* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download GENETIC TRAITS
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
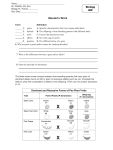
GENETIC TRAITS GOAL: Learn about the basic definitions regarding genetics (genotypes) and inherited traits (phenotypes), as well as about the role of DNA in determining traits. MATERIALS: • Multi-colored popsicle sticks, labeled with dominant and recessive alleles • Dragon baby worksheets; one per student • Human traits worksheet; one per group VOCABULARY: • Allele: The form (or identity?) of a gene/genes having a known trait • DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid): The genetic material of all living organisms (including strawberries!) • Gene: The basic unit of heredity. • Genotype: All of the inherited genes in an organism. • Phenotype: Observable traits of an organism. • Dominant: Alleles for which having a single copy results in that trait being observed. • Recessive: Alleles for which having a single copy results in that train being observed if the second copy is also recessive, or being hidden if the second copy is dominant. • Trait: A genetically determined characteristic CLASS: Discussion (~ 5 minutes) • What is a trait? Anything that identifies as both unique (e.g. hair color, eye color, height) and human (e.g. face, one heart, brain) • Where do people get their traits? These traits are encoded into our DNA, which we get from our parents. • How many genes are there for a trait? It depends, we have genes from both Mom and Dad, but only certain genes get expressed and some traits require multiple genes. We call these sets of genes, alleles. • How do we know what trait we will have? We don’t, we only know what is definitely possible by looking at our parents; these are phenotypes. To know for sure the likelihood of having a trait, we have to know our genotype AND know which alleles are dominant and which alleles are recessive. EXPERIMENT ONE: Human Traits (~15 minutes) 1. For each trait listed, explain how to identify that trait (see attached sheet). 2. For each student, have them write in YES or NO under their name (one worksheet per group). 3. Report the fraction that answered YES in your group. 4. Discuss whether or not the trait is dominant or recessive. EXPERIMENT ONE: How to Identify Traits Trait Description Dominant or Recessive? Bent pinky Hold out hand, look at top (distal) segment of Dominant pinky. Does it bend inward toward the ring finger? Tongue rolling Can you roll your tongue into a tube shape? Dominant Homozygous recessives are non-rollers and cannot learn to roll their tongues. Widow’s Peak V-shaped hairline (can be subtle, just look to see Dominant if there is a ‘point’ in the middle of the forehead). Attached ear Recessive lobes Homozygous recessives have attached ear lobes. Hitchhiker’s thumb Can you bend the distal joint of the thum backward to nearly a 90deg angle? Recessive Thumb crossing On the count of three, clasp your hand together, with fingers overlocking. Is your left thumb over your right thumb? Small indentation of the skin, commonly located in cheeks and chin. Is your second toe longer than your big toe? Is your hair curly? Wavy? Straight? Dominant, left over right Dimples Short big toe Curly hair PTC taster Dominant Dominant Curly, DD Wavy, Dd Straight, dd Place the Phenylthiocarbamide (PTC) paper on Dominant your tounge. Does it taste bitter? EXPERIMENT TWO: Dragon Babies (~30 minutes) Adapted from: Dragon Genetics Protocol 1. Have all the students pair up (does not have to be boy/girl, but each pair will have a male and female popsicle stick). 2. Each student picks up five Popsicle sticks, one of each color. 3. Start with one color stick (allele) and have each student drop his or her stick onto the table. The side of the stick that is up gets passed on to the baby. Record the results for each color in the allele. Note: A CAPITAL LETTER = DOMINANT allele, while lower case letter = recessive allele. Example for PURPLE ALLELE (BODY) is shown below. BABY GENOTYPE (Step 4): MOM DAD BABY PHENOTYPE (Step 5): G G GREEN BODY r R ORANGE SPOTS t T SPOTS ON BACK ONLY 4. Use the decoding chart on the board to figure out the phenotype associated with your baby’s genotype and write phenotype into chart. 5. Once students have correctly written in a Phenotype, pass out one dragon sheet per student and color in/draw a Dragon Baby. 6. Share results with the group/class; discuss the prevalence of dominant, mixed, or recessive traits. GENOTYPE TO PHENOTYPE DECONDING CHART Popsicle Stick Allele Green Writing Red Writing Blue Writing Purple Writing Black Writing Dominant A. Spikes along spine B. No tail spike D. No eyelids E. Round eyes F. Fangs H. External ear J. Brown horn G. Green body R. RR – red spots, Rr – orange spots T. Spots on back only X. Fire breathing Y. Male Recessive a. No spikes along spine b. Tail spike d. Eyelids e. Almond eyes f. No fangs h. Internal ear j. Yellow horn g. Purple body r. Rr – organge spots; rr – yellow spots t. Spots on back & wings x. Non-fire breathing