* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1ST SEM MT CHAP 22 REVIEW
Fallout shelter wikipedia , lookup
Muon-catalyzed fusion wikipedia , lookup
Background radiation wikipedia , lookup
Radioactive decay wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear binding energy wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear fusion wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear and radiation accidents and incidents wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear fission wikipedia , lookup
Technetium-99m wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear fission product wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear fusion–fission hybrid wikipedia , lookup
Valley of stability wikipedia , lookup
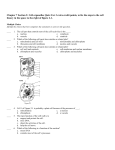
1ST SEM MT CHAP 22 REVIEW Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. (CAPITAL LETTERS ONLY PLEASE) ____ 1. Mass defect is the difference between the mass of a. a nucleus and its atom. b. a neutron and a proton. c. an atom and the sum of the masses of its nucleons. d. an atom and the sum of the masses of its constituent particles. ____ 2. What elements have the greatest nuclear binding energies per nuclear particle? a. light elements only c. heavy elements only b. elements of intermediate mass d. both light and heavy elements ____ 3. Elements with the greatest nuclear binding energies per nuclear particle are the a. smallest in size. c. most stable. b. least stable. d. largest in size. ____ 4. Compared with the sum of the masses of the separate particles that compose the nucleus, its mass a. is always less. c. is always the same. b. is always more. d. may be either less, more, or the same. ____ 5. Between protons in a nucleus, a. attraction due to nuclear force is greater than repulsion due to electrostatic force. b. repulsion due to electrostatic force is greater than attraction due to nuclear force. c. nuclear and electrostatic forces are balanced. d. electrostatic forces are negligible. ____ 6. a. even. b. The number of nucleons in a stable nucleus is commonly c. not a whole number. odd. ____ 7. A nucleus is most stable when a. its electrons are paired. b. its nucleons are paired. ____ 8. What is a magic number? a. the number of shells in the nucleus b. the number of energy levels c. the number of paired nucleons d. a magic number. c. it has an odd number of nucleons. d. some nuclear energy levels are not filled. d. ____ the number of nucleons that represents completed nuclear energy levels 9. Balance the following equation: → + _____ a. c. b. d. ____ 10. Balance the following equation: + → + _____ a. c. b. d. ____ 11. Balance the following equation: + _____ → + a. c. b. d. ____ 12. Particles or electromagnetic radiation emitted from the nucleus during radioactive decay a. is harmless nuclear fallout. c. is transmutation. b. is nuclear radiation. d. are daughter nuclides. ____ 13. Beta particles are a. electrons. c. electromagnetic waves. d. neutrons. b. helium nuclei. ____ 14. The half-life of an isotope is the time required for half the nuclei in a sample to a. undergo radioactive decay. c. undergo nuclear fusion. b. undergo nuclear fission. ____ 15. ple to decay? a. d. How many half-lives are required for three-fourths of the nuclei of one isotope in a sam- b. c. 2 d. 3 ____ 16. The half-life of radium-226 is about a. 16 seconds. c. b. react chemically. 16 hours. d. 16 years. 1600 years. ____ 17. Which of the following is the heaviest nuclide of a decay series? a. the parent nuclide c. the last radioactive nuclide b. the daughter nuclide ____ 18. A decay series ends with a. a stable nuclide. b. a parent nuclide. d. the last decaying nuclide c. a fission reaction. d. a transuranium element. ____ 19. Which nuclide is a parent for a decay series? a. uranium-238 c. radon-222 b. thorium-234 ____ 20. Artificial radioactive nuclides are a. found naturally in space. b. found naturally on Earth. d. lead-208 c. not found naturally on Earth. d. nonexistent. ____ 21. Artificial radioactive nuclides are produced by a. bombarding stable nuclei with particles. b. using an accelerator to overcome the nuclear force. c. beta emission. d. fission of stable nuclides. ____ 22. How are artificial transmutations used? a. to produce transuranium elements b. to produce technetium, astatine, francium, and promethium c. to fill gaps in the periodic table d. All of the above ____ 23. Which form of nuclear radiation is deflected LEAST by a magnetic field? a. alpha particles c. gamma rays b. beta particles d. ____ 24. Which of the following travels fastest? a. alpha particles c. b. beta particles d. None of the above gamma rays All travel at the same speed. ____ 25. Which of the following generally have the lowest penetrating ability? a. alpha particles c. gamma rays b. beta particles d. All have the same penetrating ability. ____ 26. Which of the following has the greatest penetrating ability? a. alpha particles c. gamma rays b. ____ beta particles 27. What unit measures radiation? d. All have the same penetrating ability. a. roentgen c. megaelectron-volt b. rem d. cm3 ____ 28. One rem is the quantity of ionizing radiation that does as much damage to human tissue as is done by a. 1 roentgen of high-voltage X rays. b. 100 