* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Darwin and his Origin of Species
The Selfish Gene wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Sex-limited genes wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Symbiogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Vestigiality wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
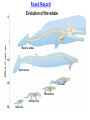
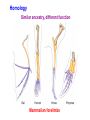
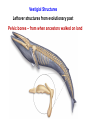
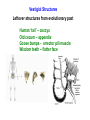
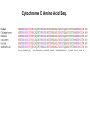
I. HISTORICAL PERSPECTIVE II. DARWIN’S IDEA III. THE EVIDENCE Voyage of the Beagle (1831-1836) 12 shirts 1 carpet bag 1 pair slippers 1 pair of light walking shoes 1 microscope (a single lens model by Bancks & Son, London) 1 geological compass 1 plain compass 2 pistols (with spare parts) 1 rifle (with spare parts) 1 telescope 1 pencil case 1 geological hammer 5 simisometers 3 mountain barometers 1 clinometer 1 camera obscura 1 hygrometer (belonged to FitzRoy) 1 taxidermy book 2-3 Spanish language books 14 other books, including Humboldt's "Personal Narrative" and Lyell’s "Principles of Geology Vol. 1" 1 coin purse (Fanny Owen's gift) 1 pin with a lock of Sarah Owen's hair (Fanny's sister) Darwin’s Dilemma 1. 1836 – 1858 developed theories on evolution 2. Reluctant to publish 3. In 1858, Alfred Russell Wallace Similar theory 4. Darwin quickly finished book Descent w/ Modification Adaptation by Natural Selection The Synthesis of Natural Selection How organisms adapt to environment Observation 1: Variation w/in pop. Observation 2: Variation is heritable Observation 3: Not all survive and reproduce • High reproductive effort • Limited resources • Unequal reproductive success Observation 4: Survival & Reproduction not Random • Those with favorable traits leave more offspring • Favorable traits accumulate in population • Population is modified by NS “Survival of the Fittest” What’s the Evidence for natural selection? Artificial Selection • • Breed for desired traits Large changes, short time Maize Teosinte Fossil Record • • Organisms in older rock look more dissimilar to present day Newer rock strata should contain fossils that more closely resemble current day organisms Youngest rocks Oldest rocks Fossil Record Oligocene 30MYA 45MYA 50MYA 55MYA 60MYA Hyracotherium (browsers) 55 Orohippus Eocene Hyracotherium 40MYA Epihippus 35MYA Mesohippus (browsers) 40 Mesohippus Anchitherium (browsers) 20 Merychippus (mixed feeders) 17 Neohipparion (grazers) 14 Nannippus (grazers) 12 Equus (grazers) 5 Equus Dinohippus Onohippidion Astrohippus Pliohippus Calippus Protohippus Cormohipparion Nannippus Merychippus Parahippus Desmatippus 25MYA Miohippus 20MYA Archaeohippus 15MYA Kalobatippus Miocene Hypohippus 10MYA Megahippus 5MYA Hipparion browsers grazers mixed feeders Anchitherium Pliocene Neohipparion Pleistocene Pseudhipparion Evolution of the Horse Fossil Record 55 mya browsers 40 mya browsers 14 mya grazers 20 mya browsers 12 mya grazers 17 mya mixed feeder 5 mya grazers Fossil Record Evolution of the whale Millions of years ago 0 Modern whales 40 Basilosaurus 45 Dorudon Rhodocetus Ambulocetus 50 Pakicetus Homology Similar ancestry, different function Mammalian forelimbs Vestigial Structures Leftover structures from evolutionary past Pelvic bones – from when ancestors walked on land Vestigial Structures Leftover structures from evolutionary past Human ‘tail’ – coccyx Old cecum – appendix Goose bumps - arrector pili muscle Wisdom teeth – flatter face Convergent Evolution Similar traits evolve separately, but in similar environments Same selectable pressures Placental vs. marsupial mammals Niche Placental Mammals Burrower Anteater Mole Nocturnal Insectivore Glider Stalking Predator Wolf Ocelot Ring-tailed lemur Numbat Thylacine Spotted cuscus Marsupial mole Marsupial mouse Chasing Predator Flying squirrel Grasshopper mouse Lesser anteater Australian Marsupials Climber Flying phalanger Tasmanian quoll Convergent Evolution Asia & Australia North America Cactus Euphorbia DNA Sequence Comparison How do these organisms relate to each other? Cytochrome C Amino Acid Seq. Evolutionary relationships based on DNA and protein sequence – cytochrome C amino acid differences 0 1 10 11 13 17 28 Pseudogenes (dead genes) Olfactory genes in mammals Dog Mouse Rat Human Total # of olf. genes % dead 1,100 1,500 1,500 900 18% 20% 19.5% 63% Functional genes 902 1200 1207 333 Pseudogenes (dead genes) Ascorbic acid (viatmin C) production Primates, guinea pigs, and fruit bats only mammals that can’t make vit C • • • Historical Perspective Georges Cuvier Catastrophism Father of paleontology Earth – 10,000 years old, catastrophic events shaped it Caused mass extinction, new species placed back Historical Perspective • • Charles Lyell Uniformitarianism Earth much older, slow gradual changes shaped it Same processes still working today Jean Baptiste Lamarck Thomas Malthus • Organisms change over • Populations outgrow food time • ‘Survival of fittest’ • Innate drive for perfection • Inheritance of acquired characteristics