* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch. 9 Review - 8th Grade Science
Survey
Document related concepts
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
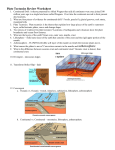
Ch. 9 Review Pgs. 356-357 #1-31 Write Questions and Answers 356-357 #1-5 Answers • 1. The layer of the upper mantle that can flow is the: A - Asthenosphere • 2. Most scientists rejected Wegener’s theory of continental drift because the theory failed to explain: D – How the continents move • 3. Subduction of the ocean floor takes place at: D - Trenches • 4. Two plates collide with each other at: B – A convergent boundary • 5. A fault in which the hanging wall slides up and over the footwall is a: A – Reverse Fault # 6-10 Answers • 6. The earth’s outer core is made of basalt and granite: False – Crust • 7. The spinning of the asthenosphere, made of iron and nickel, explains why Earth has a magnetic field: False – Inner Core • 8. Magnetic strips on the ocean floor are where oceanic crust sinks back to the mantle: False – Deep Ocean Trenches • 9. When two continental plates converge, a rift valley appears: False – Diverge • 10. Land subsidence occurs when Earth’s surface sinks as a result of geologic processes: True 11-12 • 11. How is the inner core different from the outer core? – The inner core is a dense ball of solid iron and nickel that spins. The outer core, by contrast, is a layer of molten iron and nickel that behaves like a thick liquid. • 12. Explain why there are convection currents in the mantle. – Heat from the Earth’s core heats the mantle. Some mantle material is soft and can bend like plastic. Over time, this material can flow slowly, forming convection currents. 13-14 • 13. How does a hot spot form a volcanic island? – At a hot spot on the ocean floor, magma from the mantle melts through the crust, forming a volcanic island. • 14. What evidence of Earth’s climate in the past supports the hypothesis of continental drift? – Evidence includes fossils of tropical plants found in polar regions and scratches made by continental glaciers found in places with mild climates. 15-16 • 15. What was the importance of the discovery that molten rock was coming out of cracks along the mid-ocean ridge? – The importance of that discovery is that it supported the theory that of sea-floor spreading. It also led scientists to look again at Wegener’s theory of continental drift. • 16. Describe the processes that create a faultblock mountain. – When tension caused by plate movements is great enough to break the crust, normal faults form. Along these faults, blocks of crust can slide, creating a faultblock mountain. 17-18 • 17. What happens when a plate of oceanic crust collides with a plate of continental crust? Why? – Oceanic crust is more dense than continental crust. As a result, when a plate carrying oceanic crust collides with a plate carrying continental crust, the oceanic plate sinks beneath the continental plate (subduction) • 18. Interview with Alfred Wegener – Should include mentions of evidence he used, such as fossils, landforms, and climate evidence. 19-20 • 19. Classify the layers of the earth. – Solid – Crust, Lithosphere, Inner Core – Solid but able to flow slowly – Asthenosphere – Liquid – Outer Core • 20. Comparing and contrasting oceanic and continental crust. – Both are parts of Earth’s outer layer. – Continental crust consists of less dense rocks such as granite. – Oceanic crust consists mainly of denser rocks such as basalt. 21-22 • 21. What do geologists think is the driving force of plate tectonics? Explain. – Convection currents in the mantle. The currents rise through the asthenosphere, then spread out beneath the lithosphere, dragging the overlying plate along. • 22. What events can cause land subsidence and what is formed as a result? – Geologic processes such as diverging plates or tension in the crust can cause land subsidence. With diverging plates the result may be rift valleys or ocean basins. 23-24 • 23. State in one sentence the most significant discovery geologists found through their study of plate tectonics. – Answers vary. Example: Pieces of Earth’s lithosphere are in constant, slow motion, driven by convection currents in the mantle. • 24. A community has just built a street across a strike-slip fault that has frequent earthquakes. How will movement along the fault affect the street? – Where the street intersects the fault, the street will eventually be broken and the segment will be moved sideways. 25-27 • 25. The part carrying Australia is moving to the northeast; the part carrying India is moving to the North • 26. Because the parts are moving in different directions, a divergent boundary will form • 27. This is a convergent plate boundary between two continental plates. Mountains should form. 28-31 • 28. The arrow at A represents: D – Molten magma rising from the mantle • 29. What is occuring at the feature labeled B? F – New rock is being added to the oceanic plate • 30. As sea-floor spreading occurs, the oceanic plate: C – Moves from B to C • 31. What is occuring at D? G – The oceanic plate is melting as it sinks into the mantle.