roentgens of high-voltage X rays. c. 1 roentgen of low-voltage X rays. d. the radioactive decay of 1 kg of uranium-235. ____ 29. How are the definitions of rem and roentgen related? a. The definition of roentgen depends on the rem. b. The definition of rem depends on the roentgen. c. Both are based on damage to human tissue. d. They are not related. ____ 30. Which of the following do NOT detect radiation? a. film badges c. scintillation counters b. Geiger-Müller counters d. radioactive tracers ____ 31. Which of the following instruments detect radiation by counting electric pulses carried by gas atoms ionized by radiation? a. film badges c. scintillation counters b. Geiger-Müller counters d. radioactive tracers ____ 32. Which of the following instruments detect radiation by converting light produced in radioactive process to an electric signal? a. film badges c. scintillation counters b. Geiger-Müller counters d. radioactive tracers ____ 33. How do radioactive nuclides affect photographic film wrapped in lightproof paper? a. They have no effect on the film. c. They melt the film. b. They disintegrate the film. d. They expose the film. ____ 34. Radioactive nuclides cause molecules in air to a. ionize. c. condense. b. fluoresce. d. radiate. ____ 35. To use radioactive dating for a substance, you must know the substance's a. melting point. c. rate of weathering or erosion. b. ____ half-life. 36. d. heat of reaction. Which radioactive nuclide is used to treat cancer? a. cobalt-60 c. uranium-238 b. plutonium-239 d. radon-222 ____ 37. Radioactive tracers in fertilizers can be used to measure a. how well the fertilizer is absorbed by plants. b. contaminants in the fertilizer. c. the chemical composition of the fertilizer. d. how plants respond to radioactivity. ____ 38. Which of the following processes produces nuclei of lower mass than the reactants? a. fission c. Both fission and fusion b. fusion d. Neither fission nor fusion ____ 39. If the particle that starts a nuclear reaction is also one of the products, the process is a a. chain reaction. c. nuclear fusion. b. neutron emission. d. neutron bombardment. ____ 40. Which statement about nuclear reactions is NOT true? a. Nuclear power plants use fission of uranium. b. In fission, the total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the products. c. In fission, nuclei are split, and in fusion, nuclei are combined. d. Heat and light in the sun are produced by hydrogen fusion reactions. ____ 41. a. A b. Which of the illustrations above represents a fission reaction? c. C B d. D ____ 42. Which of the following is a fission reaction? a. hydrogen-2 and hydrogen-3 combining to form a helium-4 atom and a neutron b. carbon-12 and hydrogen-1 combining to form a nitrogen-13 atom c. uranium-235 absorbing a neutron and breaking into barium-141, krypton-92, and three neutrons d. a glucose molecule being metabolized with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water ____ 43. Control rods a. cool the reactor. b. contain radiation. c. limit the number of free neutrons. d. provide fuel for nuclear fission. ____ 44. Modern nuclear power plants use pressurized water to a. produce neutrons. c. activate the fuel rods. b. cool the reactor. d. provide heat. ____ 45. The heat produced by a reactor is used to a. boil water for steam turbines. c. b. melt metal. d. produce graphite. produce coal. Short Answer 46. Why do elements such as radium, polonium, and uranium expose photographic film, kill bacteria, and warm the surrounding air? 47. Explain how a chain reaction occurs. 48. Why are claims that nuclear fusion occurs at room temperature unrealistic? 49. How does a nuclear reactor generate power? 50. How is fusion already one source of Earth's energy? 1ST SEM MT CHAP 22 REVIEW Answer Section MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. SHORT ANSWER ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: D B C A A A B D A B C B A A C D A A A C A D C C A C A A B D B C D A B A A A A B D C C A A PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: I I I I I I I I II II II I I I I I I I II I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I II I I I I OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: 22-1.2 22-1.2 22-1.2 22-1.2 22-1.3 22-1.3 22-1.3 22-1.3 22-1.4 22-1.4 22-1.4 22-2.1 22-2.2 22-2.3 22-2.3 22-2.3 22-2.4 22-2.4 22-2.4 22-2.5 22-2.5 22-2.5 22-3.1 22-3.1 22-3.1 22-3.1 22-3.2 22-3.2 22-3.2 22-3.3 22-3.3 22-3.3 22-3.4 22-3.4 22-3.4 22-3.4 22-3.4 22-4.1 22-4.1 22-4.1 22-4.1 22-4.1 22-4.2 22-4.2 22-4.2 46. ANS: All these elements undergo radioactive decay, giving off energy in the form of radiation. PTS: 1 DIF: II OBJ: 22-2.1 47. ANS: Neutrons produced by a nuclear reaction can initiate the same reaction in surrounding nuclides, producing more neutrons to initiate more reactions. PTS: 1 DIF: II OBJ: 22-4.1 48. ANS: Fusion requires tremendous energy. If reactants are at room temperature, they do not have sufficient energy. PTS: 1 DIF: II OBJ: 22-4.1 49. ANS: A controlled-fission chain reaction releases energy in a nuclear reactor. The energy is used to produce steam, which is used to drive the generators that produce the electricity. PTS: 1 DIF: I 50. ANS: Fusion is the energy source of the sun. OBJ: 22-4.2 PTS: 1 OBJ: 22-4.3 DIF: I