* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention
Survey
Document related concepts
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Clinical trial wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of beta-blockers wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of angiotensin receptor blockers wikipedia , lookup
Theralizumab wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
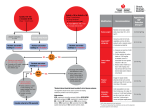
separate prescriptions or in fixed-dose combinations.129 (See figure 16.) The initiation of therapy with more than one drug increases the likelihood of achieving BP goal in a more timely fashion. The use of multidrug combinations often produce greater BP reduction at lower doses of the component agents, resulting in fewer side effects.129,130 The use of fixed-dose combinations may be more convenient and simplify the treatment regimen, and may cost less than the individual components prescribed separately. Use of generic drugs should be considered to reduce prescription costs, and the cost of separate prescription of multiple drugs available generically may be less than nongeneric, fixed-dose combinations. The starting dose of most fixed-dose combinations is usually below the doses used in Figure 16. Algorithm for treatment of hypertension LIFESTYLE MODIFICATIONS Not at Goal Blood Pressure (<140/90 mmHg) (<130/80 mmHg for those with diabetes or chronic kidney disease) Initial Drug Choices Without Compelling Indications Stage 1 Hypertension (SBP 140–159 or DBP 90–99 mmHg) Thiazide-type diuretics for most. May consider ACEI, ARB, BB, CCB, or combination ACEI, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor; ARB, angiotensin receptor blocker; BB, beta blocker; CCB, calcium channel blocker; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; SBP, systolic blood pressure With Compelling Indications Stage 2 Hypertension (SBP >160 or DBP >100 mmHg) Two-drug combination for most (usually thiazidetype diuretic and ACEI, or ARB, or BB, or CCB) Drug(s) for the compelling indications (see table 12) Other antihypertensive drugs (diuretics, ACEI, ARB, BB, CCB) as needed NOT AT GOAL BLOOD PRESSURE Optimize dosages or add additional drugs until goal blood pressure is achieved. Consider consultation with hypertension specialist. Treatment 31 S p e c i a l S i t u at i o n s i n H y p e r t e n s i o n M a n a g e m e n t Compelling Indications Hypertension may exist in association with other conditions in which there are compelling indications for use of a particular treatment based on clinical trial data demonstrating benefits of such therapy on the natural history of the associated condition (table 12). Compelling indications for specific therapy involve high-risk conditions that can be direct sequelae of hypertension (HF, IHD, chronic kidney disease, recurrent stroke) or commonly associated with hypertension (diabetes, Table 12. Clinical trial and guideline basis for compelling indications for individual drug classes Compelling Indication* ACEI ARB ● ● ● ● ● Postmyocardial infarction Aldo ANT BB ● CCB Diuretic Heart failure Clinical Trial Basis† Recommended Drugs ● ACC/AHA Heart Failure Guideline,132 MERITHF,133 COPERNICUS,134 CIBIS,135 SOLVD,136 AIRE,137 TRACE,138 ValHEFT,139 RALES,140 CHARM141 ● ACC/AHA Post-MI Guideline,142 BHAT,143 SAVE,144 Capricorn,145 EPHESUS146 High coronary disease risk ● ● ● Diabetes ● ● ● ● ● ● Chronic kidney disease Recurrent stroke prevention ● ● ● ALLHAT,109 HOPE,110 ANBP2,112 LIFE,102 CONVINCE,101 EUROPA,114 INVEST147 ● NKF-ADA Guideline,88,89 UKPDS,148 ALLHAT109 NKF Guideline,89 Captopril Trial,149 RENAAL,150 IDNT,151 REIN,152 AASK153 PROGRESS111 AASK, African American Study of Kidney Disease and Hypertension; ACC/AHA, American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association; ACEI, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor; AIRE, Acute Infarction Ramipril Efficacy; Aldo ANT, aldosterone antagonist; ALLHAT, Antihypertensive and Lipid-Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial; ANBP2, Second Australian National Blood Pressure Study; ARB, angiotensin receptor blocker; BB, beta blocker; BHAT, ßBlocker Heart Attack Trial; Capricorn, Carvedilol Post-Infarct Survival Control in Left Ventricular Dysfunction; CCB, calcium channel blocker; CHARM, Candesartan in Heart Failure Assessment of Reduction in Mortality and Morbidity; CIBIS, Cardiac Insufficiency Bisoprolol Study; CONVINCE, Controlled Onset Verapamil Investigation of Cardiovascular End Points; COPERNICUS, Carvedilol Prospective Randomized Cumulative Survival Study; EPHESUS, Eplerenone Post-Acute Myocardial Infarction Heart Failure Efficacy and Survival Study; EUROPA, European Trial on Reduction of Cardiac Events with Perindopril in Stable Coronary Artery Disease; HOPE, Heart Outcomes Prevention Evaluation Study; IDNT, Irbesartan Diabetic Nephropathy Trial; INVEST, The International Verapamil-Trandolapril Study; LIFE, Losartan Intervention for Endpoint Reduction in Hypertension Study; MERIT-HF, Metoprolol CR/XL Randomized Intervention Trial in Congestive Heart Failure; NKF-ADA, National Kidney Foundation-American Diabetes Association; PROGRESS, Peridopril Protection against Recurrent Stroke Study; RALES, Randomized Aldactone Evaluation Study; REIN, Ramipril Efficacy in Nephropathy Study; RENAAL, Reduction of Endpoints in Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus with the Angiotensin II Antagonist Losartan Study; SAVE, Survival and Ventricular Enlargement Study; SOLVD, Studies of Left Ventricular Dysfunction; TRACE, Trandolapril Cardiac Evaluation Study; UKPDS, United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study; ValHEFT, Valsartan Heart Failure Trial * Compelling indications for antihypertensive drugs are based on benefits from outcome studies or existing clinical guidelines; the compelling indication is managed in parallel with the BP. † Conditions for which clinical trials demonstrate the benefit of specific classes of antihypertensive drugs used as part of an antihypertensive regimen to achieve BP goal to test outcomes. Special Situations in Hypertension Management 33


![[ Insert Title Here ]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008479268_1-03ff748536c27aeae665c17a72e89ec4-150x150.png)