* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Learning
Impulsivity wikipedia , lookup
Insufficient justification wikipedia , lookup
Applied behavior analysis wikipedia , lookup
Behavior analysis of child development wikipedia , lookup
Remember versus know judgements wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Verbal Behavior wikipedia , lookup
Behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Classical conditioning wikipedia , lookup
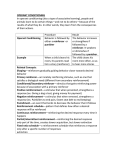
Learning https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Mt4N9GSBoMI Classical Conditioning Review • Reflexive responding that is largely controlled by stimuli that precede the response • Missing what follows certain response--consequences! Thorndike’s Law of Effect • Instrumental learning (responses are instrumental in obtaining some desired outcome) ▫ Kitty cats! ▫ Law of Effect: if a response in the presence of a stimuli leads to satisfying effects, the association between the stimulus and the response is strengthened BF Skinner • Defined “operant conditioning” ▫ An organism “operates” on the environment instead of simply reacting to stimuli A form of learning in which responses comes to be controlled by their consequences GOVERNS VOLUNTARY RESPONSES https://www.youtube.co m/watch?v=I_ctJqjlrHA “Haterz Gon Hate” –BF Skinner Skinner’s Demonstration • Demonstrated that organisms tend to repeat those are followed by favorable responses ▫ Reinforcement- occurs when an event following a responses increases an organisms tendency to make that response Response is strengthened when it leads to rewarding consequences Terminology & Procedures • “Operant Chamber”/Skinner Box- a small enclosure in which an animal can make a specific response that is recorded while the consequences of the response are systematically controlled ▫ Main responses are usually pressing a small lever down Skinner Box • Operant responses are normally VOLUNTARY and are said to be emitted rather than elicited Reinforcement Contingencies • Circumstances or rules that determine whether responses lead to the presentation of reinforcers ▫ Experimenter manipulates what positive consequences occur when the animal makes the designated response Normally a small bit of food Cumulative Recorder • Creates a graphic record of responding and reinforcement over time in a Skinner box as a function of time ▫ Response rate is a key dependent variable ▫ A slope represents the line of record of responding Rapid response rate gives steep slope, slow rate gives shallow slope Acquisition and Shaping • Like in classical conditioning, it refers to the initial stage of learning, however it is a little unique • Skinner and his contemporaries trained animals to do a variety of things! Extinction • Gradual weakening and disappearance of a response tendency because the response is no longer followed by a reinforcer Stimulus Control: Generalization and Discrimination • Operant conditioning is controlled by its consequences, as organisms learn responseoutcome (R-O) Associations ▫ Stimuli that precede a response can also exert considerable influence over operant behavior ▫ When a response is consistently followed by a reinforcer in the presence of a particular stimulus that stimulus comes to serve as a “signal” indicating that the response is likely to lead to a reinforcer A small pigeon may only peck may be reinforced only when a light is blinking…. Discriminative Stimuli • Cues that influence operant behavior by indicating the probable consequences (reinforcement or non-reinforcement of a response) ▫ These play an important role in regulation of operant behavior Kids ask for candy when parents are in a good mood Drivers slow when the roads are wet Asking people on dates Stimulus Generalization & Stimulus Discrimination • Works like in classical conditioning • Cat runs to a can opener (discriminative stimulus that it will be fed) ▫ Generalization (Blender) ▫ Discrimination (adjusting response) • Reinforcement occurs whenever an outcome strengthens a response ▫ The central process in reinforcement is the strengthening of a response tendency ▫ Reinforcement is defined after the fact, in terms of its effect on behavior Primary vs Secondary • Primary reinforcers- inherently reinforcing because they satisfy biological needs ▫ Food, water, sex, and warmth • Secondary/conditioned reinforcers-acquire reinforcing qualities by being associated with primary reinforcers ▫ Good grades, money, attention, flattery, praise, applause Schedule of Reinforcement • Determines which occurrences of a specific response result in the presentation of a reinforcer ▫ Continuous Reinforcement- occurs when every instance of a designated response is reinforced ▫ Intermittent/Partial Reinforcement- occurs when a designated response is reinforced only some of the time More effective/resistant to extinction Fixed Ratio Schedule (FR) • Reinforcer is given after a fixed number of nonreinforced respones ▫ Reward every 10th lever push ▫ Bonus every 10 magazines sold Variable Ratio (VR) • Reinforcer is given after a variable number of non-reinforced responses ▫ Rat rewarded on average every ten times ▫ Casino- averages/variations Fixed Interval Schedule (FI) • First response is rewarded after a fixed time interval has elapsed ▫ First lever press after two minutes ▫ Washer/dryer Variable Interval Schedule (VI) • Reinforcer is given for the first response after a variable time interval has elapsed ▫ Rewarded after lever press after 1 minute, then 2, then 3, etc ▫ Person dialing a busy phone Positive Reinforcement • Occurs when a response is strengthened because it is followed by the presentation of a rewarding stimulus ▫ Good grades, tasty meals, nice clothes, etc Negative Reinforcement • Occurs when a response is strengthened because it is followed by the removal of an aversive (negative) stimulus ▫ Strengthens a response tendency ▫ Removing a buzzing noise Escape Learning • Organism acquires a response that decreases or ends some aversive stimulation ▫ Leave a party you were being picked on at Avoidance Learning • Organism acquires a response that prevents some aversive stimulation from occuring Punishment • Occurs when an event following a response weakens the tendency to make that response ▫ Negative reinforcement= stimulus is removed ▫ Punishment= stimulus is added Positive Punishment • An aversive stimulus is added to decreases the likelihood of a behavior ▫ Petting a cat, cat bites you Negative Punishment • An appetitive (something good) is removed to decrease the likelihood of an event ▫ Texting at dinner, phone taken away Disciplinary Procedures • Not just being spanked ▫ Social punishments ▫ Eating at restaurants/bad service More Effective Punishments • • • • • Applied quickly Just severe enough to be effective Consistent Explanations Noncorporal