Unit 4.indd - The New Indian Model School, Dubai
... The CBSE-International is grateful for permission to reproduce and/or translate copyright material used in this publication. The acknowledgements have been included wherever appropriate and sources from where the material may be taken are duly mentioned. In case any thing has been missed out, the B ...
... The CBSE-International is grateful for permission to reproduce and/or translate copyright material used in this publication. The acknowledgements have been included wherever appropriate and sources from where the material may be taken are duly mentioned. In case any thing has been missed out, the B ...
vascular plants
... Seedless Vascular Plants • Vascular plants have several adaptive advantages over nonvascular plants, including specialized conducting tissues, the ability to grow large and live in many environments, and strong stems that allow them to grow tall and receive more sunlight. • Seedless vascular plants ...
... Seedless Vascular Plants • Vascular plants have several adaptive advantages over nonvascular plants, including specialized conducting tissues, the ability to grow large and live in many environments, and strong stems that allow them to grow tall and receive more sunlight. • Seedless vascular plants ...
PDF
... Xanthium, Bidens, and Artemisia, contain very important hosts. The number of species, botanical varieties, and more important horticultural varieties upon which, or in which, one or more stages (egg, larva, pupa, or imago 3) have been found is well over 200. The eXl>ct number variesl according to ho ...
... Xanthium, Bidens, and Artemisia, contain very important hosts. The number of species, botanical varieties, and more important horticultural varieties upon which, or in which, one or more stages (egg, larva, pupa, or imago 3) have been found is well over 200. The eXl>ct number variesl according to ho ...
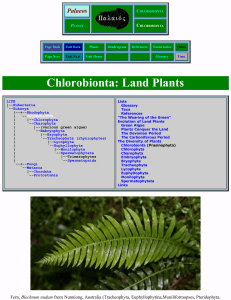
Palaeos Plants: Chlorobionta
... Aristotle divided all living things between plants, which generally do not move, and animals, which do. In Linnaeus' system, these became the Kingdoms Vegetabilia (later Plantae) and Animalia. Since then, it has become clear that the Plantae as originally defined included several unrelated groups, a ...
... Aristotle divided all living things between plants, which generally do not move, and animals, which do. In Linnaeus' system, these became the Kingdoms Vegetabilia (later Plantae) and Animalia. Since then, it has become clear that the Plantae as originally defined included several unrelated groups, a ...
Chapter 23
... continued Advantages of Flowers • The last important adaptation to appear as plants evolved was the flower, a reproductive structure that produces pollen and seeds. • Most plants living today are flowering plants—seed plants that produce flowers. • Flowering plants that are pollinated by animals pro ...
... continued Advantages of Flowers • The last important adaptation to appear as plants evolved was the flower, a reproductive structure that produces pollen and seeds. • Most plants living today are flowering plants—seed plants that produce flowers. • Flowering plants that are pollinated by animals pro ...
Intro to Plants
... continued Advantages of Flowers • The last important adaptation to appear as plants evolved was the flower, a reproductive structure that produces pollen and seeds. • Most plants living today are flowering plants—seed plants that produce flowers. • Flowering plants that are pollinated by animals pro ...
... continued Advantages of Flowers • The last important adaptation to appear as plants evolved was the flower, a reproductive structure that produces pollen and seeds. • Most plants living today are flowering plants—seed plants that produce flowers. • Flowering plants that are pollinated by animals pro ...
No Slide Title - Everglades High School
... continued Advantages of Flowers • The last important adaptation to appear as plants evolved was the flower, a reproductive structure that produces pollen and seeds. • Most plants living today are flowering plants—seed plants that produce flowers. • Flowering plants that are pollinated by animals pro ...
... continued Advantages of Flowers • The last important adaptation to appear as plants evolved was the flower, a reproductive structure that produces pollen and seeds. • Most plants living today are flowering plants—seed plants that produce flowers. • Flowering plants that are pollinated by animals pro ...
Chapter 17
... Even with so many diverse habitats occupied by plants today, we still consider the move from water to land to have been a major one. The greatest challenge to plants colonizing land was to keep their cells wet. Land plants responded to this challenge in two ways. In some—the ones we call vascular pl ...
... Even with so many diverse habitats occupied by plants today, we still consider the move from water to land to have been a major one. The greatest challenge to plants colonizing land was to keep their cells wet. Land plants responded to this challenge in two ways. In some—the ones we call vascular pl ...
