikipedia , lookup
Learning theory (education) wikipedia , lookup
Social cognitive theory wikipedia , lookup
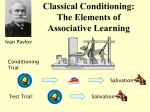
Classical conditioning wikipedia , lookup
* 11112781 Chau Yik Ting (Tina) 11142724 Choi Yue Cheung (Felicity) 11109447 Wong Sui Wai (Chris) • • • • Theme – Public speaking Target – K1-3 students Scenario – in the class, learning Public Speaking Roles – Teacher and 2 Students • • • Role Model: Tina Badly-behaved Student: Chris Teacher: Felicity 1. 2. 3. 4. Raise your hands up in the air Clap them together 1,2,3 Now rest them upon your hips And slowly bend your knees Speak with actions * • • • • Behavioral Theories of learning • • Classical Conditioning Instrumental Conditioning • Reinforcement Social Learning Theories • • Modelling Observation Constructivism • • Assimilation Scaffolding Information Processing Model • • Memory Storage * Behavioral Theories of learning •Classical Conditioning • • • Humans are born with reflexes • Later on, simply presenting the original Neutral Stimulus, the Unconditioned Response will be resulted Some stimulus do not result in reflexes However, when these Neutral Stimulus and the Unconditioned Stimulus come together * Behavioral Theories of learning •Classical Conditioning • During the performance • Under the repeated practices in the class, students performed the poem with the criteria of teacher • Example • • • • Unconditioned Stimulus = Forgetting the lines during practice Unconditioned Response = Anxiety Conditioned Stimulus = Performance on stage Conditioned Response = Anxiety * Behavioral Theories of learning • Instrumental Conditioning • • The law of effect states that • Responses to a situation that are followed by satisfaction are strengthened • Responses that are followed by discomfort are weakened Reinforcement • The process of increasing the frequency or duration of a behavior as the result of presenting a reinforcer * Behavioral Theories of learning •Instrumental Conditioning Actions with poem> Reinforcement (Appreciation) Example Simon Says Learning the actions of the song (Heads shoulders knees and toes) Learn the poem Combine the actions with the poem * Modelling and Observation Observation • Principles • People can learn by observing others’ behaviors and the consequences of that result • Learning can occur without an immediate change in behavior Modelling • • • Teaches new behavior Influences the frequency of previously learned behaviors Increases the frequency of similar behaviors * Social Learning Theories • Modelling and Observation • • Teacher would be the model of Gordon and Patience Patience would be the model of Gordon • Example • • • • • Teach other body parts Teach actions in the songs Teach actions in the poem ABC of public speaking Simon Says * Constructivism • Assimilation • The process by which people understand an experience in terms of their current stage of cognitive development and the way of thinking • • Students understood the different parts of their body Example • • • Teach other body parts Teach actions of the poem Learn the actions of the song * Constructivism • Scaffolding • Model the correct performance of a task • • Eg. Teacher and Patience Divide a complex task into several smaller, simpler activities • • Divide the poem sentence by sentence Integrate the action by songs and other activities • Example • • • • Sing heads shoulders knees and toes ABC of public speaking Teach other body parts Learn the actions of the song * Constructivism • Scaffolding • Provide a structure or set of guidelines • • ABC of public speaking Give frequent feedback about how learners are progressing • Keep communicating with Gordon and Patience * Storage • Prior Knowledge • Verbalisation, Enactment, Repetition & Review • • • Helps encoding new information More likely to engage Helps students to organise information • Example • • Sing heads shoulders knees and toes ABC of public speaking * Memory • Explicit Memory • • Recalling body parts Procedural Memory • Learning the order of the poem and the actions