* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Paleontology and Life, part 3
Plant tolerance to herbivory wikipedia , lookup
History of phycology wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Fertilisation wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Cultivated plant taxonomy wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
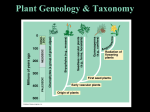
FOSSILSandFOSSILIZATION part3–LifeForms:Eukarya(Pro@stsandPlants) AlessandroGrippo,Ph.D. PaleozoicCrinoids,photographed(withpermission)inafossilsandrocksstore,LasVegas,Nevada ©AlessandroGrippo LifeForms:aSummary LifeonEarthisdividedinthreeDomains • Archaea – Prokaryotes • Bacteria – Prokaryotes • Eukarya – Eukaryotes • AlllifeformsareformedbycellscontainingDNA • ProkaryoGccellslackinternalorganizaGon • EukaryoGccellspresentinternalstructuring DomainEukarya • Eukaryainclude: 1. 2. 3. 4. ProGsts Plants Fungi(mushrooms) Animals 1.Pro@sts • Includemanykindsofsingle-celledorganisms andafewkindsofsimplemulGcellularorganisms • Plant-likeproGsts(algae)arephotosyntehGc – dinoflagellates,diatoms,coccolithophores • alltheseareveryimportantinthefossilrecord • Animal-likeproGsts(orprotozoans) – amoebas,zooflagellates,ciliates • radiolariansandforaminiferaareamoeba-likeproGststhat arealsoveryimportantinthefossilrecord ClockwisefromupperleQ:liveDiatoms;Coccolithophores;liveForaminifer;liveRadiolarian Nekton,Benthos,Plankton • Organismsthatliveintheoceancanbeclassifiedas: – Nekton:swimmers – example:dolphins,octopuses,squids,whales – Benthos:boXomdwellers • sessile(standinginoneplace,likeatreeonland) – example:sealilies • mobile(onthesurface–epifauna;diggingintothe substrate–infauna) – example:crabsandlobsters – Plankton:floaters ImportantPlanktonicPro@stsinthefossilrecord • Phytoplankton(plant-like) – DiatomsandCoccolithophores • Zooplankton(animal-like) – RadiolariansandForaminifera • Theseorganismssecretea skeleton(alsocalleda“test”,or ashell) • Whentheydie,theseskeletons sinktotheboXomoftheocean andformarock Alltheseorganismsaremicroscopic: theycanonlybeobservedundera microscope. Coccolithophoresaresosmallthat theycanonlybeimagedwithaSEM (ScanningElectronMicroscope) CaCO3shell Phytoplankton Zooplankton Coccoliths SiO2shell Coccoliths Diatoms Foraminifera Radiolarians (disksfromCoccolithophores) Foraminifer Diatom Radiolarian ChemicalSedimentaryRocks formedfromPro@sts’skeletons • Calcareousoozes – Chalk – Micrite • Siliceousoozes – DiatomaceousEarthandRadiolarite – Chert Chalk Micrite Chert 2.Plants • Allplantsevolvedfromalgaethatdevelopeda condiGoncalledendosymbiosis • Symbiosisoccurswhentwokindsoforganisms livetogetherinamannerthatbenefitsthem • “Endo”means“inside” endosymbiosis • DuringthePrecambrian,a photosyntheGcbacterial cellwas“eaten”byanon photosyntheGcone • Thesecondcouldnot digestthefirst • Theeatencellbecamea chloroplast,theorganelle insideaplantcellwhere photosynthesisoccurs Plants:GreenAlgae • MostscienGstsclassifyGreenAlgaeasPlants • SomemulGcellularalgaeareadriQintheocean, whilesomeothersareanchoredtotheboXom • MostaresoQ,fleshyorganisms,butsomesecrete askeletonofcalciumcarbonate(CaCO3) • Fragmentsofsuchskeletonsaremajor consGtuentsofmarinelimestones Halimedaincrassata(Ellis,1768)onshallow,aragoni@csandyseafloor Halimedaisacalcareousgreenalgaecontainingchipsofcalciumcarbonate(inthiscase,aragonite).AQerthealgaedieandthe soQpartsdecayaway,thearagoniGcchipsbecomesand-sizedseafloorsediments.ThesesedimentswillinGmeturntolimestone. ©JamesSt.Johnonflickr:hXps://www.flickr.com/photos/jsjgeology/16027635766 Plants:landplants • Landplantsaredifferentbecausetheirbodiesare dividedinto@ssues – Tissuesareconnectedgroupsofsimilarcellsthatperform aparGcularfuncGon • Also,theyaredifferentfromalgaebecauseof reproduc@on – Algaeshedeggsandspermintowater:ferGlizaGonis externalandoffspringdevelopindependently – InLandPlants,eggsareferGlizedwithintheparentplant, andtheembryoremainsprotectedwithintheirparents’ bodyforaGme LandPlants • Problemswithlivingonland: – lackofsupportfromwater • developmentofrigidstructures(roots,stems,trunks) forsupport – drycondiGons • rootscanabsorbwaterfromsoil • developmentofvessels(vascularplants)forwaterand nutrienttransport • Allplantsareeithernon-vascularorvascular NonvascularPlants • • • • • Liverworts,mosses,hornworts LackconducGngvessels Relyondiffusionfortransportcelltocell Haveascantfossilrecord HavenotchangedmuchingeologicGmesince LowerPaleozoic VascularPlants • VascularplantshavespecialGssuesandcanalstotransport moistureandnutrientsfromthesoiltothechlorophyllbearingleaves,wherephotosynthesisisaccomplished • VascularplantsalsohavefeaturesthatpreventdesiccaGon, supporttheweightoftheplant,andfacilitatereproducGon onland • Therearethreemajorgroupsofvascularplants: – Seedlessvascularplants – Vascularplantswithnakedseeds(Gymnosperms) – Vascularplantswithprotectedseedsandflowers(Angiosperms) SeedlessVascularPlants • Firstplantstoinvadelandwerespore-bearing,seedlessvascular plants • PossiblyfromOrdovician • • • • • Adultplantsproducespores SporesdonotrequireferGlizaGon Sporesfalltomoistgroundanddevelopintoagametophyte Agametophyteproduceseggsandsperm Thatwoulddevelopanewspore-generaGngplant • Twomaingroups – Lycophytes – Monilophytes Lycophytes Muchsmalleranduncommontoday VeryimportantandbiginsizeduringthePaleozoic LeavesleQdiamond-shapedscarsontrunks:“scaletrees” HugeforestsduringtheLatePaleozoicdiedandformed peat • Peatturnedintocoal(Carboniferous:Mississippianand Pennsylvanian) • • • • – Curiosity:arrivaloftheseplantsonlandcausedanenormous absorpGonofCO2fromatmosphereandreleaseofO2,thus creaGngacoolingeffect Fernleaveswithspores Monilophytes • Ferns • Horsetails • Psilotum Right: Horsetails (Equisetum) LeQ: Psilotum fromSporestoSeeds • Seedplantsincludemostspeciesoflargelandplantstoday • Seedsaredurablestructuresthatdispersetheoffspringsofthese plants • EvoluGonofseedsduringPaleozoictriggeredagreatecological expansionoflandplants:noneedformoistenvironmentslikefor spores • Seeddisperseindifferentways: – – – – blowninthewind aXachedthroughbarbstomobileanimals surroundedbyfruitseatenbyanimals animalsmovearoundandexpelseedsinfeces,whichareusedas ferGlizers NakedSeedsPlants(Gymnosperms) • “Naked”becauseattheGmeofpollinaGonthe seedsarenotcompletelyenclosedbytheGssues oftheparents • Include: – Seedferns(exGnctduringtheCretaceous) – Glossopteris(seeninWegener’sconGnentaldriQ) – Conifers – Cycads – Gynkgoes Glossopteris Conifers • Pines,spruces,firs,redwoods,cedars • DisGncGve,smallermalecones producepollengrainscontaining sperm • Biggerfemaleconescontainovules whereeggsdevelop • FerGlizedseedsdevelopontopof scalesthatformacone • AppearedduringLateCarboniferous Maleandfemalecones(strobili)fromapinetree Conifers:pineconesandnuts Pinenuts(inshells)fromfemalecones Unshelledandshelledpinenuts CycadsandGinkgoes • Cycadswerecommoninthe Mesozoicbutmanyspeciesare nowexGnct • Thosesurvivingtodayare knownas“sagopalms” • Ginkgoesarecharacterizedby bilobedfan-shapedleaves • AppearedduringPermian, boomedinTriassicandJurassic • Today,onlyGinkgobiloba survives ProtectedSeedsandFlowersPlants (Angiosperms) • StartedintheCretaceousandboomedright aQer • OneofmostdramaGceventsinplant evoluGon • Mostplantsalivetodayareangiosperms (“seedswithinavessel”) ferGlizaGoninAngiosperms • Seedsdevelopinachamberoftheflowercalledovule,or ovary • Pollenisproducedonstamens,thentransferredtopisGls • ApollentubedevelopswhenpollenrestsontoapisGl,through whichspermmovesandferGlizestheeggintheovary ferGlizaGoninAngiosperms fromflowertofruit • ferGlizaGonoftheeggproducesafruitwithseeds • enclosedseedsallowformaGonofediblefruits • ediblefruitsenhancedispersalofseedsby animalsthateatthem ferGlizaGoninAngiosperms • coloredpetalsaXract birdandinsect pollinators • thereisadirect relaGonshipbetween angiospermandinsect evoluGon AngiospermsthroughGme • AngiospermsdiversifiedrapidlyaQertheir Cretaceousearlystart • BytheendoftheCretaceous,allthemajor groupsoftodayhadappeared • Manyofthoseplantsareverysimilartotheones oftoday • Grassesfinallyappearedbythemid-Cenozoic similaritybetweenEarlyCenozoicandtoday’sAngiosperms • LeQ:Angiospermsand Gymnospermsfossils(leaves, cones,berries)fromFlorissant, Colorado(about35myago) • BoXom:Angiospermsleaves fromFossilBuXe,Wyoming (about50myago) Palynology • OQen,sporesandpollensfromplantsare muchmoreabundantinthefossilrecordthan plantsthemselves • Theycanbetransportedtogreatdistancesby watercurrentsandwinds • Theirstudyiscalledpalynology FossilsandFossiliza@on LifeForms:Pro@stsandPlants endofpart3