Did auxin play a crucial role in the evolution of
... major events in bryophyte evolution can be found in many sources (e.g. Kenrick and Crane, 1997; Niklas, 1997; Edwards, 2000; Kenrick, 2000). It is irrefutable that a considerable time interval exists between the first putative land plant spores in mid-Ordovician strata and the first protracheophyte ...
... major events in bryophyte evolution can be found in many sources (e.g. Kenrick and Crane, 1997; Niklas, 1997; Edwards, 2000; Kenrick, 2000). It is irrefutable that a considerable time interval exists between the first putative land plant spores in mid-Ordovician strata and the first protracheophyte ...
kingdom plantae
... The classification of algae is mainly based on the photosynthetic pigments. In addition to this, cell wall composition and stored food are also the base of classification. Algae is divided into following divisions (1) CHLOROPHYTA ...
... The classification of algae is mainly based on the photosynthetic pigments. In addition to this, cell wall composition and stored food are also the base of classification. Algae is divided into following divisions (1) CHLOROPHYTA ...
video slide - Summit Public Schools
... imagine the land without any plants or other organisms • For more than the first 3 billion years of Earth’s history, the terrestrial surface was lifeless • Since colonizing land, plants have diversified into roughly 290,000 living species ...
... imagine the land without any plants or other organisms • For more than the first 3 billion years of Earth’s history, the terrestrial surface was lifeless • Since colonizing land, plants have diversified into roughly 290,000 living species ...
Chapter 29 - Cloudfront.net
... imagine the land without any plants or other organisms • For more than the first 3 billion years of Earth’s history, the terrestrial surface was lifeless • Since colonizing land, plants have diversified into roughly 290,000 living species ...
... imagine the land without any plants or other organisms • For more than the first 3 billion years of Earth’s history, the terrestrial surface was lifeless • Since colonizing land, plants have diversified into roughly 290,000 living species ...
Phylogeny and evolution of charophytic algae and land plants
... Abstract Charophytic algae and land plants together make up a monophyletic group, streptophytes, which represents one of the main lineages of multicellular eukaryotes and has contributed greatly to the change of the environment on earth in the Phanerozoic Eon. Significant progress has been made to u ...
... Abstract Charophytic algae and land plants together make up a monophyletic group, streptophytes, which represents one of the main lineages of multicellular eukaryotes and has contributed greatly to the change of the environment on earth in the Phanerozoic Eon. Significant progress has been made to u ...
How Plants Colonized Land PowerPoint
... • The life cycles of mosses and other bryophytes are dominated by the gametophyte stage • Bryophytes are represented today by three phyla of small herbaceous (nonwoody) plants ...
... • The life cycles of mosses and other bryophytes are dominated by the gametophyte stage • Bryophytes are represented today by three phyla of small herbaceous (nonwoody) plants ...
Chapter 21: Introduction to Plants
... about 4.6 billion years old. Can you imagine ancient Earth without land plants? That was the case until about 400 million years ago when primitive land plants appeared. However, fossil evidence from about 500 million years ago indicates that the shallow waters of ancient Earth were filled with a var ...
... about 4.6 billion years old. Can you imagine ancient Earth without land plants? That was the case until about 400 million years ago when primitive land plants appeared. However, fossil evidence from about 500 million years ago indicates that the shallow waters of ancient Earth were filled with a var ...
chapter23
... Root through strobilus Root Young sporophyte Mature (attached to female sporophyte gametophyte) Fig. 23-18, p. 460 ...
... Root through strobilus Root Young sporophyte Mature (attached to female sporophyte gametophyte) Fig. 23-18, p. 460 ...
Investigating Simple Plants
... 10. ... and others as we investigate some of the fascinating features of simple plants. 11. Graphic Transition – Origin of Nonvascular Plants 12. It is hard to imagine Earth without plants. 13. Even in incredibly hostile environments, such as Death Valley, plants are still able to thrive. 14. Plants ...
... 10. ... and others as we investigate some of the fascinating features of simple plants. 11. Graphic Transition – Origin of Nonvascular Plants 12. It is hard to imagine Earth without plants. 13. Even in incredibly hostile environments, such as Death Valley, plants are still able to thrive. 14. Plants ...
Document
... •Divergenge of entire clade from green algae •All Plantae lineages; cellulose-based cell walls, chlorophyll a and b, starch as storage molecule in chloroplasts •Two of the three earliest lineages (nontracheophytes) lack water transport cells; mosses have have limited numbers of them •Seedless vascul ...
