* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Landforms
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Overdeepening wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Surface runoff wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
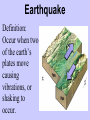
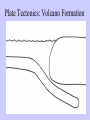
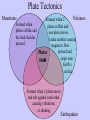
Physical Processes: Mrs. Walker 4th Grade Earth’s Surface: • The surface of the earth is made up of many different landforms. • A landform is a natural shape and type of land on Earth’s surface. Landforms: • Mountains • Hills • Plateau • Plains • Valley • River • Peninsula • Canyon • Glacier • Volcano Guided Practice: Landform Review Complete Land and Water Formations Worksheet. Lets Think!!! • Does Earth’s surface ever change? • What causes those changes? • Why? How? Examples? Physical Processes: • Earth’s surface is constantly changing. • Different natural events, such as earthquakes and volcanoes, change the size and shape of landforms. • These events are known as physical processes. Example: Mt. Saint Helens (1980) Before After Example: Earthquake/Tsunami in Japan Before After Lets Review: • Earth’s surface is made up of many different types of landforms. • Physical processes, such as volcanos, earthquakes, flooding, and erosion shape and reshape earth’s surface. Preview: • In our next lesson we will learn about a theory that explains why earthquakes and volcanos happen and how mountains are formed. Plate Tectonics Plate Tectonics The theory that Earth’s plates float on magma and slowly shift over time. Plate Definition: A large sheet of rock that makes up Earth’s outer crust. Mountain Definition: A natural rise of the earth with steep sides. Mountains are formed when plates collide and the land buckles upwards. Towel Demonstration: How are mountains formed? Earthquake Definition: Occur when two of the earth’s plates move causing vibrations, or shaking to occur. Earth’s crust has many weak spots along plate edges. When plates rub against each other, Earth’s crust cracks and chips under the pressure. These cracks are called faults. When the crust moves along faults, great amounts of energy are released in the form of earthquakes. Earthquakes cause dramatic changes to the surface of the earth. Bam, Iran 12/26/2003 Volcano Definition: An opening in the earth’s crust from which lava flows. Plates move in different directions. In some places, plates move apart and magma leaks out through cracks in the crust. In other places the plates push against each other. This pressure forces one plate to slide under the other. Overtime, tremendous pressure and heat build up. Molten rock gushes upward, exploding from beneath the ground. This is how volcanos are formed. Plate Tectonics: Volcano Formation Mt. St. Helens 5/18/1980 Plate Tectonics Video Plate Tectonics Mountains Volcanos Formed when 2 Formed when plates collide and plates collide and one plate moves the land buckles under another causing upward. magma to flow upward and Plates erupt onto Shift Earth’s surface. Formed when 2 plates move and rub against each other causing vibrations, or shaking Earthquakes Weathering and Erosion Weathering Definition: The wearing away of a surface through weather conditions, such as wind, rain or ice. Erosion Definition: A process that breaks rocks down into tiny pieces and moves them to another location. Erosion • Wind, rain, and ice cause erosion which slowly wear away Earth’s landforms. • Erosion helps create soil. (Tiny fragments of rock mix with decay mix with decayed animal and plant material to form soil.) • Over time, erosion can create new landforms. Erosion: The Grand Canyon was formed by erosion. What’s the Difference? • Erosion involves running water, blowing wind, or moving ice that picks up and moves the particles to another location. • Weathering takes place as rocks are broken down into smaller pieces by the effects of weather. These pieces do not move to a new location, they simply break down, but remain next to one another. KWL Chart Topic: Weathering and Erosion What I Know 1. Weathering and erosion cause Earth’s surface to change. 2. Weathering breaks down Earth’s surface into smaller particles but doesn’t move them. 3. Erosion breaks down Earth’s surface into smaller particles and moves them to another place. What I Want to Know 1. 2. 3. 4. How quickly does weathering and erosion happen? What forces cause weathering and erosion to happen? What happens to the particles after they have been broken down. How does weathering and erosion affect people? What I Learned Weathering and Erosion Video KWL Chart Topic: Weathering and Erosion What I Know 1. Weathering and erosion cause Earth’s surface to change. 2. Weathering breaks down Earth’s surface into smaller particles but doesn’t move them. 3. Erosion breaks down Earth’s surface into smaller particles and moves them to another place. What I Want to Know 1. 2. 3. 4. How quickly does weathering and erosion happen? What forces cause weathering and erosion to happen? What happens to the particles after they have been broken down. How does weathering and erosion affect people? What I Learned 1. Most (but not all) weathering and erosion occur very slowly. 2. Water, ice, wind, temperature, and gravity are all forces that cause weathering and erosion. 3. Broken down particles can become soil or sand. Also, new landforms can be formed. 4. Can damage housing or crops. Flooding Definition: An overflow of water onto land that is normally dry. Flooding is often caused by heavy rains. Flooding • Overflowing rivers add nutrients to the surrounding soil. • If the Mississippi River were to flood, there would be an increase in fertile soil in the MS River Valley. Check for Understanding: 1. What creates new landforms? a) Earthquakes b) Volcanoes c) Erosion d) All of the Above Check for Understanding: 2. Which of these does not cause weathering? a) sunshine b)wind c) rain d)ice Check for Understanding: 3. Which United States landform was most likely caused by erosion? a) The Great Lakes b)The Mississippi River c) The Rocky Mountains d)The Grand Canyon Check for Understanding: 4. Which physical process most likely formed the Great Smoky Mountains? a) Flooding rivers b)Erupting volcanoes c) Plate tectonics d)Wind erosion Check for Understanding: 5. Which physical process most likely causes a river to overflow, adding nutrients to the local soil? a) Heavy rains b)Volcanic eruptions c) Strong Winds d)Melting Snow Check for Understanding: 6. Which physical process most likely shaped the feature shown? a) Plate tectonics b) Volcanic eruptions c) Water erosion d) Coastal flooding Check for Understanding: 7. Which physical process most likely created the mountain range shown on the map? a) erosion b) flooding c) plate tectonics d) volcanic eruptions