* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Beyond the light microscope
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Confocal microscopy wikipedia , lookup
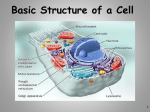
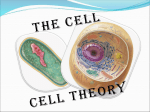
Student objectives: •To understand how the development of the microscope has improved our understanding of cells and allows for continued research. •To explain the work of key scientists in developing the Cell Theory. The Microscope A Short History Janssen – Lenses in a Tube Around 1590, two Dutch spectacle makers, Hans Janssen and his son Zacharias, reputedly discovered that nearby objects appear greatly enlarged if they are viewed through several lenses in a tube. In 1609, the Italian inventor and scientist Galileo Galilei developed his first occhiolino or compound microscope. This included both a convex and a concave lens. Robert Hooke – the English Microscopist In the mid-17th century, the English microscopist Robert Hooke made a series of improvements upon Galileo’s design. Hooke noticed that samples of cork were made up of microscopic box-like units. He called them cells. We now know that there are thousands of different types of cells in animals and plants. Leeuwenhoek – the Father of Microbiology The Dutch scientist, Anton van Leeuwenhoek, developed new methods for grinding and polishing tiny lenses about ten years after Hooke’s discoveries. These lenses could magnify objects up to 270 times their normal size. Leeuwenhoek was the first to be able to see and describe bacteria, yeast and blood cells. He also saw and described microscopic plants and animals, which he called “animalcules”. Microscope improvements • In the 1850s, German engineer Carl Zeiss began making refinements to the lenses he used in the microscopes he manufactured. • Ernst Abbe was hired by Zeiss to improve the manufacturing process of optical instruments, which back then was largely based on trial and error. Abbe carried out theoretical studies of optical principles, improving the understanding of the optical quality of a microscope. • In the 1880s, Zeiss hired glass specialist Otto Schott, who conducted research on optical glass, greatly contributing to the improvement of the optical quality of the microscope. Beyond the light microscope • 1931 - Ernst Ruska starts to build the first electron microscope. This microscope can view objects as small as the diameter of an atom and is able to magnify objects up to 1 million times. However, no living specimen can survive under the microscope’s high vacuum, so the ever-changing movements of a living cell cannot be seen. • 1981 – Gerd Binnig and Heinrich Rohrer invented the scanning tunnelling microscope that gives three-dimensional images of objects down to the atomic level. This is the strongest microscope to date. THE CELL THEORY and the scientists who developed it 1665 - Robert Hooke was the first person to use the term CELLS when he looked at thin slices of cork. Cork is dead plant tissue. Hooke’s drawing of cells Cork cells (stained) Anton van Leeuwenhoek 1670 - Anton van Leeuwenhoek looks at pond water and becomes the first person to see living cells with a simple microscope. 1833 - Robert Brown was the first to note that all plant cells contained a small round mass that he called the nucleus. He also suggested that this structure was the centre of cellular creation. 1838 - Matthias Schleiden: German botanist that suggests that all plant tissues are composed of cells, and that cells are the basic building blocks of all plants. 1839 – Theodor Schwann: a German botanist who reached the conclusion that not only plants, but animal tissue as well is composed of cells. 1855 - Rudolf Virchow: a German physiologist/physician/pathologist states that all cells develop only from existing cells. Student Activities: •Complete the worksheet on the timeline of microscope development •Complete worksheet questions on the Cell Theory.