... •Divergenge of entire clade from green algae •All Plantae lineages; cellulose-based cell walls, chlorophyll a and b, starch as storage molecule in chloroplasts •Two of the three earliest lineages (nontracheophytes) lack water transport cells; mosses have have limited numbers of them •Seedless vascul ...
Physiological correlates of the morphology of early vascular plants
... portion and, indeed, is lost from the shoot system as a concomitant of CO, fixation. An even larger contrast is found in comparison with benthic submerged haptophytes (and phytoplankters) where CO,, other nutrients and water, as well as light, can be absorbed all over the plant surface. A major attr ...
... portion and, indeed, is lost from the shoot system as a concomitant of CO, fixation. An even larger contrast is found in comparison with benthic submerged haptophytes (and phytoplankters) where CO,, other nutrients and water, as well as light, can be absorbed all over the plant surface. A major attr ...
EVOLUTION AND DIVERSITY OF GREEN AND LAND PLANTS
... The green plants, formally called the Viridiplantae or Chiorobionta, are a monophyletic group of eukaryotic organ isms that includes what have traditionally been called “green algae” plus the land plants or embryophytes (Figure 3.1). Like all eukaryotes, the Viridiplantae have cells with membrane-bo ...
... The green plants, formally called the Viridiplantae or Chiorobionta, are a monophyletic group of eukaryotic organ isms that includes what have traditionally been called “green algae” plus the land plants or embryophytes (Figure 3.1). Like all eukaryotes, the Viridiplantae have cells with membrane-bo ...
Introduction to Plants
... even with the presence of a cuticle on a plant Openings in the outer cell layer of leaves and some stems ...
... even with the presence of a cuticle on a plant Openings in the outer cell layer of leaves and some stems ...
ch 29 plant diversity
... Overview: The Greening of Earth • For more than the first 3 billion years of Earth’s history, the terrestrial surface was lifeless • Cyanobacteria likely existed on land 1.2 billion years ago • Around 500 million years ago, small plants, fungi, and animals emerged on land ...
... Overview: The Greening of Earth • For more than the first 3 billion years of Earth’s history, the terrestrial surface was lifeless • Cyanobacteria likely existed on land 1.2 billion years ago • Around 500 million years ago, small plants, fungi, and animals emerged on land ...
Slide 1
... even with the presence of a cuticle on a plant Openings in the outer cell layer of leaves and some stems ...
... even with the presence of a cuticle on a plant Openings in the outer cell layer of leaves and some stems ...
Chapter 21
... The club mosses (lycophytes) and horsetails (sphenophytes) alive today are the only living descendants of large and ancient groups of land plants. The first of these primitive tra¬ cheophytes appeared more than 400 million years ago. Over the next 100 to 200 million years, many more species evolved. ...
... The club mosses (lycophytes) and horsetails (sphenophytes) alive today are the only living descendants of large and ancient groups of land plants. The first of these primitive tra¬ cheophytes appeared more than 400 million years ago. Over the next 100 to 200 million years, many more species evolved. ...
Plant

Plants, also called green plants, are multicellular eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. They form an unranked clade Viridiplantae (Latin for green plants) that includes the flowering plants, conifers and other gymnosperms, ferns, clubmosses, hornworts, liverworts, mosses and the green algae. Green plants excludes the red and brown algae, the fungi, archaea, bacteria and animals.Green plants have cell walls with cellulose and obtain most of their energy from sunlight via photosynthesis by primary chloroplasts, derived from endosymbiosis with cyanobacteria. Their chloroplasts contain chlorophylls a and b which gives them their green color. Some plants are parasitic and have lost the ability to produce normal amounts of chlorophyll or to photosynthesize. Plants are also characterized by sexual reproduction, modular and indeterminate growth, and an alternation of generations, although asexual reproduction is also common.Precise numbers are difficult to determine, but as of 2010, there are thought to be 300–315 thousand species of plants, of which the great majority, some 260–290 thousand, are seed plants (see the table below). Green plants provide most of the world's molecular oxygen and are the basis of most of the earth's ecologies, especially on land. Plants that produce grains, fruits and vegetables form mankind's basic foodstuffs, and have been domesticated for millennia. Plants are used as ornaments and, until recently and in great variety, they have served as the source of most medicines and drugs. The scientific study of plants is known as botany, a branch of biology.