* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download • What does DNA stand for? • Where do we find DNA? • How do
DNA sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Homologous recombination wikipedia , lookup
DNA profiling wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
DNA replication wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
DNA nanotechnology wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
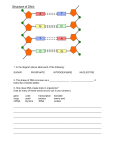
DNA • What does DNA stand for? • Where do we find DNA? • How do crime scene investigators use DNA to solve crimes? NUCLEIC ACIDS Flow of biological information: DNA RNA protein I. trait DNA deoxyribonucleic acid carries the genetic code (stores and transmits the genetic information from one generation to the next) parents offspring A. Chromosomes are made of DNA B. Located in the nucleus only Model of DNA: The model was developed by James Watson and Francis Crick. They received a Nobel Prize in 1962 for their work. First picture of DNA (X-ray) – Rosalind Franklin The model looks like a twisted ladder – double helix http://katyisd.discoveryeducation .com/player/view/assetGuid/17A 264FD-1D09-46AF-8985558CBB014D82 Died in 2004 Untwisted it looks like this: The sides of the ladder are P = phosphate group S = deoxyribose sugar The steps of the ladder are C, G, T, A = nitrogenous bases (contain N) Purine Pyrimidine A and G = purines T and C = pyrimidines Nucleotide Read from top to bottom as: 3’ 5’ 5’ 3’ Three to Five Five to Three prime prime prime prime 2 H bonds pairs A = adenine T = thymine pairs C = cytosine G = guanine 3 H bonds One Phosphate + one Sugar + one Base = one nucleotide Nucleotides are the building blocks (monomer) of DNA (polymer) II. DNA Replication A. Cell division produces 2 daughter cells that are genetically identical to each other and genetically identical to the parent cell B. Remember that for this to happen, DNA in the parent cell must be replicated (copied) before cell division -this process occurs during S phase of Interphase STEP 1 Hydrogen bonds between base pairs are broken by the enzyme Helicase and DNA molecule unzips STEP 2 DNA molecule separates into complementary halves STEP 3 Nucleotides match up with complementary bases Free nucleotides abundant in nucleus STEP 4 Nucleotides are linked into 2 new strands of DNA by the enzyme, DNA polymerase—DNA Polymerase also proofreads for copying errors New Strand Original Strand III. Ribonucleic acid – RNA -- acts as a messenger between DNA and ribosomes, and carries out the process by which proteins are made from amino acids. Protein = polymer Amino Acids = monomer A. Different from DNA: 1. RNA’s sugar -- ribose DNA’s sugar – deoxyribose 2. RNA – single strand of nucleotides DNA – double strand of nucleotides (double helix) 3. RNA has uracil instead of – thymine When RNA pairs with DNA to get its code: RNA cytosine (C) pairs with DNA – guanine G RNA guanine (G) pairs with DNA – cytosine C RNA adenine (A) pairs with DNA – thymine T RNA uracil (U) pairs with DNA – adenine A 4. RNA found – inside and outside nucleus (small – single strand) DNA found – inside nucleus only (large – double strand) B. 3 types of RNA involved in Protein Synthesis– mRNA messenger RNA tRNA transfer RNA rRNA ribosomal RNA Complete the chart by reading each term or phrase and placing a check in the appropriate column. DNA Deoxyribose single stranded nucleotides found in nucleus only Both Ribose double stranded RNA found in and out of nucleus Cytosine Guanine Adenine Thymine Uracil double helix replication