* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Notes 8.6 – Types of Evolution
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary mismatch wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
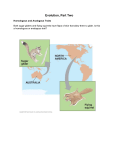
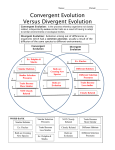
Science Starter #9 – 2/14/17 What are the four steps of natural selection? Does natural selection act on genotypes or phenotypes? TAKE OUT YOUR STEPS OF NATURAL SELECTION (Stamp) Sheet of paper for Notes: Types of Evolution Chapter 15-3 pp. 308-311 Evolution is… Change of heritable traits of a population over time Evolution of a population is due to environment AND the interaction of other species Artificial Selection Humans breed for specific traits causing differences in species (i.e. dog breeding) Natural selection: nature is “selecting” which traits will survive in the population Examples of Evolution Convergent evolution: Organisms with different ancestors become more alike due to common environment Ex. fish and whales- compare analogous structures: Same function but different development Examples of Evolution (cont.) Divergent evolution: populations become more and more dissimilar to adapt to the environment Compare homologous structures to see shared ancestry Ex: Appearance of birds with different sized beaks that are specific for size of bird seed Homologous structure: similar body part but may have different functions Adaptive radiation Population undergoes divergent evolution until it fills all areas of the environment Examples of Evolution (cont.) Co-evolution: two species evolve in response to each other over a long period of time Ex: parasites and hosts, plants and pollinators EX: Rough-skinned newt and garter snake Newt evolved to produce neurotoxins then the snake evolved resistance to this toxin through genetic mutations. Birds and flowers, Humans and bacteria are other examples